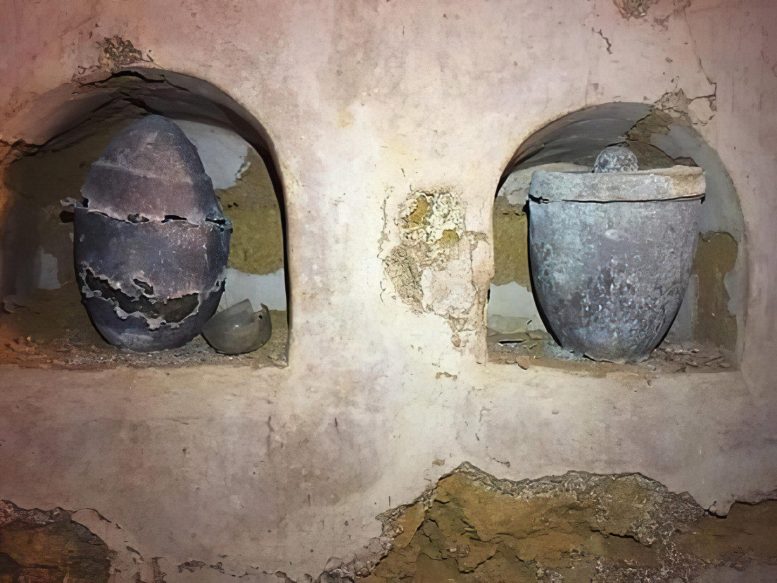

Researchers from the University of Cordoba have, for the first time, identified the components of a 2,000-year-old Roman perfume discovered in a sealed vessel in Carmona, Spain. Chemical analysis revealed that the perfume, found in an affluent family’s mausoleum, was based on olive oil and contained patchouli, an Indian-origin scent previously unknown in Roman times. Credit: University of Córdoba
A small vessel of ointment discovered in a funerary urn from the ancient Roman city of Carmo, present-day Carmona in Seville province, has allowed a research team from the University of Cordoba to chemically unravel the composition of a perfume that dates back to the first century AD.
This ground-breaking research, undertaken by the FQM346 team led by Professor of Organic Chemistry José Rafael Ruiz Arrebola in collaboration with the City of Carmona, marks the first time the composition of a Roman perfume over 2,000 years old has been identified.
The results were published in the Swiss scientific journal Heritage in an article in which Ruiz Arrebola, the municipal archaeologist of Carmona, Juan Manuel Román; and UCO researchers Daniel Cosano and Fernando Lafontshare the whole technical and scientific process enabling the world to”smell” the bygone Roman Empire.
The residue of the perfume, discovered in 2019 during an archaeological intervention in a mausoleum found during the construction of a house on the Calle Sevillat, had been preserved, solidified, inside a vessel carved in quartz, which was still perfectly sealed. As Román explains, it was a collective tomb, possibly belonging to an affluent family, and in which, in addition to numerous objects related to funeral rituals (offerings and trousseaus), the cinerary urns of six adult individuals – three women and three men – were found.
In one of the urns, made of glass, over the cremated skeletal remains of the deceased (in this case a woman between 30 and 40 years old)a cloth bag had been placed (remains of it having been preserved) containing three amber beads and a small rock crystal (hyaline quartz) flask, carved in the shape of an amphora, containing ointment.
Perfume containers used to be made of blown glass and, on very rare occasions, examples have been found made of this material which, owing to its characteristics and difficult carving, due to its hardness, made them very valuable and extremely expensive. In addition to the uniqueness of the receptacle, the truly extraordinary aspect of the find was that it was perfectly sealed and that the solid residues of the perfume had been preserved inside, which made it possible to carry out this study.
Ruiz Arrebola stresses that the use of dolomite, a type of carbon, as a stopper, and the bitumen used to seal it, were the key to the magnificent state of preservation of the piece and its contents.
To ascertain what the perfume was made of, different instrumental techniques were used, such as X-ray diffraction and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry, among others. According to Ruiz, from the analyses it has been possible to determine that the small cylindrical stopper was made of dolomite (limestone), and that bitumen was used for its perfect fit and airtight seal.
With respect to the perfume, two components have been identified: a base or binder, which allowed for the preservation of the aromas, and the essence itself, these findings according with descriptions by none other than Pliny the Elder. In this case, the base was a vegetable oil; possibly, according to some indications reflected in the analysis, olive oil, although this point could not be confirmed with certainty.
And the essence?
According to the results of chemical analyses carried out by the University of Cordoba, Rome smelled of patchouli, an essential oilobtained from a plant of Indian origin, Pogostemon cablin, widely used in modern perfumery, and whose usein Roman times was not known. The monumental characteristics of the tomb where it was found and, above all, the material of which the vessel containing it was made, suggest that it was a highly valuable product.
This study constitutesa breakthrough in the field of Roman perfumery and as regards the use of patchouli as an essential oil. Further studies are currently being carried out on other unique materials (such as amber, fabrics, and pigments used in the wall paintings) preserved in the Carmona mausoleum.
Reference: “Archaeometric Identification of a Perfume from Roman Times” by Daniel Cosano, Juan Manuel Román, Fernando Lafont and José Rafael Ruiz Arrebola, 23 May 2023, Heritage.
DOI: 10.3390/heritage6060236






Be the first to comment on "Unmasking Ancient Aromas: Scientists Identify Composition of 2000-Year-Old Roman Perfume"