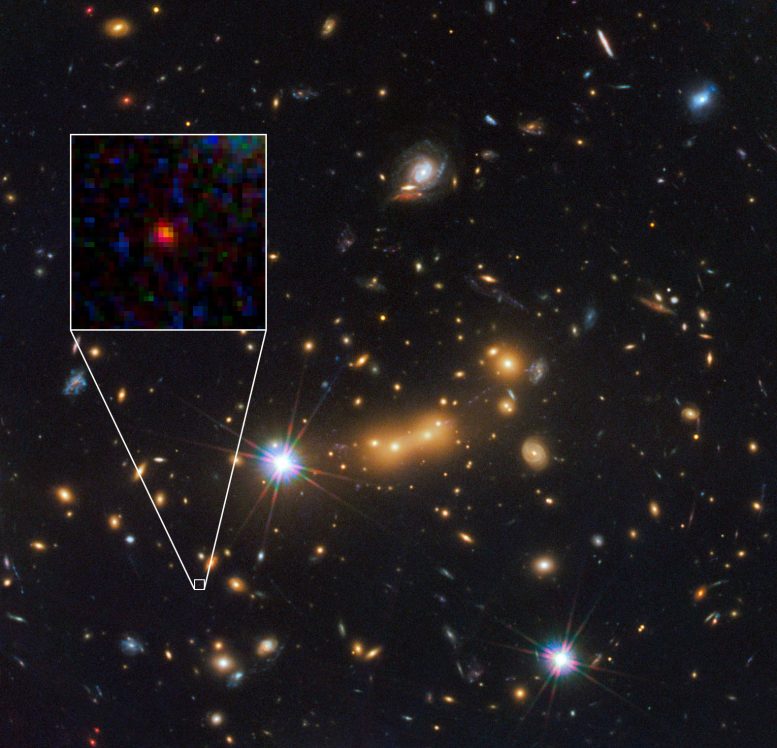

In this image, astronomers use the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and a cosmic zoom lens to uncover the farthest known galaxy in the Universe. The newly discovered galaxy, named MACS0647-JD, is very young and only a tiny fraction of the size of our Milky Way. The object is observed 420 million years after the Big Bang, when the Universe was 3 percent of its present age of 13.7 billion years. The inset at left shows a close-up of the young dwarf galaxy. Credit: NASA, ESA, and M. Postman and D. Coe (Space Telescope Science Institute), and the CLASH team
The galaxy known as MACS0647-JD is located behind an enormous galactic cluster MACS J0647+7015 that lies between the Big and Little Dipper. Data shows that MACS0647-JD is probably the most distant galaxy ever seen.
Either MACS0647-JD is a very red object, only shining at red wavelengths, or it is extremely distant and its light has been ‘redshifted’ to these wavelengths, or some combination of the two, states D. Coe, lead author of the study. “Over the next 13 billion years, it may have dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of merging events with other galaxies and galaxy fragments.” The paper will appear in the December 20 issue of The Astrophysical Journal.
MACS0647-JD would have existed 13.3 billion years ago, roughly 420 million years after the Big Bang. This would place it 200 million years earlier than some of the previous candidates for the most distant objects ever spotted.
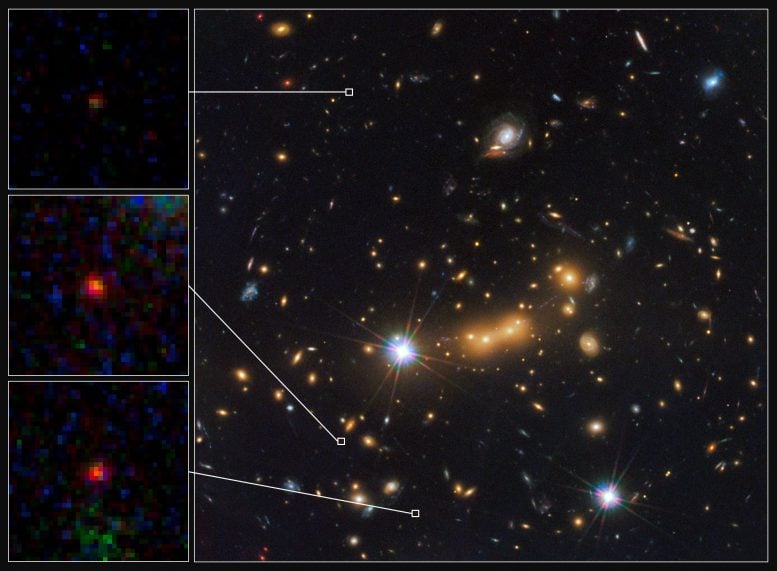

Credit: NASA, ESA, and M. Postman and D. Coe (Space Telescope Science Institute), and the CLASH team
Astronomers combined data from Hubble with NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope to make this discovery. The galaxy cluster in front of MACS0647-JD helped astronomers find it, since the gravitational pull of the cluster bends light around it. This gravitational lens makes distant objects appear much brighter. If the existence of MACS0647-JD is confirmed, then it could help scientists understand how the Universe came into being when the first stars and galaxies formed.
MACS0647-JD is a small galaxy, about 600 light-years across and roughly 250 times smaller than the Milky Way which is 150,000 light-years across. Earlier galaxies are thought to have had a turbulent past, crashing into one another and combining together over billions of years to give rise to the enormous cosmic structures we see in the Observable Universe.
Since this galaxy is stretching Hubble’s and Spitzer’s abilities, it may be much closer than expected. No other telescopes can confirm MACS0647-JD’s existence, but NASA’s future James Webb Space Telescope, set to launch in 2018, could definitively determine how far MACS0647-JD is located from Earth.
Reference: “CLASH: Three Strongly Lensed Images of a Candidate z ~ 11 Galaxy” by Dan Coe, Adi Zitrin, Mauricio Carrasco, Xinwen Shu, Wei Zheng, Marc Postman, Larry Bradley, Anton Koekemoer, Rychard Bouwens, Tom Broadhurst, Anna Monna, Ole Host, Leonidas A. Moustakas, Holland Ford, John Moustakas, Arjen van der Wel, Megan Donahue, Steven A. Rodney, Narciso Benitez, Stephanie Jouvel, Stella Seitz, Daniel D. Kelson and Piero Rosati, 13 December 2012, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.1088/0004-637X/762/1/32








Be the first to comment on "Hubble Views What Is Probably the Most Distant Known Galaxy"