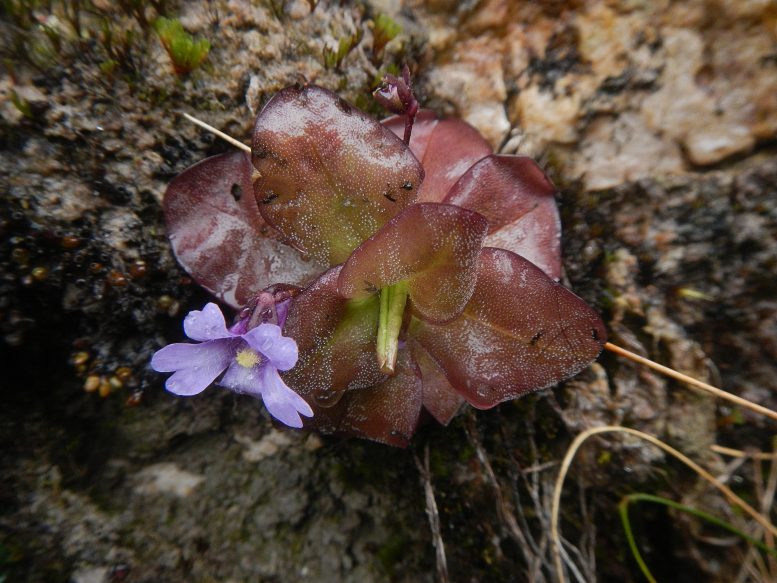

Photograph of Pinguicula ombrophila sp. nov. Credit: Álvaro J. Pérez
A group of botanists from Ecuador, Germany, and the United States have identified two new distinct species of carnivorous plants notable for their striking appearance. These species are a part of the butterworts family (known scientifically as the genus Pinguicula), a group of insectivorous flowering plants consisting of around 115 species. Their leaves have a sticky texture enabling them to capture and digest small insects. While the majority of butterworts are found in the northern hemisphere, these recently discovered species were located in the elevated regions of southern Ecuador, near the Peru border.
Carnivorous plants, often found in nutrient-poor soil, use animals (typically small insects) as supplementary nutrient sources. This unique adaptation gives them a competitive edge over other plants, facilitating their survival in difficult environments. The tropical high Andes host a range of such challenging environments, which include marshlands and rocky terrains constantly drenched in rainfall and shrouded in clouds.
The two new species described in the study, Pinguicula jimburensis and Pinguicula ombrophila, were found on the shore of a highland lagoon at 3400 m and on a nearly vertical rock face at 2900 m, respectively. Their small-scale habitats lie within the so-called Amotape-Huancabamba zone, which encompasses large portions of southern Ecuador and northern Peru. This area is characterized by exceptional biodiversity, due in part to the fact that the rugged terrain and varied climate of the Andes provide so many microhabitats.
“And as small and scattered as the species’ suitable habitats are, so is the species composition,” says senior author Tilo Henning of Leibniz Center for Agricultural Landscape Research (ZALF), who is a specialist in this plant family in this region. His colleague Álvaro Pérez of the Pontifica Universidad Catolica del Ecuador and his team were the first to discover the plants. They then got in touch with Henning.
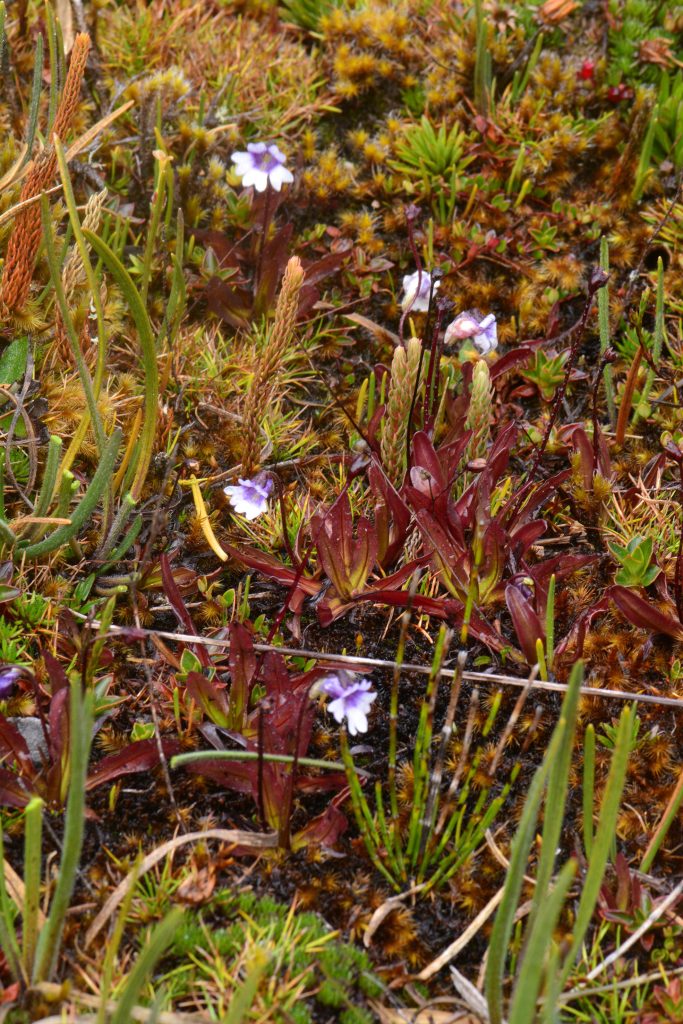

Photograph of Pinguicula jimburensis sp. nov. Credit: Kabir Montesinos
“Both of these new species are only known from a single location, where only a few dozens of plant individuals occur in each case.” For one of them, only one population with about 15 mature individuals was discovered, making it vulnerable even if it is hidden in an isolated, difficult-to-access area. This narrow endemism (limited distribution in a particular area) is typical of the Amotape-Huancabamba zone, and there are many more new plant and animal species awaiting discovery, Henning says.
With the description of these two new species, the number of Pinguicula species recorded in Ecuador has tripled, as previously only P. calyptrata was known, discovered by none other than Alexander von Humboldt. The authors are convinced that there are many more new species awaiting formal scientific recognition but admit that lately, it has been a race against time.
“The results presented in this study show that the assessment of the Neotropical biodiversity is far from complete. Even in well-known groups such as the carnivorous plants, new taxa are continuously discovered and described, in particular from remote areas that become accessible in the course of the unlimited urban sprawl,” Henning, Pérez, and their colleagues write in a scientific article dedicated to the new plants that was published in the peer-reviewed journal PhytoKeys. “This is both encouraging and worrying at the same time“.
“Relentless urban sprawl and the accompanying destruction of habitats pose a massive threat to biodiversity in general, and to the tightly-knit and specialized organisms that depend on their fragile microhabitats in particular,” Henning points out. Although the two new species are relatively safe from direct human interference – as they both occur within protected areas – human-induced climate change is increasingly affecting ecosystems regardless of location, especially those that rely on regular precipitation, such as mountain wetlands.
The dependence on a constant climate is even reflected in the name of one of the two new species: Pinguicula ombrophila means “rain-loving butterwort”, as the plant prefers very wet conditions, receiving moisture from the waterlogged paramo-soil and enjoying the frequent rain and fog typical for this area.
Reference: “Contributions to Ecuadorian butterworts (Lentibulariaceae, Pinguicula): two new species and a re-evaluation of Pinguicula calyptrata” by Álvaro J. Pérez, Francisco Tobar, Kevin S. Burgess and Tilo Henning, 24 March 2023, PhytoKeys.
DOI: 10.3897/phytokeys.222.98139
Funding: Secretaría de Educación Superior, Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación de la República del Ecuador (SENESCYT)), International Palm Society (IPS), H2020 European Research Council, Open Access Fund of the Leibniz Association.








This article, it uses the comma, in a way in which, if you are reading, and continue to read, you will find that, given that you are paying attention, and can read english, and are doing both, while reading it, ultimately you will notice, but not quickly, from here on, that the sentence, if considered as a whole, finally and as a consequence, actually