
Astronomers and citizen scientists have discovered over 1,000 previously unknown asteroids using archival Hubble images, offering new insights into the asteroid belt’s evolution and supporting theories of collisional fragmentation. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Deep-Sky Exposure Yields Telltale Evidence for Asteroid Moving Across the Celestial Background
Over 4 billion years ago, the eight major planets around our Sun formed by sweeping up debris from a vast disk of dust and gas surrounding the Sun. This is common to the planet birthing process, and the Hubble Space Telescope was the first to optically see similar disks surrounding newborn stars, providing a peek into the solar system’s formative years. Now, 4 billon years later, the planet construction yard is still cluttered with leftover debris.
Most of this ancient space rubble, called asteroids, can be found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter within the main asteroid belt. The census of the asteroid population is ongoing. Hubble’s unique capabilities allow it to be used as an “asteroid hunter” for this task. Asteroids appear as curved trails in Hubble images. The trails are due to parallax because Hubble is not stationary, but orbiting Earth. This gives the illusion that the faint asteroids are swimming along curved trajectories.
The Hubble archives, spanning many years, are loaded with images that capture wayward asteroids trekking along their orbits. They were not the intended targets, but instead photobombed background stars and galaxies. Finding these asteroids is sort of a game of Where’s Waldo. It was recognized this would be a Herculean effort for any group of astronomers, so the researchers relied on a small army of volunteer citizen scientists to peruse the gaggle of Hubble photos. What they found was applied to machine learning to dig out even more asteroids. The project identified 1,701 asteroid trails. Most of the asteroids are too small to have been previously detected without Hubble’s sharp resolution and ultraviolet-light sensitivity.
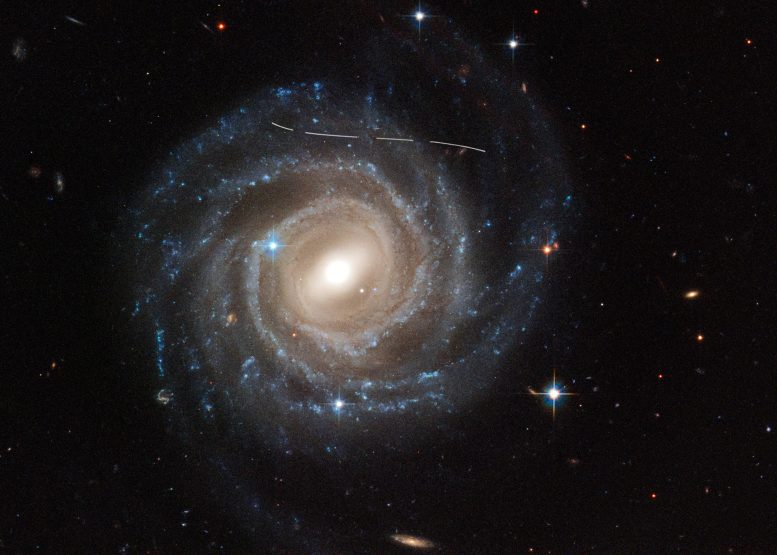

This Hubble Space Telescope image of the barred spiral galaxy UGC 12158 looks like someone took a white marking pen to it. In reality it is a combination of time exposures of a foreground asteroid moving through Hubble’s field-of-view, photobombing the observation of the galaxy. Several exposures of the galaxy were taken, what is evidence in the dashed pattern. The asteroid appears as a curved trail due to parallax: because Hubble is not stationary, but orbiting Earth, and this gives the illusion that the faint asteroid is swimming along a curved trajectory. The uncharted asteroid is in inside the asteroid belt in our solar system, and hence is 10 trillion times closer to Hubble than the background galaxy. Rather than a nuisance, this type of data are useful to astronomers for doing a census of the asteroid population in our solar system. Credit: NASA, ESA, Pablo García Martín (UAM); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI); Acknowledgment: Alex Filippenko (UC Berkeley)
Hubble Space Telescope Goes Hunting for Small Main Belt Asteroids
Like boulders, rocks, and pebbles scattered across a landscape, asteroids come in a wide range of sizes. Cataloging asteroids in space is tricky because they are faint and they don’t stop to be photographed as they zip along their orbits around the Sun.
Astronomers recently used a trove of archived images taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope to visually snag a largely unseen population of smaller asteroids in their tracks. The treasure hunt required perusing 37,000 Hubble images spanning 19 years. The payoff was finding 1,701 asteroid trails, with 1,031 of the asteroids previously uncatalogued. About 400 of these uncatalogued asteroids are below 1 kilometer in size.
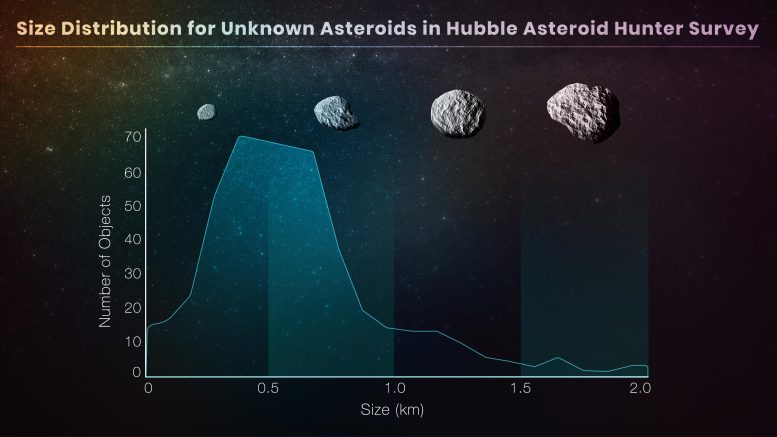
This graph is based on Hubble Space Telescope archival data that was used to identify a largely unseen population of very small asteroids in their tracks. The asteroids were not the intended targets, but instead photobombed background stars and galaxies in Hubble images. The comprehensive treasure hunt required perusing 37,000 Hubble images spanning 19 years. This was accomplished by using “citizen science” volunteers and artificial intelligence algorithms. The payoff was finding 1,701 asteroid trails of previously undetected asteroids. Credit: Pablo García Martín (UAM), Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)
Citizen Science and Machine Learning in Astronomy
Volunteers from around the world known as “citizen scientists” contributed to the identification of this asteroid bounty. Professional scientists combined the volunteers’ efforts with machine learning algorithm to identify the asteroids. It represents a new approach to finding asteroids in astronomical archives spanning decades, which may be effectively applied to other datasets, say the researchers.
“We are getting deeper into seeing the smaller population of main belt asteroids. We were surprised with seeing such a large number of candidate objects,” said lead author Pablo García Martín of the Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain. “There was some hint of this population existing, but now we are confirming it with a random asteroid population sample obtained using the whole Hubble archive. This is important for providing insights into the evolutionary models of our solar system.”
Insights Into Asteroid Evolution
The large, random sample offers new insights into the formation and evolution of the asteroid belt. Finding a lot of small asteroids favors the idea that they are fragments of larger asteroids that have collided and broken apart, like smashed pottery. This is a grinding-down process spanning billions of years.
An alternative theory for the existence of smaller fragments is that they formed that way billions of years ago. But there is no conceivable mechanism that would keep them from snowballing up to larger sizes as they agglomerated dust from the planet-forming circumstellar disk around our Sun. “Collisions would have a certain signature that we can use to test the current main belt population,” said co-author Bruno Merín of the European Space Astronomy Centre, in Madrid, Spain.
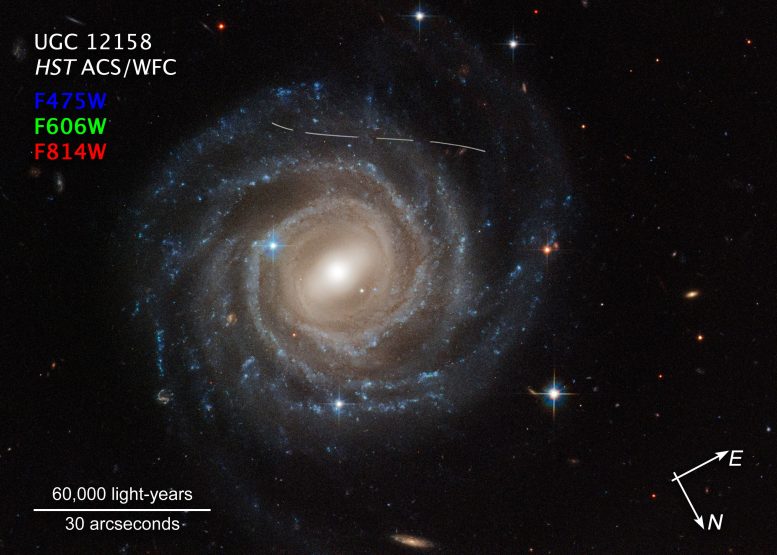

This Hubble Space Telescope image of the barred spiral galaxy UGC 12158 looks like someone took a white marking pen to it. In reality it is a combination of time exposures of a foreground asteroid moving through Hubble’s field-of-view, photobombing the observation of the galaxy. Several exposures of the galaxy were taken, what is evidence in the dashed pattern.
The asteroid appears as a curved trail due to parallax: Hubble is not stationary, but orbiting Earth, and this gives the illusion that the faint asteroid is swimming along a curved trajectory. The uncharted asteroid is inside the asteroid belt in our solar system, and hence is 10 trillion times closer to Hubble than the background galaxy.
Rather than a nuisance, this type of data are useful to astronomers for doing a census of the asteroid population in our solar system. Credit: NASA, ESA, Pablo García Martín (UAM)
Amateur Astronomers Teach AI to Find Asteroids
Because of Hubble’s fast orbit around the Earth, it can capture wandering asteroids through their telltale trails in the Hubble exposures. As viewed from an Earth-based telescope, an asteroid leaves a streak across the picture. Asteroids “photobomb” Hubble exposures by appearing as unmistakable, curved trails in Hubble photographs.
As Hubble moves around the Earth, it changes its point of view while observing an asteroid, which also moves along its own orbit. By knowing the position of Hubble during the observation and measuring the curvature of the streaks, scientists can determine the distances to the asteroids and estimate the shapes of their orbits.
The asteroids snagged mostly dwell in the main belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Their brightness is measured by Hubble’s sensitive cameras. And comparing their brightness to their distance allows for a size estimate. The faintest asteroids in the survey are roughly one forty-millionth the brightness of the faintest star that can be seen by the human eye.
“Asteroid positions change with time, and therefore you cannot find them just by entering coordinates, because at different times, they might not be there,” said Merín. “As astronomers we don’t have time to go looking through all the asteroid images. So we got the idea to collaborate with over 10,000 citizen-science volunteers to peruse the huge Hubble archives.”
Citizen Science and Future Research
In 2019 an international group of astronomers launched the Hubble Asteroid Hunter, a citizen-science project to identify asteroids in archival Hubble data. The initiative was developed by researchers and engineers at the European Science and Technology Centre (ESTEC) and the European Space Astronomy Centre’s science data center (ESDC), in collaboration with the Zooniverse platform, the world’s largest and most popular citizen-science platform, and Google.
A total of 11,482 citizen-science volunteers, who provided nearly 2 million identifications, were then given a training set for an automated algorithm to identify asteroids based on artificial intelligence. This pioneering approach may be effectively applied to other datasets.
The project will next explore the streaks of previously unknown asteroids to characterize their orbits and study their properties, such as rotation periods. Because most of these asteroid streaks were captured by Hubble many years ago, it is not possible to follow them up now to determine their orbits.
The findings are published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Reference: “Hubble Asteroid Hunter – III. Physical properties of newly found asteroids” by Pablo García-Martín, Sandor Kruk, Marcel Popescu, Bruno Merín, Karl R. Stapelfeldt, Robin W. Evans, Benoit Carry and Ross Thomson, 15 March 2024, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202346771
To learn how you can participate in citizen science projects related to NASA, visit https://science.nasa.gov/citizen-science/. Participation is open to everyone around the world, not limited to U.S. citizens or residents.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a joint project of NASA and the European Space Agency, built by NASA with contributions from the European Space Agency. Launched into orbit in 1990, it operates outside the distortion of Earth’s atmosphere, providing high-resolution images of space phenomena across ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths. Hubble has been instrumental in various key discoveries, including determining the rate of expansion of the universe and observing distant galaxies. Its ongoing operations are managed by the Space Telescope Science Institute, ensuring that Hubble continues to contribute valuable insights into the cosmos.







Be the first to comment on "Stellar Sleuths: Citizen Scientists and AI Uncover Hidden Asteroids With Hubble"