
University of Toronto geoscientists have made a significant breakthrough in plate tectonics, discovering that the Pacific Plate is not as rigid as previously thought but is instead torn by large undersea faults. This challenges traditional views and suggests a more complex interaction between oceanic plates and the Earth’s mantle. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Research indicates that the Pacific Plate is being torn apart at undersea plateaus across the ocean, due to the weight of the oceanic plate subducting along the Western Pacific Ring of Fire.
Recent research conducted by geoscientists from the University of Toronto is refining the long-standing model of plate tectonics, which suggests that the oceanic plates are inflexible as they glide over the Earth’s mantle.
Instead, the researchers found the Pacific Plate is scored by large undersea faults pulling it apart. The newly discovered faults, some thousands of meters deep and hundreds of kilometers long, are the result of enormous forces within the plate tugging it westward.
The researchers describe their findings in a paper published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. The authors include Erkan Gün, a postdoctoral fellow, and Professor Russell Pysklywec in the Department of Earth Sciences in the Faculty of Arts & Science at U of T, Phil Heron, an assistant professor in the Department of Physical & Environmental Sciences at University of Toronto Scarborough, as well as researchers from the Eurasia Institute of Earth Sciences, Istanbul Technical University.
Refining Plate Tectonic Theory
“We knew that geological deformations like faults happen on the continental plate interiors far from plate boundaries,” says Gün. “But we didn’t know the same thing was happening to ocean plates.” Says Pysklywec, “What we’re doing is refining plate tectonics — the theory that describes how our planet works — and showing those plates really aren’t as pristine as we previously thought.”
For millions of years, the Pacific Plate — which constitutes most of the floor of the ocean — has drifted westward to plunge down into Earth’s mantle along undersea trenches or subduction zones that run from Japan to New Zealand and Australia. As the western edge of the plate is pulled down into the mantle, it drags the rest of the plate with it like a tablecloth being pulled from a table.
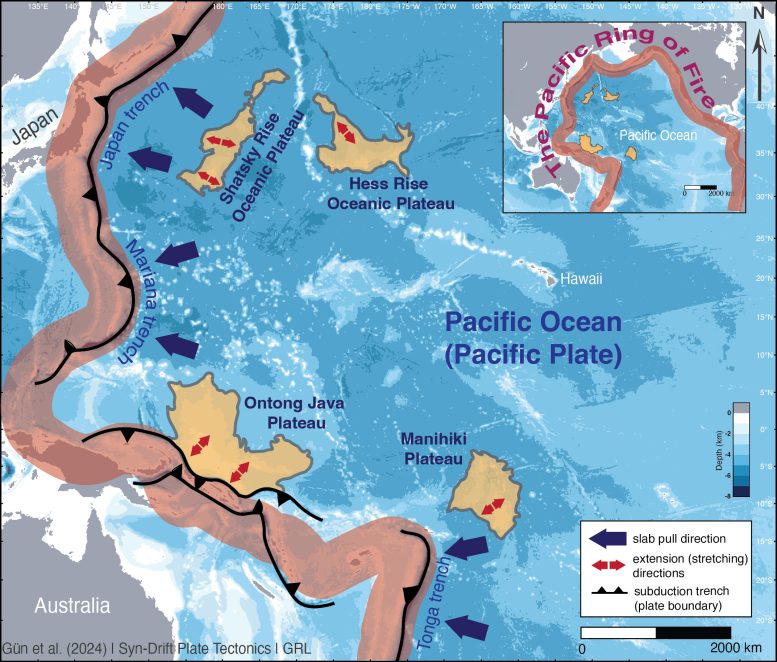
The map highlights in yellow the zones of the Pacific Plate that are being pulled apart by the sinking tectonic plate along the Pacific Ring of Fire. Credit: Erkan Gün & Russell Pysklywec/University of Toronto
The newly discovered plate damage at the faults occurs within extensive, sub-oceanic plateaus formed millions of years ago when molten rock from the Earth’s mantle extruded onto the ocean floor; the faults tend to run parallel to the closest trench.
“It was thought that because the sub-oceanic plateaus are thicker, they should be stronger,” says Gün. “But our models and seismic data show it’s actually the opposite: the plateaus are weaker.”
If the Pacific Plate is like a tablecloth being pulled across a tabletop, the plateaus are patches of weaker cloth more prone to tearing.
Implications for Understanding Oceanic Plates
The researchers studied four plateaus in the western Pacific Ocean — the Ontong Java, Shatsky, Hess, and Manihiki — in a vast area roughly bounded by Hawaii, Japan, New Zealand, and Australia. They made their discovery using supercomputer models and existing data, some collected in studies done in the 1970s and 1980s.
“There is evidence that volcanism occurred at these sites in the past as a result of this type of plate damage — perhaps episodically or continuously — but it isn’t clear if that’s happening now,” says Gün. “Still, we can’t be certain because the plateaus are thousands of meters below the ocean surface, and sending research vessels to collect data is a major effort. So, in fact, we’re hopeful our paper brings some attention to the plateaus and more data will be collected.”
The theory of plate tectonics has been refined over many decades by numerous earth scientists — including U of T’s John Tuzo Wilson who made significant contributions to it during his career.
“But the theory is not carved in stone and we’re still finding new things,” says Pysklywec. “Now we know this fault damage is tearing apart the center of an ocean plate —and this could be linked to seismic activity and volcanism.
“A new finding like this overturns what we’ve understood and taught about the active Earth,” he says. “And it shows that there are still radical mysteries about even the grand operation of our evolving planet.”
Reference: “Syn-Drift Plate Tectonics” by Erkan Gün, Russell N. Pysklywec, Gültekin Topuz, Oğuz H. Göğüş and Philip J. Heron, 21 January 2024, Geophysical Research Letters.
DOI: 10.1029/2023GL105452
The study was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.







No, no it does not! There is No such thing as continental drift, subduction zones or tectonic plates pushing against each other to form mountains. Geophysics is a Fraud, 100% made-up bs.
Search for ‘The World’s largest impact crater’ on YouTube.
You can’t look at a single geo-point from ground level and determine how a geological feature was formed.
I could go on and on about this, but, once you view the World’s largest impact crater video, you will feel embarrassed you even wrote this garbage.
Cheers Steve Jeffs
“…, once you view the World’s largest impact crater video, …
Which one?
I’m reminded of Carl Sagan’s Standard: “Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”. Claiming that an entire scientific discipline (geophysics), which one can obtain a degree in, is “fraud,” is an extraordinary claim. I don’t think a YouTube video rises to the level of “extraordinary evidence.”
Agreed with last comment! Carl Sagan said it best!
I live in New Zealand, and the South Island is being torn along the Alpine Fault by 36 mm/yr dextral strike-slip and 11 mm/yr convergence. This is easily measurable. However I could easily make a youtube video showing that the moon is made of cheese if I wanted too. Why would you trust anything you see on youtube?