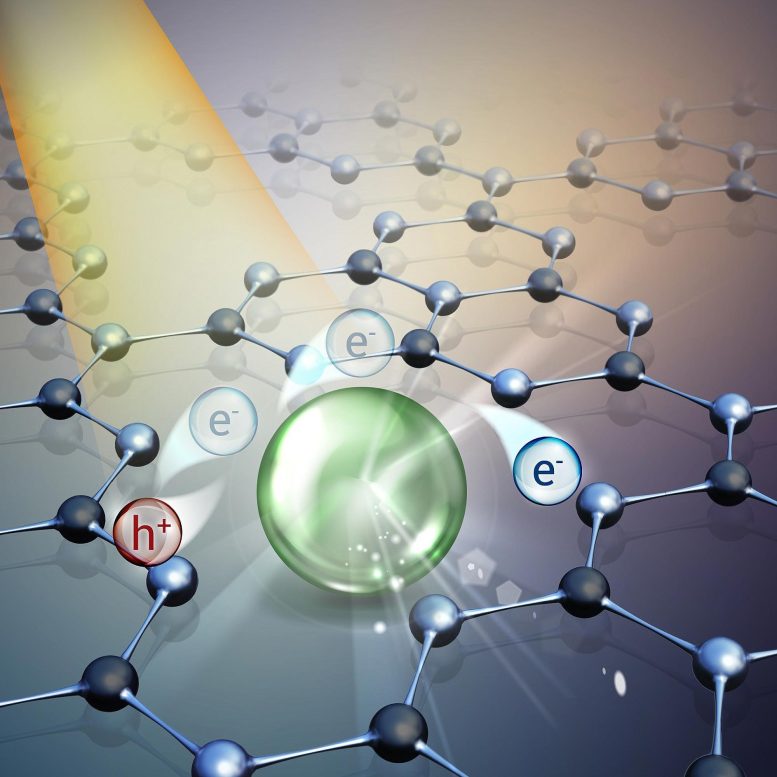
Researchers have pioneered a more efficient, eco-friendly method for chemical synthesis, promising significant improvements in sustainability. The innovative technique involves the dispersion of isolated atoms on carbon nitride supports, forming a catalyst more active in esterification reactions—crucial for producing items like medicines, food additives, and polymers. The catalyst reduces reliance on rare metals and can be activated by sunlight, curbing energy consumption. Credit: Politecnico di Milano
Scientists developed a novel, sun-activated catalyst that reduces reliance on rare metals and enhances the efficiency of esterification reactions, crucial for products like medicines and polymers. This breakthrough in chemical synthesis promises significant sustainability improvements by conserving finite resources and lowering environmental impact.
A new discovery by the Politecnico di Milano opens up new perspectives in the field of sustainable chemical synthesis, promoting innovative solutions that allow chemicals to be created in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way. The research was published in the prestigious journal Nature Synthesis.
Using the innovative technique of dispersing isolated atoms on carbon nitride supports, the team developed a catalyst that is more active and selective in esterification reactions. This is an important reaction in which carboxylic acids and bromides are combined to form products used in the manufacture of medicines, food additives and polymers.
The revolutionary feature of this new catalyst is that it reduces the use of rare metals, a significant step towards conserving critical resources and making processes more sustainable. In addition, the catalyst can be activated by sunlight, eliminating the need for energy-intensive methods. This discovery holds enormous potential in reducing dependence on finite resources and lowering the environmental impact of catalytic processes.
Reference: “Light-driven C–O coupling of carboxylic acids and alkyl halides over a Ni single-atom catalyst” by Mark A. Bajada, Giovanni Di Liberto, Sergio Tosoni, Vincenzo Ruta, Lorenzo Mino, Nicolò Allasia, Alessandra Sivo, Gianfranco Pacchioni and Gianvito Vilé, 15 June 2023, Nature Synthesis.
DOI: 10.1038/s44160-023-00341-3
Professor Gianvito Vilé, Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering at the ‘Giulio Natta’ Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering, coordinated the project, while Mark Bajada, a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellow at the Politecnico di Milano, is the first author of the paper. The study was conducted in close collaboration with researchers from the University of Milan Bicocca and the University of Turin, and was funded by the European Commission through a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship and a Horizon Europe project recently awarded to the Politecnico di Milano (SusPharma).







Be the first to comment on "Harnessing Sunlight: Breakthrough in Sustainable Catalysts for Chemical Synthesis"