
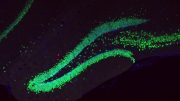
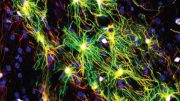
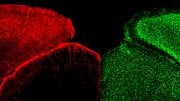
Dr. Corrado Cali explores 3D reconstructions of extremely complex brain cells known as astrocytes, a key cell involved in memory formation and learning, within KAUST’s Visualization Core Laboratories. Credit: KAUST
Researchers at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) are officially one-step closer to understanding the brain and its function.
Dr. Corrado Calì, a Research Scientist specializing in brain imaging at KAUST, and Swiss scientists from the Blue Brain Project (BBP), have shown how lactate is necessary for memory formation and learning, which could lead to improved learning and memory function. The project falls under the umbrella of the ambitious European Human Brain Project consortium framework.
Through a number of imaging experiments at KAUST’s Visualization Core labs in the past five years, Dr. Calì was able to produce three-dimensional models of astrocytes, necessary to simulate with spatial accuracy the metabolic coupling between neurons and glial cells using mathematical models developed by the BBP.
“Astrocytes are cells that store energy, and give energy to neurons at multiple levels,” Dr. Cali explains. “To do that, it was important to produce accurate 3D reconstructions of these astrocytes.”
The research, published in the journal Progress in Neurobiology, uses a technique called serial block-face electron microscopy to generate an image stack — a collection of images that can produce a volumetric image of a piece of tissue that contains astrocytes — he was then able to segment them and reconstruct the cells.
Astrocytes are known to be extremely complex in structure, rendering it impossible to image them in their entirety using light or fluorescence microscopy techniques, unless performed through electro-microscopy.
As of yet, astrocytes, which are types of brain cells, and the role they play in brain function is not well understood. Increasingly, work is suggesting that designing drugs that can help these cells to better function during pathological conditions, helps the brain recover during a stroke or Alzheimer’s Disease. “We could help to slow down the disease by acting specifically on these cells,” Dr. Calì noted.
“The first step to understand how the cell works is to understand how it is structured and this is the first work in literature where we see in detail, in 3D, the full structure of an astrocyte.”
The ground-breaking work could allow scientists to understand if different compartments of astrocytes behave differently.
Dr. Calì believes learning how the brain uses lactate is important, as several studies from the CHUV Hospital in Lausanne, Switzerland show, for instance, that lactate injections within 30 minutes from a stroke can significantly reduce the infarcted brain areas. It can also drastically improve the recovery of normal functions in affected patients, while other studies demonstrate the efficacy of lactate in reversing depression.
“By understanding deeply, from a cellular and molecular point of view its mechanism of action, we can design and maximize the efficiency of treatments based on lactate,” Dr. Cali concluded.
Reference: “3D cellular reconstruction of cortical glia and parenchymal morphometric analysis from Serial Block-Face Electron Microscopy of juvenile rat” by Corrado Calì, Marco Agus, Kalpana Kare, Daniya J.Boges, Heikki Lehväslaiho, Markus Hadwiger and Pierre J.Magistretti, 21 September 2019, Progress in Neurobiology.
DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.101696


Be the first to comment on "Ground-Breaking Work & Incredible Imaging Improves Understanding of Brain Function"