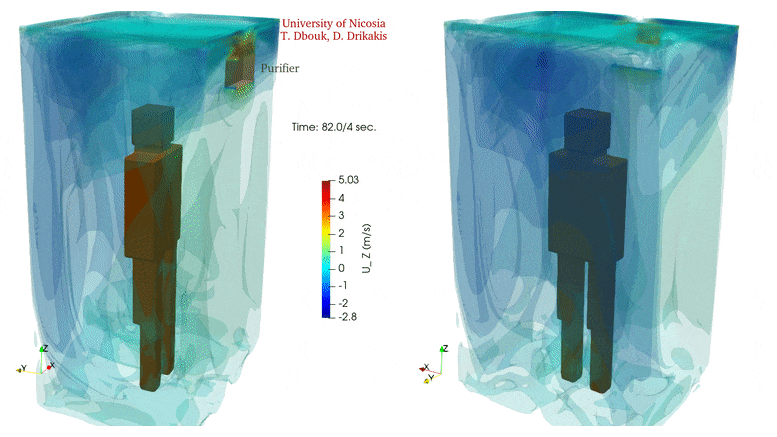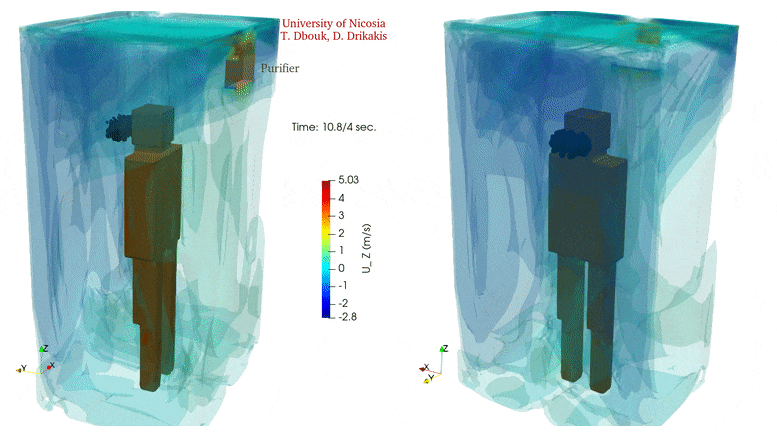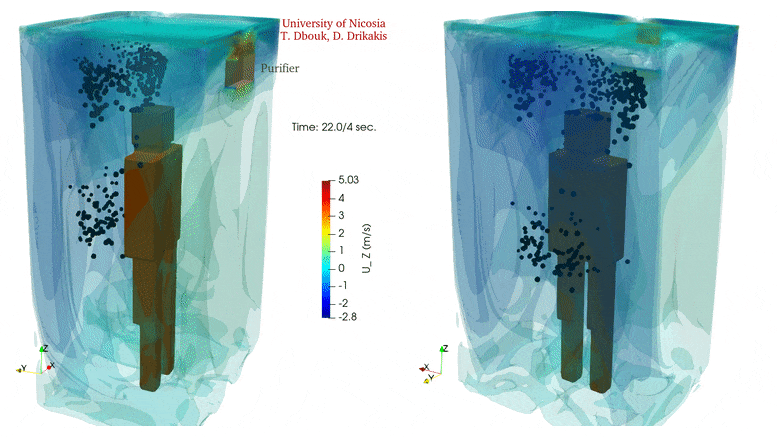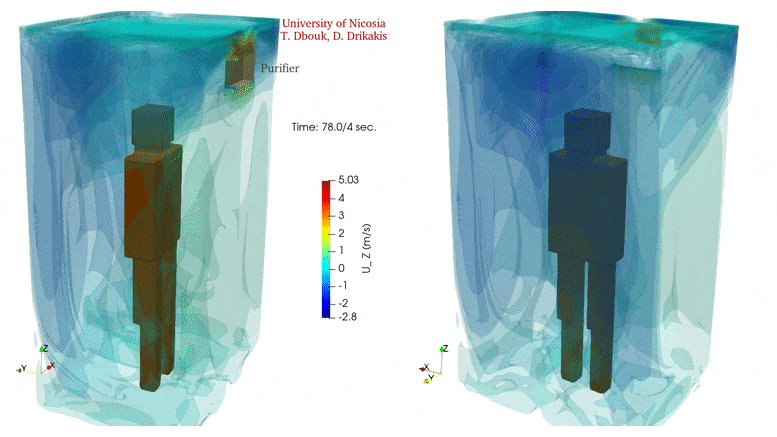
In confined spaces, air quality declines rapidly without ventilation. Yet, introducing ventilation can also escalate the circulation of potentially virus-laden air in the same space.
A computation shows air purifiers in elevators and other confined spaces can actually increase saliva droplet dispersal, spreading COVID-19.
The positions of air inlets and outlets in confined spaces, such as elevators, greatly affect airborne virus transmission. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from University of Nicosia in Cyprus show while air purifiers would be expected to help, they may actually increase the spread.
Air quality in small spaces can quickly degrade without ventilation. However, adding ventilation will increase the rate at which air, possibly laden with viruses, can circulate in the small space. Elevator manufacturers have added air purifiers to take care of this problem, but the systems have not been designed to account for their effect on overall air circulation.
Air purifiers use ultraviolet radiation to kill viruses and other microbes, but they also circulate air, sucking it in and exhausting cleaned air. This adds to overall circulation, an aspect that has not been considered in previous research.
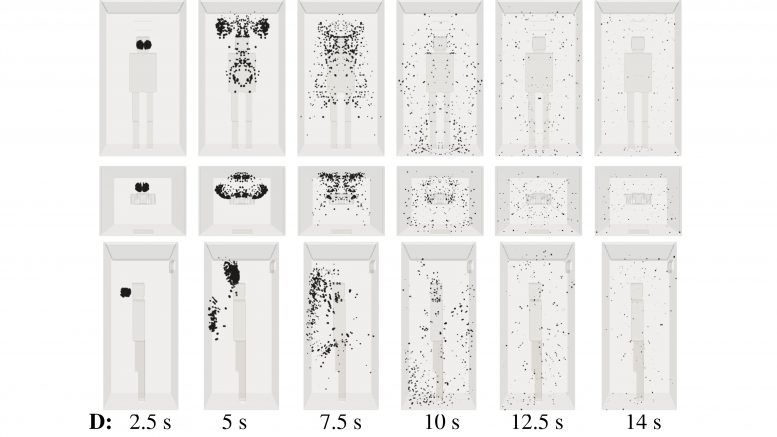
Installing an air purifier inside an elevator alters the air circulation significantly but does not eliminate airborne transmission. In contrast, an air purifier may increase the droplet spread because the air intake integrated inside the purifier equipment induces flow circulation that can add to the transport of contaminated saliva droplets in the cabin. Credit: Talib Dbouk and Dimitris Drikakis
Previous work from the scientists indicated droplets of saliva can travel 18 feet (5.5 meters) in five seconds when an unmasked person coughs. The authors extended the same model to examine the effects of face masks and weather conditions.
Investigators carried out calculations for a 3D space equivalent to an elevator capable of holding five people. A mild cough was simulated at one position in the space, and air inlets and outlets were added in various locations to study their influence on circulation. An air purifier was also included in the simulation.
“We quantified the effect of air circulation on airborne virus transmission and showed that installing an air purifier inside an elevator alters the air circulation significantly but does not eliminate airborne transmission,” said author Dimitris Drikakis.
The video shows the velocity contour isosurfaces and droplet spread inside an elevator when using an air purifier. The air purifier increases the droplet spread because the air intake integrated inside the purifier equipment induces flow circulation that can add to the transport of contaminated saliva droplets in the cabin. Credit: Talib Dbouk and Dimitris Drikakis
The investigators found the risk of airborne virus transmission is lowest for low ventilation rates.
“This is due to reduced flow mixing inside the elevator,” said author Talib Dbouk. “Regulatory authorities should thus define the minimum ventilation required depending on the type of building.”
The study looked at the role of an air purifier, considering only the air intake and exhaust associated with the purifier, but not the mechanism inside the purifier that kills the virus. Even with an air purifier in place, airborne virus transmission is still significant.
“Our results show that installing an air purifier may increase the droplet spread,” Drikakis said. “The air intake integrated inside the purifier equipment induces flow circulation that can add to the transport of contaminated saliva droplets in the cabin.”
The observed effect increases with the number of infected persons in the elevator. Restricting the number of people allowed in an elevator would minimize the spread of the virus as would better design of air purifier and ventilation systems.
Reference: “On airborne virus transmission in elevators and confined spaces” by Talib Dbouk and Dimitris Drikakis, 26 January 2021, Physics of Fluids.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0038180








I am troubled by whomever writes the headlines for your articles. A quick Google search finds most other sources about this article about air purifiers with an accurate headline, limiting the concern to use in confined spaces. Your headlines does not limit the potential for spread to small confined spaces like the elevators in the study. Instead it gives the impression that air purifiers in ALL spaces or ANY space “can actually increase the spread.”
This is not the first time. On January 10 your headline was “Surprising New Study Finds That People Who Wear Masks Are More Likely to Become Infected With COVID-19 Than Those Who Don’t.” It is not the mask that increases infection risk. The article clearly states the risk increases because mask wearers tend to have a false sense of safety, so increase their out of home activities and increase time in crowds.
Both headlines can influence people to not use air cleaners and to NOT WEAR masks. Both of which, especially mask wearing, are important behaviors to control the spread of the virus.
A correction to both articles would be helpful.
I guess the real take from this that one should change your air filters more often, in this Age of Covid. Once every month?