Scientists have taken a significant step forward in the study of the properties of quarks and gluons, the particles that make up atomic nuclei, by resolving a long-standing issue with a theoretical calculation method known as “axial gauge.” MIT and University of Washington researchers found that the method had mistakenly suggested two properties of quark-gluon plasma were identical. They also made a prediction on gluon distribution measurement, set to be tested in future experiments with the Electron-Ion Collider.
The Science
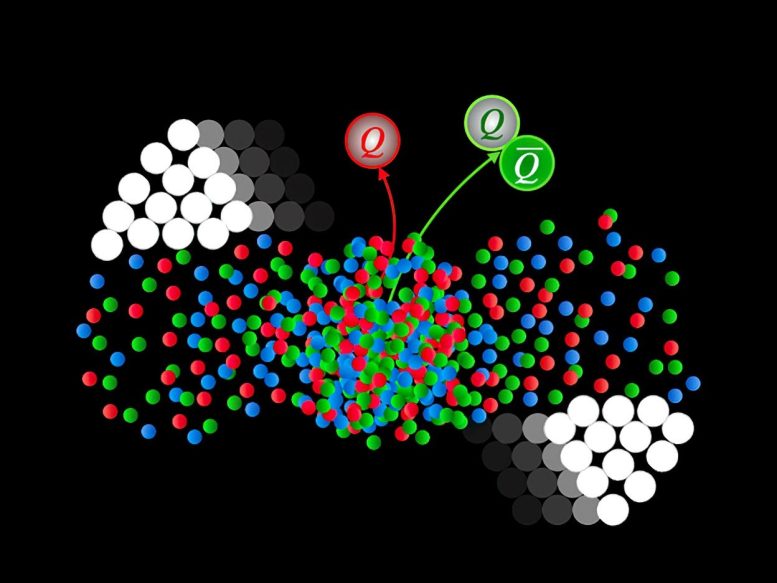
The building blocks of atomic nuclei are protons and neutrons, which are themselves made of even more fundamental particles: quarks and gluons. These particles interact via the “strong” force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. They make up the nuclei at the heart of every atom. They also make up forms of hot or dense nuclear matter that exhibit exotic properties. Scientists study the properties of hot and cold nuclear matter in relativistic heavy ion collision experiments and will continue to do so using the future Electron-Ion Collider. The ultimate goal is to understand how complex forms of matter emerge from elementary particles affected by strong forces.
The Impact
Theoretical calculations involving the strong force are complex. One aspect of this complexity arises because there are many ways to perform these calculations. Scientists refer to some of these as “gauge choices.” All gauge choices should produce the same result for the calculation of any quantity that can be measured in an experiment. However, one particular choice, called “axial gauge,” has puzzled scientists for years because of difficulties in obtaining consistent results upon making this choice. This recent study resolves this puzzle and paves the way for reliable calculations of hot and cold nuclear matter properties that can be tested in current and future experiments.
Summary
The exotic form of nuclear matter that physicists study in relativistic heavy ion collisions is called the quark-gluon plasma (QGP). This form of matter existed in the early universe. Physicists explore its properties in heavy ion collision experiments by recreating the extremely high temperatures last seen microseconds after the Big Bang. By analyzing experimental data from the collisions and comparing them with theoretical calculations, physicists can ascertain various properties of the QGP. Using a calculation method called “axial gauge” had previously seemed to imply that two QGP properties that describe how heavy quarks move through the QGP were the same.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the University of Washington have now found this implication to be incorrect. The study also carefully analyzed the subtle conditions for when axial gauge can be employed and explained why the two properties are different. Finally, it showed that two distinct methods for measuring how gluons are distributed inside nuclei must yield different results. Gluons are the particles that carry the strong force, This prediction will be tested at the future Electron-Ion Collider.
Reference: “Gauge Invariance of Non-Abelian Field Strength Correlators: The Axial Gauge Puzzle” by Bruno Scheihing-Hitschfeld and Xiaojun Yao, 2 February 2023, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.052302
This work is supported by the Department of Energy Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics and by the Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics, InQubator for Quantum Simulation (IQuS).
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
5 Comments
🤭
The wanton delusion of distorting and deviating from mathematics is the biggest failure of physical science today. Under the framework of topological vortex gravitational field, everything will become simple and real. The so-called God particles and Angel particles are myths that are detached from mathematics and arbitrary delusions, and they have nothing to do with science.
According to the topological vortex gravitational field theory, the results of relativistic heavy ion collisions must be colorful and endless. Because in a topological architecture, each particle cannot exist independently of spacetime.
… when one observes star and its planets, one would notice that it wobbles a bit… and that is used in order to note that there is a planet around the star…
… but in atoms that should be more, because there are more forces…
… order with bit of chaos… beauty full physics… and dripping faucet…
Astonishing