Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have engineered a nanochip, thinner than a tenth of a human hair, enabling the production of stable quantum-encoded photons. This breakthrough could lead to achieving ‘quantum advantage,’ where a quantum device outpaces the world’s most powerful supercomputer in specific computational tasks.
University of Copenhagen researchers have advanced their quantum technology to such a degree that classical computing technology can no longer keep up. They have developed a chip that, with financial backing, could be scaled up and used to build the quantum simulator of the future. Their results are now published in Science Advances.
First came Google. Now, researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute in collaboration with University of Bochum have joined Google in the race to build the world’s first quantum computer with what they are calling a “major breakthrough.”
“We now possess the tool that makes it possible to build a quantum simulator that can outperform a classical computer. This is a major breakthrough and the first step into uncharted territory in the world of quantum physics,” asserts Professor Peter Lodahl, Director of the Center for Hybrid Quantum Networks (Hy-Q).
Specifically, the researchers developed a nanochip less than one-tenth the thickness of a human hair. The chip allows them to produce enough stable light particles, known as photons, encoded with quantum information to scale up the technology, and in so doing, may achieve what is known as ‘quantum advantage’: the state where a quantum device can solve a given computational task faster than the world’s most powerful supercomputer.
A 10 million Euro experiment
While the researchers have yet to conduct an actual ‘quantum advantage’ experiment, their article in Science Advances proves that their chip produces a quantum mechanical resource that can be used to reach ‘quantum advantage’ with already demonstrated technology.
To achieve this state demands that one can control about 50 quantum bits, “qubits” — quantum physics’ equivalent of the binary bits of zeros and ones used in our classical computers — in a comprehensive experimental set-up that is well beyond the university’s own financial means.
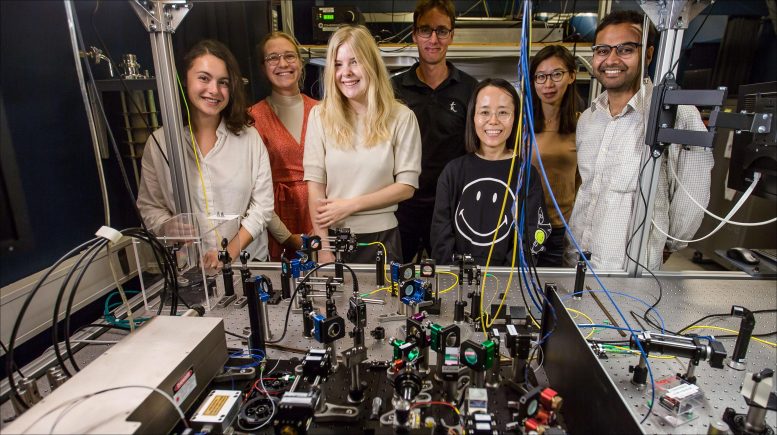
The team behind the new discovery from Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark. Credit: Niels Bohr Institute
“It could cost us 10 million Euro to perform an actual experiment that simultaneously controls 50 photons, as Google did it with superconducting qubits. We simply can’t afford that. However, what we as scientific researchers can do is to develop a photon source and prove that it can be used to achieve ‘quantum advantage’. We have developed the fundamental building block,” explains Assistant Professor Ravitej Uppu, lead author of the results.
“In the meantime, we will use our photon sources to develop new and advanced quantum simulators to solve complex biochemical problems that might, for example, be used to develop new medicines. So, we are already preparing the next steps for the technology. Being at a university allows one to establish the foundation of a technology and demonstrate the possibilities, whereas definitive technology upscaling requires greater investment. We will work to establish a strong European consortium of academic and industrial partners with a focus on building photonic quantum simulators with ‘quantum advantage’,” continues Peter Lodahl.
A bright future for upscaling quantum computers
Various schools exist in the world of qubit development for quantum computers, depending upon which “quantum building blocks” one starts with: atoms, electrons, or photons. Each platform has pros and cons, and it remains difficult to predict, which technology will triumph.
The primary advantage of light-based quantum computers is that technology is already available for scaling up to many qubits because of the availability of advanced photonic chips, which have been developed for the telecom industry. A major challenge to generating photon qubits has been to do so with sufficiently high quality. This is precisely where the Copenhagen researchers achieved their breakthrough.
“Denmark and Europe have proud traditions in quantum optics research, and at the same time a strong telecom industry and infrastructure. It would be really exciting to combine these strengths in a large-scale initiative dedicated to photonic quantum computers. It would be fantastic to be part of a process that extends all the way from fundamental quantum physics to new technological applications,” says Peter Lodahl.
Facts:
- Researchers have developed a nanochip capable of producing hundreds of light particles (photons) that can be used to store huge amounts of data in the form of quantum information.
- The nanochip produces light particles containing information, and can be used as hardware in tomorrow’s quantum computers, much in the same way that electrical transistors are used in today’s conventional computers.
- The research is funded by the Danish National Research Foundation, the European Research Council, and the Danish Agency for Science, Technology, and Innovation and is a collaboration with the University of Bochum, Germany.
Reference: “Scalable integrated single-photon source” by Ravitej Uppu, Freja T. Pedersen, Ying Wang, Cecilie T. Olesen, Camille Papon, Xiaoyan Zhou, Leonardo Midolo, Sven Scholz, Andreas D. Wieck, Arne Ludwig and Peter Lodahl, 9 December 2020, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc8268






“Possessing the tool that makes it possible” is a far cry from “classical computers can no longer keep up”. It appears they’re on a good path, having created a scalable light source.