
Research on marine snails has demonstrated that significant evolutionary innovations occur gradually through small steps, challenging the notion of dramatic ‘monster’ leaps. This discovery, by elucidating the genetic basis of the snails’ shift from egg-laying to live birth, offers a new perspective on how major evolutionary changes unfold and highlights the importance of incremental progress in the course of evolution.
Biologists have found that significant evolutionary transformations occur incrementally rather than through sudden, dramatic “monster” steps, addressing the longstanding debate on how major innovations such as flight, vision, and live birth evolved.
Evolution is usually a gradual process, taking place over small, incremental steps, but occasionally producing striking new functions, like feathers that eventually allowed birds to fly.
Until now, it has been difficult to understand how these significant evolutionary changes have happened, partly because many of them took place so long ago and partly because it is hard to imagine intermediate stages. Some have suggested that they occur in big steps, when large-effect mutations give rise to ‘hopeful monsters’; others have argued that innovations are built gradually, with natural selection favoring intermediate steps.

Live-bearing has allowed Littorina snails to occupy and adapt to a diverse range of habitats. This has led to the evolution many ‘ecotypes’ that vary in their size, shape and behavior. Credit: Fredrik Pleijel
New Insights from Marine Snails
By obtaining and studying whole-genome sequences from a group of marine snails, which have made a recent shift from egg-laying to live-birth, scientists at the University of Sheffield and their collaborators at the University of Gothenburg and Institute of Science and Technology Austria, are now able to settle the debate for at least one example.
The study used new methodology to discover whether this new shift in birthing style happened rapidly or gradually, findings which could then be applied to help explain other dramatic shifts in evolution.

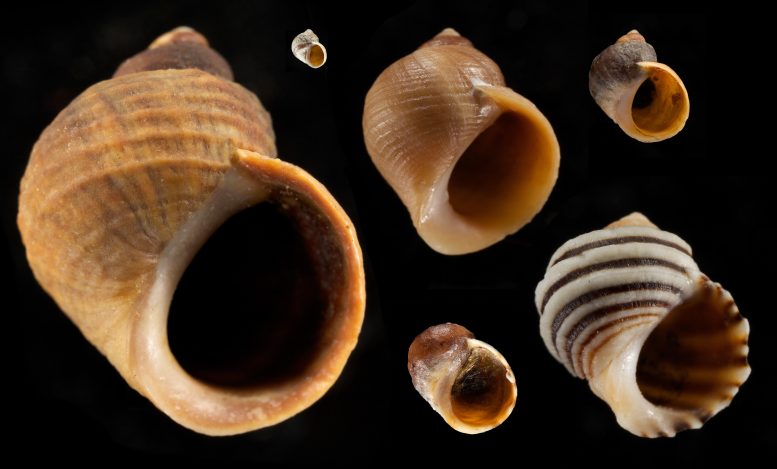
Adult snails adapted to different habitats. The larger snail is adapted for defense against crab attacks, while the small snail is adapted to live in areas with strong wave exposure. Credit: Sophie Webster
Scientists were able to identify 50 genes that are perfectly associated with reproductive mode, as well as estimate the time of their origin. The results showed they accumulated gradually, spreading at different times in the past. This demonstrates that innovation can evolve progressively, rather than in a single evolutionary step.
Implications for Understanding Evolutionary Processes
Professor Roger Butlin, from the University of Sheffield’s School of Biosciences, said: “The evolutionary origin of key innovations is important to understand because they can dramatically change the course of evolution, like when live-bearing led to the diversification of mammals or feathers helped birds to evolve flight. Until now, however, there have been few opportunities to study these, mainly because most evolutionary changes happened so long ago.
“By discovering and studying the recent evolutionary shift in the way marine snails give birth, we’re now able to understand these major changes and apply our methods to many other evolutionary shifts.”

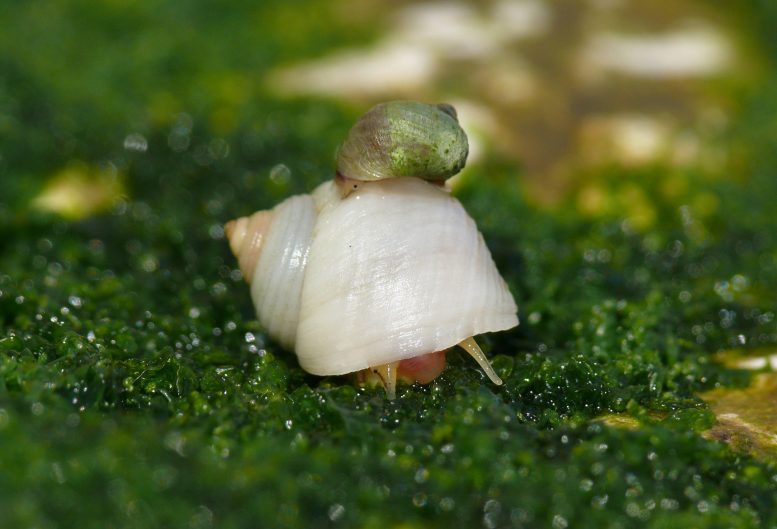
Littorina snails are common on the rocky shores of Europe, the UK, and the East Coast of the USA. Credit: Daria Shipilina
He added: “Our results will change the way biologists view major evolutionary transitions, shifting the focus away from big leaps in evolution towards understanding the progressive benefits of small evolutionary steps. They will also help others dissect the genetic and historical basis of other adaptive traits, which is important when many organisms are being forced to adapt rapidly to a changing world.”
The team now plans to study the functions of the genes they have identified, in order to understand the series of evolutionary steps that led to live birth. They also hope that their methods will be applied to other types of adaptation, including things like thermal tolerance, which must evolve if some species are to survive climate change.
Reference: “The genetic basis of a recent transition to live-bearing in marine snails” by Sean Stankowski, Zuzanna B. Zagrodzka, Martin D. Garlovsky, Arka Pal, Daria Shipilina, Diego Garcia Castillo, Hila Lifchitz, Alan Le Moan, Erica Leder, James Reeve, Kerstin Johannesson, Anja M. Westram and Roger K. Butlin, 4 January 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adi2982







And all the fauna on this planet uninanimously agreed seaslug being good representative of their kind? In genetic algorithms re-forming the initial vector or increased randomness will accelerate evolution. One can interprete it as major change of the habitat, for eaxmple when the best population member is lost due to accidents, predator etc