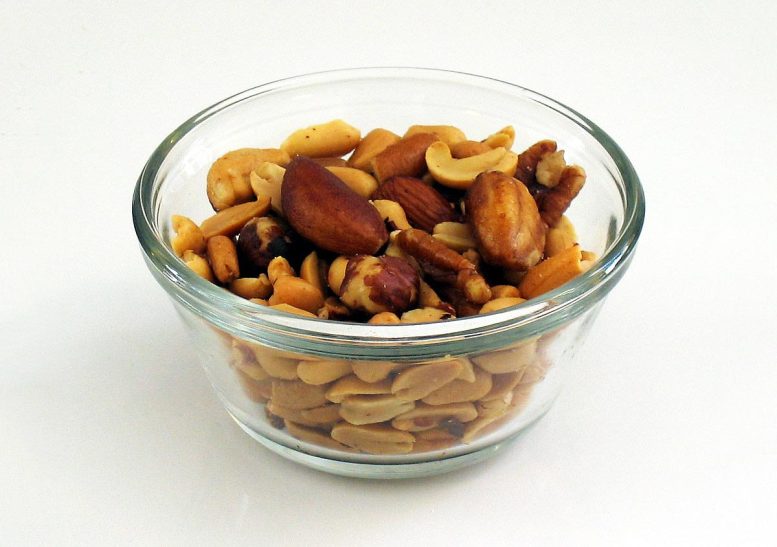

In a bag of mixed nuts, after shaking, smaller nuts fill in the gaps created at the bottom, pushing the larger Brazil nuts to the top. Credit: Melchoir, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Physicists from the University of Utrecht and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have observed — for the first time experimentally — the Brazil nut effect in a mixture of charged colloidal particles. Until now, it was thought that an influx of external energy was required to create this effect — but the researchers were able to confirm that the process can occur spontaneously. The findings, published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), could find applications in a wide range of fields, from geology to soft matter physics.
When you open a can of mixed nuts, it is common to give it a shake. Have you noticed that after such an action, the largest nuts in the mixture — Brazil nuts — float to the top? The phenomenon of large objects rising to the surface of a mixture of small objects, bearing the professional name of granular convection, is popularly referred to “the Brazil nut effect” and occurs commonly in nature. It can also be observed by shaking, for example, a bucket of sand and pebbles.
This unusual effect contradicts the intuition that heavier objects should sink to the bottom due to gravity and inertia force. This is the case with the phenomenon of sedimentation, common in nature, a process involving the sinking of solid particles dispersed in a liquid, under the influence of gravity or inertia forces. Sedimentation plays a role in processes such as the formation of sedimentary rocks, and is also used to purify water and wastewater or isolate cells from blood.
Brazil nut effect in charged colloids
Until now, it was thought that an influx of external energy, such as shaking the bag, was necessary to create the Brazil nut effect. However, theoretical models being developed suggested that the phenomenon could occur spontaneously, without the supply of external energy. The theoretical calculations were confirmed experimentally for the first time by a group of experimental and theoretical physicists from the University of Utrecht and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw. The results of the study appeared in a paper published in the journal The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS).
“We have shown that the Brazil nut effect can take place in a mixture of charged colloidal particles driven solely by Brownian motions and repulsion of electric charges,” emphasizes Jeffrey Everts from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, who, under the direction of René van Roij of the Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Utrecht University, carried out the theoretical calculations for the experiment. Marjolein van der Linden, working under the direction of Alfons van Blaaderen of the Debye Institute for Nanomaterials Science of Utrecht University, was responsible for the experimental part of the study.
Colloidal mixture
The researchers used charged polymethylmethacrylate particles with different diameters (large and small) to carry out the experiment. A low-polar solvent, cyclohexyl bromide, was used as a dispersing agent.
As the researchers point out, although in both granular (e.g., nut) and colloidal mixtures the “Brazil nut effect” occurs, the mechanisms for its formation are completely different. In the case of a nut mixture, as a result of shaking, smaller nuts fill in the gaps created at the bottom, pushing the larger nuts to the top. Meanwhile, the charged particles in the colloid make Brownian motion as a result of collisions with the surrounding solvent molecules.
“Each particle is positively charged. Heavier but larger particles have a greater charge, so they repel each other more strongly, making them move upward more easily than smaller but lighter particles,” Jeffrey Everts explains.
The discovery of the “Brazil nut effect” in mixtures of colloidal particles can be used in many fields from geology to soft matter physics. It can also find application in industry such as in the stability of paint and ink.
Reference: “Realization of the Brazil-nut effect in charged colloids without external driving” by Marjolein N. van der Linden, Jeffrey C. Everts, René van Roij and Alfons van Blaaderen, 24 February 2023, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2213044120








Be the first to comment on "Nuts About Science: The Brazil Nut Effect Shakes Up Physics"