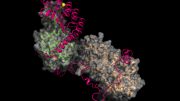
Actin is the second most abundant protein on earth, and scientists have extensively detailed the chemistry that enables it to string together into filaments that support the structures for muscle contraction and other cell movements. However, some questions have perplexed researchers for decades, such as why one end of the filament grows so much faster than the other end and how actin, once assembled into filaments, interacts with the energy-storing molecule ATP. Yale scientists Steve Chou and Tom Pollard used advanced cryo-microscopy to determine the highest resolution structures of actin filaments, which answered these and other questions. “We understood the chemistry, but until now we could not see how the processes work at the atomic level,” Pollard said. In the accompanying video, Chou and Pollard illustrate the intricate steps involved.
Reference: “Mechanism of actin polymerization revealed by cryo-EM structures of actin filaments with three different bound nucleotides” by Steven Z. Chou and Thomas D. Pollard, 17 December 2018, PNAS.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1807028115



Be the first to comment on "Yale Scientists Show Actin in Action"