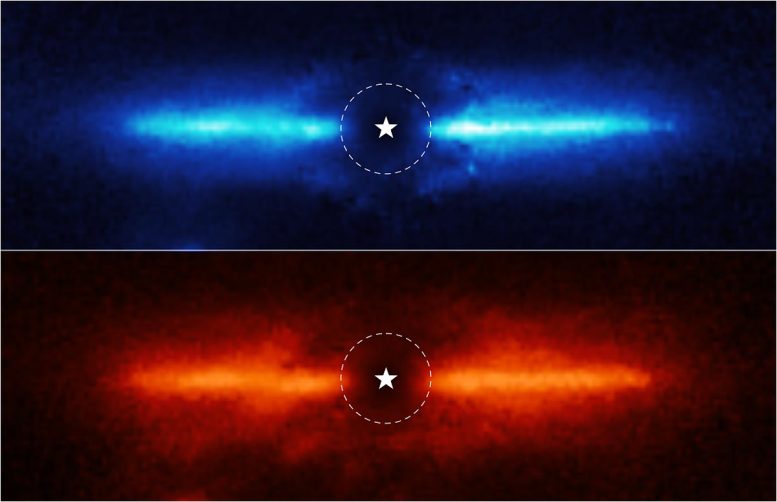
These two images are of the dusty debris disk around AU Mic, a red dwarf star located 32 light-years away in the southern constellation Microscopium. The team used Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to study AU Mic. NIRCam’s coronagraph, which blocked the intense light of the central star, allowed the team to study the region very close to the star. The location of the star, which is masked out, is marked by a white, graphical representation at the center of each image. The region blocked by the coronagraph is shown by a dashed circle.
Webb provided images at 3.56 microns (top, blue) and 4.44 microns (bottom, red). The team found that the disk was brighter at the shorter or “bluer” wavelength, likely meaning that it contains a lot of fine dust that is more efficient at scattering shorter wavelengths of light.
The NIRCam images allowed the researchers to trace the disk, which spans a diameter of 60 astronomical units (5.6 billion miles), as close to the star as 5 astronomical units (460 million miles) – the equivalent of Jupiter’s orbit in our solar system. The images were more detailed and brighter than the team expected, and scientists were able to image the disk closer to the star than expected.
Credit: Science: NASA, ESA, CSA, Kellen Lawson (NASA-GSFC), Joshua E. Schlieder (NASA-GSFC), Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
Results will aid in future searches for giant planets in wide orbits
Not so very far away in cosmic terms, the dusty leftovers of planet formation surround the red dwarf star AU Mic. Caused by smash-ups of small, solid objects called planetesimals, these remnants encircle the small star in an enormous debris disk. Now, Webb is providing scientists with detailed, never-before-seen views of AU Mic’s dusty disk in infrared light, including the region very close to the star. These images offer clues to the makeup of the debris disk and the history of the star system.
Although imaging the disk is significant, the team’s ultimate goal is to search for giant planets in wide orbits, similar to the gas and ice giants of our solar system. By delving into new, uncharted territory in direct imaging around low-mass stars, this work brings them one, huge step closer to achieving that goal.
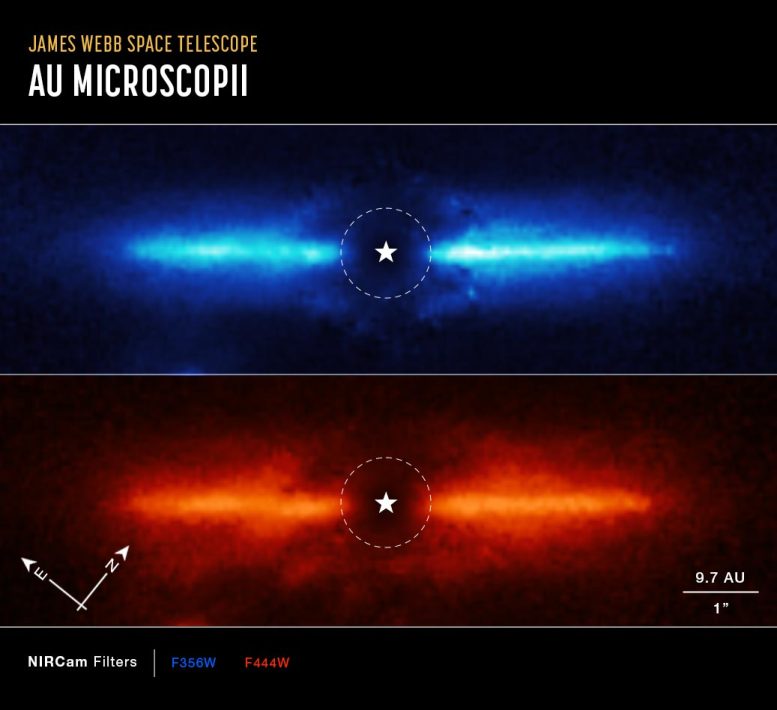
These coronagraphic images of a disk around the star AU Microscopii, captured by Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), show compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference.
The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above).
The scale bar is labeled in astronomical units, or A.U., which is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. The field of view shown in this image is approximately 100 A.U. across.
This image shows invisible near-infrared and mid-infrared wavelengths of light that have been translated into visible-light colors. The color key shows which NIRCam filters were used when collecting the light. The color of each filter name is the visible light color used to represent the infrared light that passes through that filter.
Credit: Science: NASA, ESA, CSA, Kellen Lawson (NASA-GSFC), Joshua E. Schlieder (NASA-GSFC), Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has imaged the inner workings of a dusty disk surrounding a nearby red dwarf star. These observations represent the first time the previously known disk has been imaged at these infrared wavelengths of light. They also provide clues to the composition of the disk.
The star system in question, AU Microscopii or AU Mic, is located 32 light-years away in the southern constellation Microscopium. It’s approximately 23 million years old, meaning that planet formation has ended since that process typically takes less than 10 million years. The star has two known planets, discovered by other telescopes. The dusty debris disk that remains is the result of collisions between leftover planetesimals – a more massive equivalent of the dust in our solar system that creates a phenomenon known as zodiacal light.
“A debris disk is continuously replenished by collisions of planetesimals. By studying it, we get a unique window into the recent dynamical history of this system,” said Kellen Lawson of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, lead author on the study and a member of the research team that studied AU Mic.
“This system is one of the very few examples of a young star, with known exoplanets, and a debris disk that is near enough and bright enough to study holistically using Webb’s uniquely powerful instruments,” said Josh Schlieder of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, principal investigator for the observing program and a study co-author.
The team used Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to study AU Mic. With the help of NIRCam’s coronagraph, which blocks the intense light of the central star, they were able to study the region very close to the star. The NIRCam images allowed the researchers to trace the disk as close to the star as 5 astronomical units (460 million miles) – the equivalent of Jupiter’s orbit in our solar system.
“Our first look at the data far exceeded expectations. It was more detailed than we expected. It was brighter than we expected. We detected the disk closer in than we expected. We’re hoping that as we dig deeper, there’s going to be some more surprises that we hadn’t predicted,” stated Schlieder.
The observing program obtained images at wavelengths of 3.56 and 4.44 microns. The team found that the disk was brighter at the shorter wavelength, or “bluer,” likely meaning that it contains a lot of fine dust that is more efficient at scattering shorter wavelengths of light. This finding is consistent with the results of prior studies, which found that the radiation pressure from AU Mic — unlike that of more massive stars — would not be strong enough to eject fine dust from the disk.
While detecting the disk is significant, the team’s ultimate goal is to search for giant planets in wide orbits, similar to Jupiter, Saturn, or the ice giants of our solar system. Such worlds are very difficult to detect around distant stars using either the transit or radial velocity methods.
“This is the first time that we really have sensitivity to directly observe planets with wide orbits that are significantly lower in mass than Jupiter and Saturn. This really is new, uncharted territory in terms of direct imaging around low-mass stars,” explained Lawson.
These results are being presented today in a press conference at the 241st meeting of the American Astronomical Society. The observations were obtained as part of Webb’s Guaranteed Time program 1184.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).








Be the first to comment on "Webb Space Telescope Reveals Dusty Leftovers of Planet Formation Like Never Seen Before"