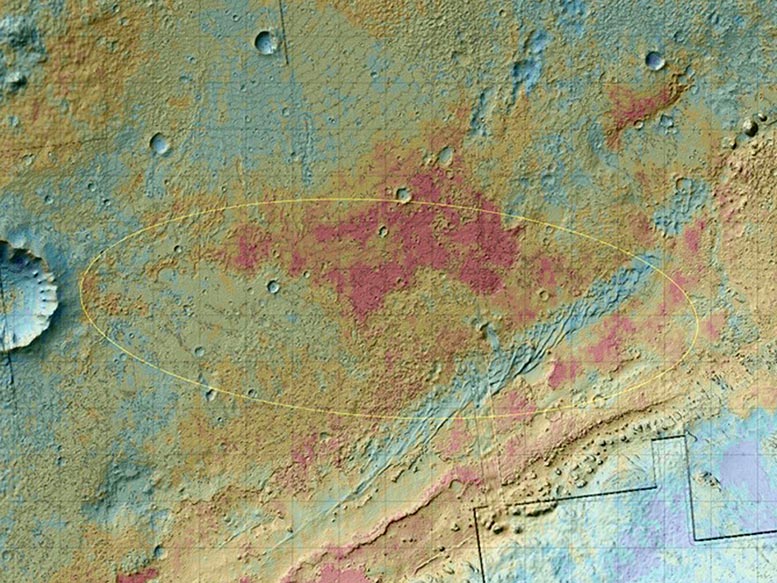

The area where NASA’s Curiosity rover will land on August 5 PDT (August 6 EDT) has a geological diversity that scientists are eager to investigate, as seen in this false-color map based on data from NASA’s Mars Odyssey orbiter. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU
Mission engineers continue to ready for the August Curiosity landing inside Gale Crater and the critical seven minute period when Curiosity must decelerate from about 5,900 meters per second to allow the rover to land on the surface at about three-fourths of a meter per second.
NASA’s most advanced planetary rover is on a precise course for an early August landing beside a Martian mountain to begin two years of unprecedented scientific detective work. However, getting the Curiosity rover to the surface of Mars will not be easy.
“The Curiosity landing is the hardest NASA mission ever attempted in the history of robotic planetary exploration,” said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “While the challenge is great, the team’s skill and determination give me high confidence in a successful landing.”
The Mars Science Laboratory mission is a precursor for future human missions to Mars. President Obama has set a challenge to reach the Red Planet in the 2030s.
To achieve the precision needed for landing safely inside Gale Crater, the spacecraft will fly like a wing in the upper atmosphere instead of dropping like a rock. To land the 1-ton rover, an airbag method used on previous Mars rovers will not work. Mission engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, designed a “sky crane” method for the final several seconds of the flight. A backpack with retro-rockets controlling descent speed will lower the rover on three nylon cords just before touchdown.
During a critical period lasting only about seven minutes, the Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft carrying Curiosity must decelerate from about 13,200 mph (about 5,900 meters per second) to allow the rover to land on the surface at about 1.7 mph (three-fourths of a meter per second). Curiosity is scheduled to land at approximately 10:31 p.m. PDT on August 5 (1:31 a.m. EDT on August 6).
“Those seven minutes are the most challenging part of this entire mission,” said Pete Theisinger, the mission’s project manager at JPL. “For the landing to succeed, hundreds of events will need to go right, many with split-second timing and all controlled autonomously by the spacecraft. We’ve done all we can think of to succeed. We expect to get Curiosity safely onto the ground, but there is no guarantee. The risks are real.”
During the initial weeks after the actual landing, JPL mission controllers will put the rover through a series of checkouts and activities to characterize its performance on Mars, while gradually ramping up scientific investigations. Curiosity then will begin investigating whether an area with a wet history inside Mars’ Gale Crater ever has offered an environment favorable for microbial life.
“Earlier missions have found that ancient Mars had wet environments,” said Michael Meyer, lead scientist for NASA’s Mars Program at NASA Headquarters. “Curiosity takes us the next logical step in understanding the potential for life on Mars.”
Curiosity will use tools on a robotic arm to deliver samples from Martian rocks and soils into laboratory instruments inside the rover that can reveal chemical and mineral composition. A laser instrument will use its beam to induce a spark on a target and read the spark’s spectrum of light to identify chemical elements in the target.
Other instruments on the car-sized rover will examine the surrounding environment from a distance or by direct touch with the arm. The rover will check for the basic chemical ingredients for life and for evidence about energy available for life. It also will assess factors that could be hazardous for life, such as the radiation environment.
“For its ambitious goals, this mission needs a great landing site and a big payload,” said Doug McCuistion, director of the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters. “During the descent through the atmosphere, the mission will rely on bold techniques enabling use of a smaller target area and a heavier robot on the ground than were possible for any previous Mars mission. Those techniques also advance us toward human-crew Mars missions, which will need even more precise targeting and heavier landers.”
The chosen landing site is beside a mountain informally called Mount Sharp. The mission’s prime destination lies on the slope of the mountain. Driving there from the landing site may take many months.
“Be patient about the drive. It will be well worth the wait and we are apt to find some targets of interest on the way,” said John Grotzinger, MSL project scientist at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. “When we get to the lower layers in Mount Sharp, we’ll read them like chapters in a book about changing environmental conditions when Mars was wetter than it is today.”
In collaboration with Microsoft Corp., a new outreach game was unveiled Monday to give the public a sense of the challenge and adventure of landing in a precise location on the surface. Called “Mars Rover Landing,” the game is an immersive experience for the Xbox 360 home entertainment console that allows users to take control of their own spacecraft and face the extreme challenges of landing a rover on Mars.
“Technology is making it possible for the public to participate in exploration as it never has before,” said Michelle Viotti, JPL’s Mars public engagement manager. “Because Mars exploration is fundamentally a shared human endeavor, we want everyone around the globe to have the most immersive experience possible.”
NASA has several other forthcoming experiences geared for inspiration and learning in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Information about many ways to watch and participate in the Curiosity’s landing and the mission on the surface of Mars is available at: http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/participate.
Mars Science Laboratory is a project of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. The mission is managed by JPL. Curiosity was designed, developed and assembled at JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.






Be the first to comment on "Mission Engineers Prepare for Curiosity’s Landing on Mars"