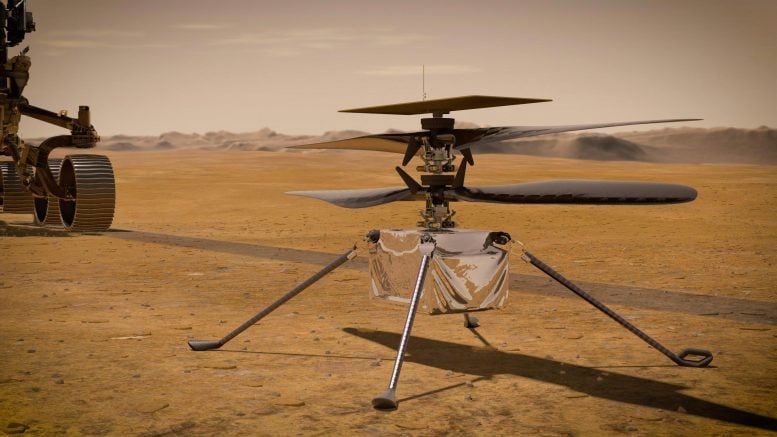

In this illustration, NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter stands on the Red Planet’s surface as NASA’s Perseverance rover (partially visible on the left) rolls away. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Making it through the frigid Martian temperatures after being deployed by NASA’s Perseverance rover is a major milestone for the small rotorcraft.
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter has emerged from its first night on the surface of Mars.
Evening temperatures at Jezero Crater can plunge as low as minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 90 degrees Celsius), which can freeze and crack unprotected electrical components and damage the onboard batteries required for flight. Surviving that first night after being deployed from where it was attached to the belly of NASA’s Perseverance rover on April 3 is a major milestone for the 4-pound (1.8 kilograms) rotorcraft. In the days to come, Ingenuity will be the first aircraft to attempt powered, controlled flight on another planet.
“This is the first time that Ingenuity has been on its own on the surface of Mars,” said MiMi Aung, Ingenuity project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “But we now have confirmation that we have the right insulation, the right heaters, and enough energy in its battery to survive the cold night, which is a big win for the team. We’re excited to continue to prepare Ingenuity for its first flight test.”
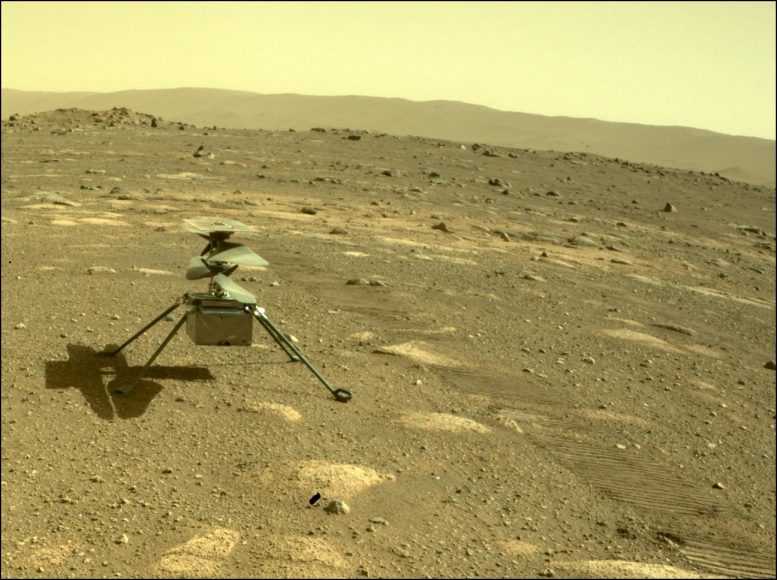

NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter can be seen on Mars as viewed by the Perseverance rover’s rear Hazard Camera on April 4, 2021, the 44th Martian day, or sol of the mission. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Devising a craft small enough to fit onto the rover, light enough to fly in Mars’ thin atmosphere, yet hardy enough to withstand the Martian cold presented significant challenges. To ensure the solar array atop the helicopter’s rotors could begin getting sunlight as soon as possible, Perseverance was instructed to move away from Ingenuity shortly after deploying it.
Until the helicopter put its four legs onto the Martian surface, Ingenuity remained attached to the belly of the rover, receiving power from Perseverance, which touched down at Jezero Crater on February 18. The rover serves as a communications relay between Ingenuity and Earth, and it will use its suite of cameras to observe the flight characteristics of the solar-powered helicopter from “Van Zyl Overlook.”

The location where NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover will observe the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter’s attempt at powered controlled flight at Mars is called “Van Zyl Overlook,” after Jakob van Zyl. Van Zyl was the team’s longtime colleague, mentor, and leader at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. He passed away unexpectedly in August 2020, about a month after the launch of Perseverance. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The sole mission of Ingenuity, a technology demonstration, is to conduct flight tests in the thin atmosphere of Mars; the helicopter carries no science instruments. Within 30 Martian days, or sols (a Martian day is 24.6 hours), on the surface, Ingenuity will complete its testing, and Perseverance’s scientific exploration of Jezero Crater will kick into high gear.
“Our 30-sol test schedule is frontloaded with exciting milestones,” said Teddy Tzanetos, deputy operations lead for the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at JPL. “Whatever the future holds, we will acquire all the flight data we can within that timeframe.”
The Month of Ingenuity
On April 4, Perseverance downlinked the first of the images of the helicopter on the surface of Mars. Taken by the rover’s rear left Hazard Avoidance camera, the image shows the helicopter’s rotor blades still stacked in alignment on top of each other (a configuration used to save room during the trip to Mars) and its four footpads firmly planted into the surface of Mars.

The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter took this image with its color camera from beneath the Perseverance rover after the rover had deployed the rotorcraft to the surface of Mars. Image was taken on April 3, 2021. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
For the next two days, Ingenuity will collect information about how well the thermal-control and power systems perform now that the small helicopter is standing on its own in the Mars environment. That information will be used to fine tune Ingenuity’s thermal-control system to help it survive the harsh Mars nights through the entire flight experiment period.
On April 7, the restraints that have been holding the rotor blades together since before launch are scheduled to be released. If the mission team meets that milestone, the next several sols will involve more testing of the rotor blades as well as the motors that drive them. There are also checkouts of the inertial measurement unit (an electronic device that measures a body’s orientation and angular rate) and onboard computers tasked with autonomously flying the helicopter. Additionally, the team will continue to monitor the helicopter’s energy performance, including assessment of solar-array power and state of charge of the craft’s six lithium ion batteries.
If all goes well with each of the myriad preflight checks, Ingenuity’s first attempt to lift off from the middle of its 33-by-33-foot (10-by-10-meter) “airfield” – chosen for its flatness and lack of obstructions – will be no sooner than the evening of April 11.
Subsequent flight tests will be scheduled throughout the Month of Ingenuity, with Perseverance’s cameras providing plenty of high-definition images of the historic mission.
More About Ingenuity
The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, the NASA Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and the NASA Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA’s Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance.
At NASA Headquarters, Dave Lavery is the program executive for the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. At JPL, MiMi Aung is the project manager and J. (Bob) Balaram is chief engineer.
JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter.







Be the first to comment on "NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter Survives First Frigid Martian Night on Its Own"