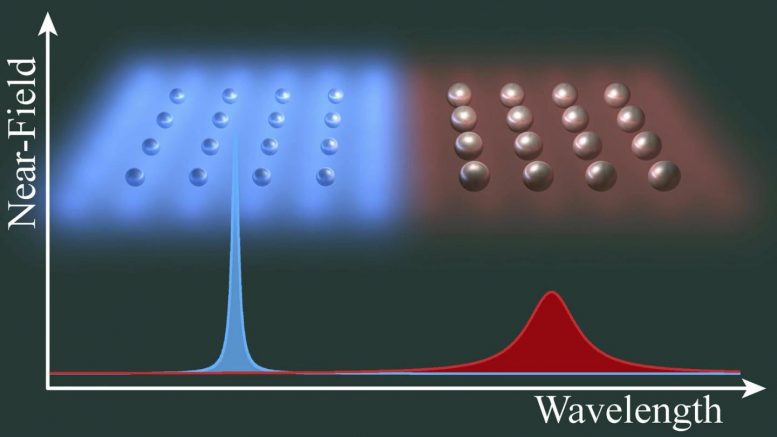
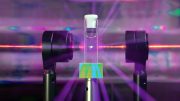
Artistic depiction of the system under study. As the size of the particles is reduced, the field enhancement increases. Credit: University of New Mexico Department of Physics
University of New Mexico researchers find decreasing the density of nanoparticles in ordered arrays produces exceptional field enhancements.
Controlling the interactions between light and matter has been a long-standing ambition for scientists seeking to develop and advance numerous technologies that are fundamental to society. With the recent rise in nanotechnology, nanoscale light manipulation has become both a promising path to further this advancement and a distinct difficulty owing to unexpected behaviors that emerge when the size of structures becomes equivalent to the wavelength of light.
Scientists in the Theoretical Nanophotonics Group at The University of New Mexico’s Department of Physics and Astronomy have made an exciting new advancement to this end, in a pioneering research effort titled “Analysis of the Limits of the Near-Field Produced by Nanoparticle Arrays,” published recently in the journal, ACS Nano, a top journal in the field of nanotechnology.
The group, led by Assistant Professor Alejandro Manjavacas, studied how the optical response of periodic arrays of metallic nanostructures can be manipulated to produce strong electric fields in their vicinity.
The arrays they analyzed are built of silver nanoparticles, which are silver spheres hundreds of times smaller than the width of a human hair and arranged in a repeating pattern; nevertheless, their findings also apply to nanostructures made of other materials. Because of the strong interactions between each of the nanospheres, these systems can be used for different applications, ranging from vivid, high-resolution color printing to biosensing that could revolutionize healthcare.
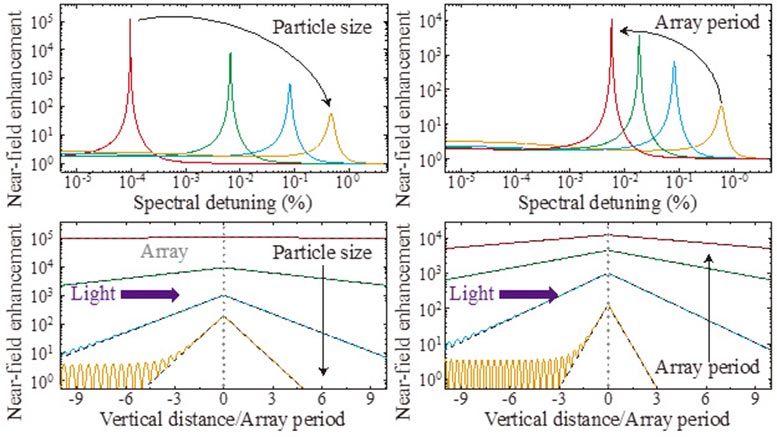
Analysis of the field enhancement as a function of different geometrical parameters of the array. Credit: University of New Mexico Department of Physics and Astronomy
“This new work will help to advance the many applications of nanostructure arrays by providing fundamental insights into their behavior,” says Manjavacas. “The near-field enhancements we predict could be a game changer for technologies like ultrasensitive biosensing.”
Manjavacas and his team, composed of Lauren Zundel and Stephen Sanders, both graduate students in the Department of Physics and Astronomy, modeled the optical response of these arrays, finding exciting new results. When periodic arrays of nanostructures are illuminated with light, each of the particles produces a strong response, which, in turn, results in enormous collective behaviors if all of the particles can interact with one another. This happens at certain wavelengths of the incident light, which are determined by the interparticle spacing of the array, and can result in electric fields that are thousands, or even tens of thousands, of times that of the light shined on the array.
The strength of this field enhancement depends on the geometrical properties of the array, such as the spacing between the nanospheres, as well as the size of the spheres themselves. Completely counterintuitively, Manjavacas and his group found that decreasing the density of nanoparticles in the array, either by increasing the spacing between each of them, or by decreasing their size, produces field enhancements that are not only larger, but extend farther away from the array.
“It was really exciting to find out that the key to these huge field enhancements actually lies in making the particles smaller and farther apart,” says Zundel of the discovery.
“The reason for this is that the interactions between the nanoparticles, and thus the collective response, is strengthened,” according to Sanders.
###
The research was sponsored in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and made use of the high-performance computational resources made available by the UNM Center for Advanced Research Computing.
Reference: “Analysis of the Limits of the Near-Field Produced by Nanoparticle Arrays” by Alejandro Manjavacas, Lauren Zundel and Stephen Sanders, 5 September 2019, ACS Nano.
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b05031



Be the first to comment on "Nanoscale Manipulation of Light Leads to Exciting New Nanophotonics Advancement"