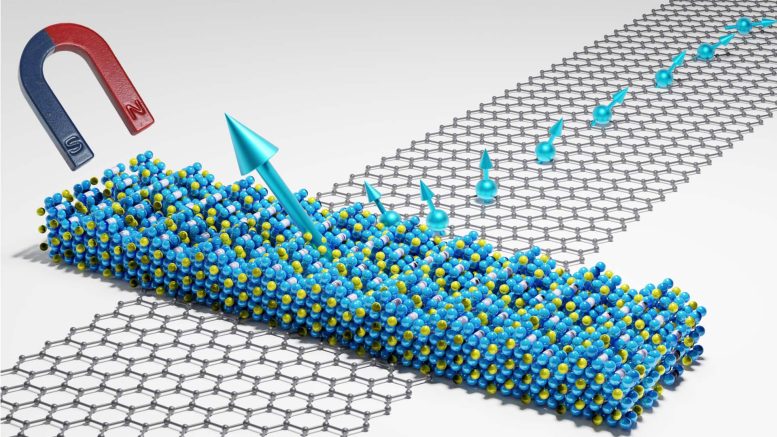
The researchers have for the first time succeeded in demonstrating a device, based on a 2D magnetic material, in room temperature. The 2D magnetic crystal is shown as the blue, yellow and white balls and is a mix of Iron, Tellurium and Germanium atoms. The big turquoise arrow indicates the magnetization direction of the 2D magnet. The crystal with gray color is the carbon atoms of the graphene channel. The smaller turquoise arrows indicate the spin-polarized electrons injected from the 2D magnet into the graphene channel. Here, the 2D magnet act as a source for spin-polarized electrons and the graphene channel for spin transport and communication. Credit: Chalmers/Bing Zhao
The discovery of new quantum materials with magnetic properties are believed to pave the way for ultra-fast and considerably more energy efficient computers and mobile devices. So far, these types of materials have been shown to work only in extremely cold temperatures. Now, a research team at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden are the first to make a device made of a two-dimensional magnetic quantum material work in room temperature.
Today’s rapid IT expansion generates enormous amounts of digital data that needs to be stored, processed, and communicated. This comes with an ever-increasing need for energy – projected to consume over 30 percent of the world’s total energy consumption by 2050. To combat the problem, the research community has entered a new paradigm in materials science. The research and development of two-dimensional quantum materials, that form in sheets and are only a few atoms thick, have opened new doors for sustainable, faster, and more energy-efficient data storage and processing in computers and mobiles.
The first atomically thin material to be isolated in a laboratory was graphene, a single-atom-thick plane of graphite, that resulted in the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics. And in 2017, two-dimensional materials with magnetic properties were discovered for the first time. Magnets play a fundamental role in our everyday lives, from sensors in our cars and home appliances to computer data storage and memory technologies, and the discovery opened for new and more sustainable solutions for a wide range of technology devices.

Bing Zhao, post-doc in Quantum Device Physics, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden. Credit: Chalmers
“Two-dimensional magnetic materials are more sustainable because they are atomically thin and offer unique magnetic properties that make them attractive for developing new energy-efficient and ultra-fast applications for sensors and advanced magnetic memory and computing concepts. This makes them promising candidates for a range of different technologies,” says Saroj Dash, Professor in Quantum Device Physics at Chalmers University of Technology.
The first to demonstrate 2D magnet-based devices at room-temperature
So far, researchers have only been able to demonstrate two-dimensional magnets in extremely low temperatures in laboratory environments, so called cryogenic temperatures, inhibiting their broader use in society. But now a group of researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have been able to demonstrate, for the very first time, a new two-dimensional magnetic material-based device at room temperature. They used an iron-based alloy (Fe5GeTe2) with graphene which can be used as a source and detector for spin polarised electrons*. And the breakthrough is now believed to enable a range of technical applications in several industries as well as in our everyday lives.

Saroj Dash, Professor, Quantum Device Physics Laboratory, Chalmers University of Technology. Credit: Chalmers/Oscar Mattsson
“These 2D magnets can be used to develop ultra-compact, faster and more energy-efficient memory devices in computers. They may also be used to develop highly sensitive magnetic sensors for a wide range of applications, including biomedical and environmental monitoring, navigation, and communication,” explains Bing Zhao, post-doc in Quantum Device Physics and first author of the study.
*Conventional electronic logic devices are based on nonmagnetic semiconductors and use the flow of electric charges to achieve information processing and communication. Spintronic devices, on the other hand, exploit the spin of electrons to generate and control charge currents, and to interconvert electrical and magnetic signals. By combining processing, storage, sensing, and logic within a single integrated platform, spintronics could complement and, in some cases, outperform semiconductor-based electronics, offering advantages in terms of scaling, power consumption, and data processing speed.
The demonstration is described in the study “Room Temperature Spin-Valve with van der Waals Ferromagnet Fe5GeTe2/Graphene Heterostructure” published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials. The authors of the study are Bing Zhao, Roselle Ngaloy, Sukanya Ghosh, Soheil Ershadrad, Rahul Gupta, Khadiza Ali, Anamul Md. Hoque, Bogdan Karpiak, Dmitrii Khokhriakov, Craig Polley, Balasubramanian Thiagarajan, Alexei Kalaboukhov, Peter Svedlindh, Biplab Sanyal and Saroj P. Dash.
Reference: “Room Temperature Spin-Valve with van der Waals Ferromagnet Fe5GeTe2/Graphene Heterostructure” by Bing Zhao, Roselle Ngaloy, Sukanya Ghosh, Soheil Ershadrad, Rahul Gupta, Khadiza Ali, Anamul Md. Hoque, Bogdan Karpiak, Dmitrii Khokhriakov, Craig Polley, Balasubramanian Thiagarajan, Alexei Kalaboukhov, Peter Svedlindh, Biplab Sanyal and Saroj P. Dash, 15 January 2023, Advanced Materials.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.202209113
The researchers are active at Chalmers University of Technology, Uppsala University and Max IV laboratory at Lund University, Sweden.
The project was financed by: European Union Graphene Flagship, Swedish Research Council, 2DTECH Vinnova Competence center, Wallenberg initiative on Materials Science for a Sustainable World (WISE), and European Union FLAG-ERA projects




I like the picture. It’s clear enough to overcome some issues with the caption.
I mean why not delete “2D” from the description of the magnet material since it’s much thicker, with several layers of atoms, than the single-atom thick graphene sheet that it is sitting on.
That six lines of text include the same misdescriptive term, “2D magnet,” a grand total of 5 times, it’s pretty clear to me someone on the other side is rather selfishly indulging themselves a bit too much in captioning the picture. My apologies to the readers for taking 3 comments to tie up a single thought here.
Advances in organic chemistry will be the next, big technological break-through. Digital devices are not only energy hogs but emit an enormous about of heat in their environments. Heat pollution.
Next; organic energy storage… it will be a game changer!