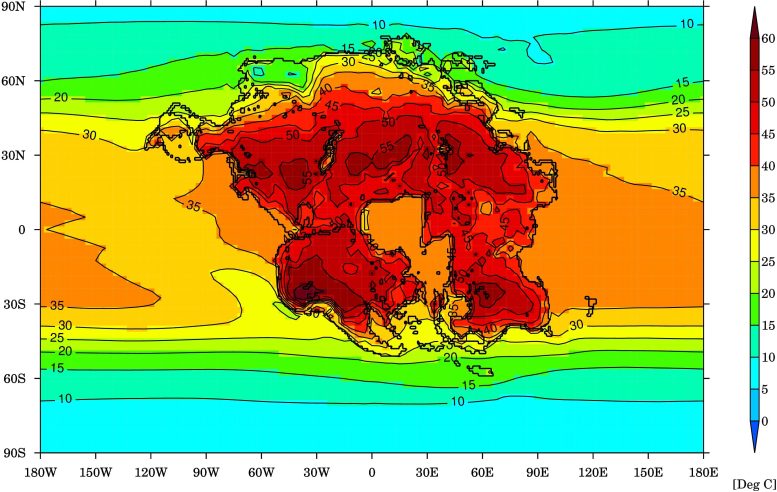
This image shows the warmest month average temperature (degrees Celsius) for Earth and the projected supercontinent (Pangea Ultima) in 250 million years, when it would be difficult for almost any mammals to survive. Credit: University of Bristol
A study predicts that the formation of a supercontinent, Pangea Ultima, 250 million years in the future could lead to extreme temperatures, threatening mammalian survival due to increased volcanism and a hotter Sun.
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience uses supercomputer climate models to examine how a supercontinent, dubbed Pangea Ultima (also called Pangea Proxima), that will form 250 million years from now will result in extreme temperatures, making this new supercontinent uninhabitable for life, specifically mammals. This study was conducted by an international team of researchers led by the University of Bristol and holds the potential to help scientists better understand how Earth’s climate could change in the distant future from natural processes, as opposed to climate change.
The Earth’s temperatures are estimated to rise drastically 250 million years from now due to two reasons: increased volcanism from the tectonic activity merging all the continents together, and our Sun giving off more energy and heat as it ages. While volcanoes act as temperature moderators by releasing carbon dioxide and naturally warming the planet, too much volcanism results in too much carbon dioxide, which results in drastic temperature increases. Additionally, like mammals, our Sun also grows with age, and as it grows it gives off more heat and energy.
“The newly emerged supercontinent would effectively create a triple whammy, comprising the continentality effect, hotter sun and more CO2 in the atmosphere, of increasing heat for much of the planet,” said Dr. Alexander Farnsworth, who is a Senior Research Associate at the University of Bristol and lead author of the study. “The result is a mostly hostile environment devoid of food and water sources for mammals. Widespread temperatures of between 40 to 50 degrees Celsius, and even greater daily extremes, compounded by high levels of humidity would ultimately seal our fate. Humans – along with many other species – would expire due to their inability to shed this heat through sweat, cooling their bodies.”
The reason mammals, including humans, have survived for so long on the Earth is due to their uncanny ability to adapt to extreme weather conditions. However, while evolution has resulted in mammals being able to lower their survivable limit in cold temperatures, they aren’t able to increase their survivable limit in hot temperatures. This means that as the Earth’s temperatures continue to rise, it will make the likelihood of mammals surviving in these new conditions unlikely.
“The outlook in the distant future appears very bleak,” said Dr. Farnsworth. “Carbon dioxide levels could be double current levels. With the Sun also anticipated to emit about 2.5% more radiation and the supercontinent being located primarily in the hot, humid tropics, much of the planet could be facing temperatures of between 40 to 70 °C. This work also highlights that a world within the so-called ‘habitable zone’ of a solar system may not be the most hospitable for humans depending on whether the continents are dispersed, as we have today, or in one large supercontinent.”
While Pangea Ultima might be dominating the Earth 250 million years from now, it won’t be the first supercontinent to grace the Earth’s surface in the planet’s history. Scientists hypothesize there have been 10 supercontinents that have existed throughout Earth’s history, with the most well-known being Pangea, the most recent supercontinent to exist. The reason all these supercontinents have existed throughout the Earth’s approximately 4.5 billion-year history is due to plate tectonics since the Earth’s surface is divided into 7 major and 8 minor plates that collide and subduct beneath each other over vast geologic periods of time.
How will Pangea Ultima change the habitability of the Earth and what new discoveries about supercontinents will scientists make in the coming years and decades? Only time will tell, and this is why we science!
As always, keep doing science & keep looking up!
Adapted from an article originally published on Universe Today.
Reference: “Climate extremes likely to drive land mammal extinction during next supercontinent assembly” by Alexander Farnsworth, Y. T. Eunice Lo, Paul J. Valdes, Jonathan R. Buzan, Benjamin J. W. Mills, Andrew S. Merdith, Christopher R. Scotese and Hannah R. Wakeford, 25 September 2023, Nature Geoscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01259-3







If evolution is true then wouldnt humans, along with other life, have evolved during this 250 million years to deal with the conditions on Earth?
There have been mass extinctions about every 27 million years. It is unlikely that whatever evolves from modern humans will even remotely resemble what we look like and how we behave.
Not to worry – humans will have managed to wipe out most of the life on Earth long before then.
The actual surface temperature will vary with elevation because of the lapse rate. Furthermore, it seems that the authors and their ‘super’ climate model don’t take into consideration the type of volcanic eruptions. Mafic, quiet eruptions that result from flood basalts rich in CO2 are the result of mantle hot spots or spreading centers. Compression, and consequent subduction, result in more effusive eruptions that put more ash and sulfate aerosols into the air, resulting in cooling, such as happened during the Oligocene. I’m left with the impression that the authors have more expertise in atmospheric physics and mammalian physiology than they are in petrology.
The authors state unequivocally, “At 280 ppm, most of the Tropics become uninhabitable.” Yet, during the Eocene, the CO2 was higher than that and it was a period of extreme tropical heat, rapid evolution of mammals, with diversity in size and form. The heat of the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum seems to have been good for mammals. Perhaps they should have included a paleontologist on their team.
“To prevent millennial-scale salinity drift during model spin-up, the total ocean volume integral is calculated and is re-adjusted to back to ice-free world global mean after each ocean time step.”
What sort of physical processes in the real world would allow this continuous adjustment to take place. If there are none, then I would suggest that there is a problem with the model lacking physical realism.
‘What If’ speculations can be a fun cocktail party game. However, when one is skating on thin evidence, it shouldn’t be taken too seriously.
Thanks for your observations. It does seem like they jumped to conclusions a bit.