New research has uncovered the mechanism by which amino acids activate TORC1, a key protein in cell growth and autophagy. The research reveals that cysteine activates TORC1 via the Pib2 protein and highlights the varied influences of all 20 amino acids on TORC1 through two pathways. This discovery offers new insights into cellular processes and potential treatments for diseases linked to TORC1 malfunctions.
Researchers at Osaka University uncover the mechanism by which cysteine activates a crucial regulator of cell growth in yeast.
Amino acids serve as life’s fundamental components. They are sourced from our diet, and our bodies utilize them to create proteins. These proteins are crucial for growth, development, and various other processes. Yet, prior to utilizing these building blocks, the body must first detect their presence.
When amino acids are available, a master regulator protein called TORC1 is switched on, causing proteins to be manufactured and cells to grow. If no amino acids are available, TORC1 is switched off, and cells start to recycle themselves in a process known as autophagy. Until now, it was unclear exactly how amino acids triggered the TORC1 switch in yeast.
Discovery in Amino Acid Sensing
Now, in a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Osaka University have revealed how TORC1 is activated: detection of the amino acid cysteine.
“We investigated the relationships between amino acids and TORC1 activation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae,” says the study’s lead author Qingzhong Zeng. “We found that cysteine is sensed by a protein called Pib2 and that the two bind together and activates TORC1. This stimulates the synthesis of proteins and lipids, promoting cell proliferation.”
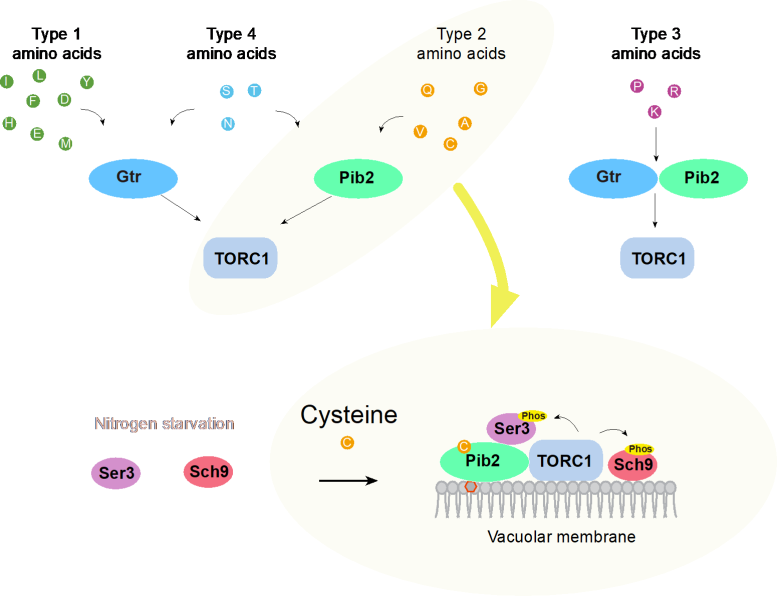
Pib2 senses Cysteine to activate TORC1. Credit: 2023 Noda et al., Pib2 is a cysteine sensor involved in TORC1 activation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell Reports
The Role of Amino Acids in TORC1 Activation
What’s more, cysteine is not the only amino acid that triggers TORC1. All 20 amino acids were found to differently affect TORC1 using two ‘pathways’: Pib2 and Gtr. A pathway can be thought of as a specific chain reaction that leads to certain outcomes in a cell. The team set out to elucidate how each amino acid uses these pathways to affect TORC1.
“Some amino acids primarily use the Pib2 pathway, while others primarily use Gtr,” explains senior author Takeshi Noda. “We also identified amino acids that can use either pathway and some that need both. This work excites us because it deepens our understanding of how amino acids control cell growth and autophagy, and how each amino acid is detected.”
In humans, faulty TORC1 function has been linked to diseases like cancer, diabetes, and dementia. A fuller understanding of how TORC1 is switched on and off, and how each amino acid is detected, could help researchers find new treatments for these diseases – an exciting prospect indeed.
Reference: “Pib2 is a cysteine sensor involved in TORC1 activation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae” by Qingzhong Zeng, Yasuhiro Araki and Takeshi Noda, 20 December 2023, Cell Reports.
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113599





Be the first to comment on "Scientists Elucidate Key Mechanism to Cell Growth"