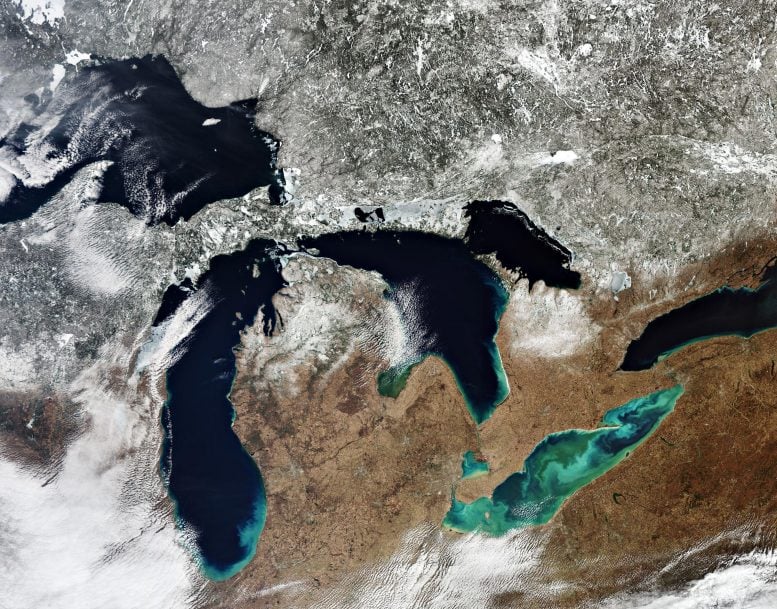

Spectacular image captured on March 15 , 2020, by the Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission of North America’s Great Lakes: Lake Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. A large quantity of ice and snow coverage is visible north of the lakes, yet the amount of ice cover on the lakes is minimal – extremely unusual for the ice season which typically runs from December 1 through April 30. Credit: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
All five of North America’s Great Lakes are pictured in this spectacular satellite image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission: Lake Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario.
The Great Lakes are a chain of deep freshwater lakes. With a combined area of around 244,000 sq km (94,250 sq miles), the lakes represent the largest surface of freshwater in the world – covering an area exceeding that of the United Kingdom.
Around 100,000 years ago, a major ice sheet formed over most of Canada and part of the US. As it formed, giant glaciers flowed into the land carving out valleys and leveling mountains. As higher temperatures began to melt the ice sheet, meltwater filled the holes left by the glaciers.
Many of these holes today still contain water and formed the thousands of lakes across the central USA and Canada. The biggest remnants of this process are the Great Lakes. The lakes drain roughly from west to east and empty into the Atlantic Ocean.
Lake Superior, the northernmost and westernmost lake, is the largest and deepest of the Great Lakes. It drains into Lake Huron via the St. Marys River at an average rate of 2000 cubic meters (530,000 gallons) per second. Lake Michigan lies south of Lake Superior and connects with Lake Huron through the six km-wide (3.7-mi-wide) channel Straits of Mackinac in the north. Lake Huron is the second largest of the Great Lakes and is bounded by Michigan, US, on the north and by Ontario, Canada, to the east.
Lake Erie is the shallowest and southernmost of the Great Lakes. Green algal blooms are visible on the lake. These toxic blooms have been a problem for the lake in recent years. Caused by heightened levels of phosphorus – found in fertilizers and common household products – finding its way into the water, these blooms have caused harm to the lake’s fish population.
Lake Ontario is the easternmost of the Great Lakes and also the smallest in surface area. It is bounded on the north by Ontario, Canada and on the south by New York, US, whose water boundaries meet in the middle of the lake.
In this image (at the top of the page), captured on March 15 , 2020, a large quantity of ice and snow coverage is visible north of the lakes, yet the amount of ice cover on the lakes is minimal – extremely unusual for the ice season which typically runs from December 1 through April 30.
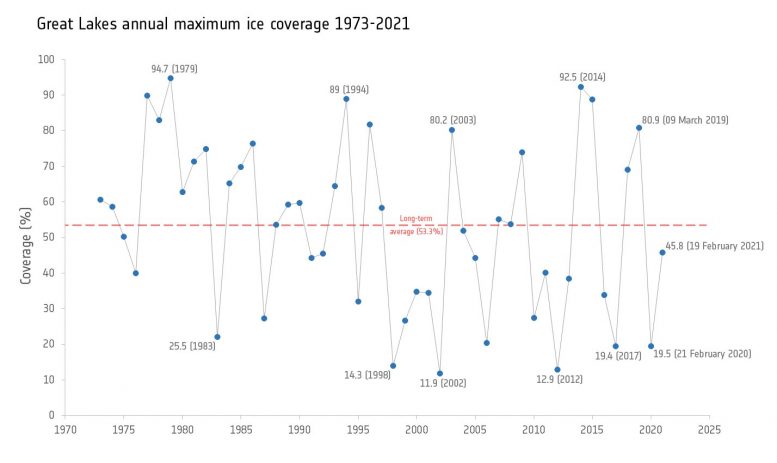
Great Lakes annual maximum ice coverage 1973-2021. Ice cover on the Great Lakes can fluctuate dramatically from year to year, depending on several patterns of climate variability. Years with lower-than-normal ice cover appear to have become more frequent during the past two decades. The graph indicates that 1979 was the year with the highest ice coverage (94.7%), while 2002 had the lowest maximum ice coverage (11.8%) meaning that the Great Lakes were almost ice-free for the entire year. Credit: ESA (Data source: NOAA GLERL)
Parts of the Great Lakes typically freeze every winter. As Earth’s climate changes, rising air and water temperatures have led to less ice cover on many lakes in North America, including the Great Lakes.
Ice cover on the Great Lakes can fluctuate dramatically from year to year, depending on several patterns of climate variability. Years with lower-than-normal ice cover appear to have become more frequent during the past two decades. The graph above indicates that 1979 was the year with the highest ice coverage (94.7%), while 2002 had the lowest maximum ice coverage (11.8%) meaning that the Great Lakes were almost ice-free for the entire year.
Sentinel-3 is a two-satellite mission to supply the coverage and data delivery needed for Europe’s Copernicus environmental monitoring program. Each satellite’s instrument package includes an optical sensor to monitor changes in the color of Earth’s surfaces. It can be used, for example, to monitor ocean biology and water quality.






Be the first to comment on "Exploring Earth From Space: Spectacular View of the Great Lakes"