
Beta decay, the primary mechanism for radioactive decay in unstable isotopes, involves the transformation of neutrons into protons (beta-minus decay) or protons into neutrons (beta-plus decay), with the emission of electrons, positrons, neutrinos, or antineutrinos. Additionally, rare and theoretical forms like two-neutrino double-beta decay and the hypothetical neutrino-less double-beta decay could significantly impact our understanding of particle physics, particularly concerning the mass and nature of neutrinos. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
What Is Beta Decay?
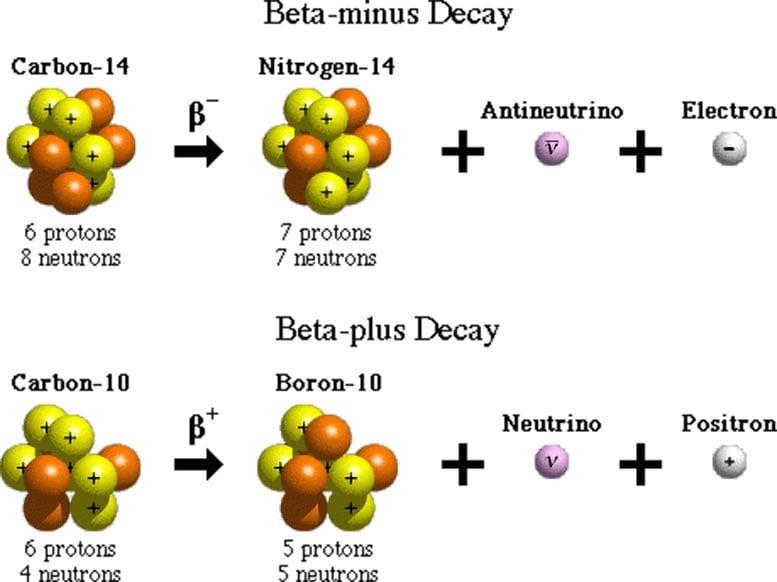
Beta decay is the most common form of radioactive decay. It happens in one of two ways. In one type of beta decay, an unstable atomic nucleus emits an electron and an antineutrino while converting a neutron to a proton. In the second type, the unstable nucleus emits a positron (a positively charged electron, also called an antielectron) and a neutrino while converting a proton to a neutron. Positrons and electrons are beta particles. Scientists have observed beta decay in 97% of all known unstable isotopes. It occurs in nuclei with too many neutrons or too many protons.
Scientists have observed two main types of beta decay. The first is beta-minus decay. In this form, a nucleus emits an electron and an antineutrino (the antimatter form of a neutrino). This process changes a neutron in the nucleus into a proton. The second type of beta decay is beta-plus decay. In this form, the nucleus emits a neutrino and a positron (the antimatter form of an electron). This process changes a proton in the nucleus into a neutron.
Beta decay occurs primarily through the transformation of neutrons to protons or vice versa, releasing particles like electrons and neutrinos. Credit: Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (JLab)
There are also rare types of beta decay. One example is two-neutrino double-beta decay. This is a transition inside a nucleus where two neutrons simultaneously undergo beta decay. In other words, two neutrons decay to two protons by emitting two neutrinos and two electrons.
Another theoretically possible type of beta decay is neutrino-less double-beta decay. In this form of beta decay, a nucleus would decay to two protons by emitting two electrons. This form has never been observed. If neutrino-less double-beta decay exists, it would mean that the neutrino has mass and is what scientists call a Majorana particle. These are particles that are identical to their antiparticles.
If scientists observe neutrino-less double-beta decay, it would help to explain missing pieces of the Standard Model of Particle Physics. The Standard Model cannot explain how neutrinos have mass. Neutrino-less double-beta decay could be the mechanism that generates the neutrino’s mass.
Beta Decay Facts
- The carbon dating technique that archaeologists use to determine age relies on the properties of beta decay.
- Beta particles from beta decay can be a health hazard. Learn more.
- Learn more about beta decay and other terms at the JLab glossary.
DOE Contributions to Radioactive Decay Research
DOE has a long history of supporting research into nuclear physics, including radioactive decay and the subatomic particles this decay involves. Researchers supported by the DOE Office of Science, often in collaboration with scientists from around the world, have contributed to Nobel Prize-winning discoveries and measurements that refined the Standard Model. These efforts continue today, with experiments that make precision tests of the Standard Model and beyond. To address neutrino-less double-beta decay specifically, DOE is participating in the Large Enriched Germanium Experiment for Neutrino-less Double beta decay (LEGEND) Collaboration at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the CUORE experiment in Italy, and the MAJORANA DEMONSTRATOR experiment in South Dakota.








Another theoretically possible type of beta decay is neutrino-less double-beta decay. In this form of beta decay, a nucleus would decay to two protons by emitting two electrons. This form has never been observed. If neutrino-less double-beta decay exists, it would mean that the neutrino has mass and is what scientists call a Majorana particle. These are particles that are identical to their antiparticles.
VERY GOOD—-These are particles that are identical to their antiparticles.
Please ask researchers to think deeply:
1. Can physical theories be imagined without mathematical models?
2. What is the difference between two-dimensional matter and three-dimensional matter?
3. Can low dimensional spacetime matter be the understructure of high-dimensional spacetime matter?
4. Are your electrons, positrons, neutrinos, or antineutrinos high-dimensional spacetime matter or low dimensional spacetime matter?
5. Is topological vortex high-dimensional spacetime matter or low dimensional spacetime matter?
6. Are topological vortices and their antivortices the same about spacetime structures ?
7. Can topological vortices form what you call neutrinos?
8. Does topological vortex violate mathematical rules?
9. Is mathematical graphics related to the physical world?
and so on.
Is this the fairy tale world of contemporary physics?
Please witness the exemplary collaboration between theoretical physicists and experimentalists (https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/701032654).
Space has physical properties of zero viscosity and absolute incompressibility. Zero viscosity and absolute incompressibility are physical characteristics of ideal fluids. The space with ideal fluid physical characteristics forms vortices via topological phase transitions, which is not difficult to understand mathematically. Once the topological vortex is formed, it occupies space and maintains its presence in time. This is the transition from chaos to order via two bidirectional coupled continuous chaotic systems.
If researchers are truly interested in science and physics, you can browse https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/695926158.
Scientific research guided by correct theories can help humanity avoid detours, failures, and pomposity.
I can see it just can not mathematically compute, what all the notable points in this article sum up as a total, the total being the meaning of everything. I would ponder to say the combinations have similarities between the quantum , standard , vastness, are these three the same that stand in different realms of physics evidence shows Yes. what are the missing links ? could the links be randomness, available quantities’, longevity , thermal direction , force plus or minus , geometry , charge state , size and so on the amount of combinations baffles the mind. the tidbits keep arising to further complication of the equation . To guess I would say the Divine being the rule, not necessarily the biblical meaning but a multifaceted equation. I would not diminish the Divine in the biblical sense because most of that resides past the veil into to infinity. Our understandings need to focus on what advantages benefit our systems of life not simply to know.