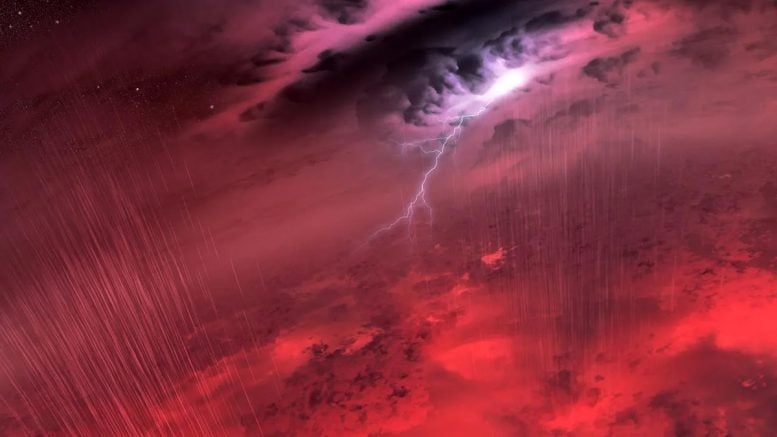

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have conducted detailed atmospheric studies on two brown dwarfs, uncovering the dynamics of gases such as water and methane. This study enhances our understanding of such celestial bodies, potentially linking the characteristics of stars to planets. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Western Ontario/Stony Brook University
Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to create a comprehensive weather report for two brown dwarfs located about six light years from Earth.
Researchers have created the most detailed weather report ever for two distant worlds beyond our own solar system.
The international study – the first of its kind – reveals the extreme atmospheric conditions on the celestial objects, which are swathed in swirling clouds of hot sand amid temperatures of 950°C (1750°F).
Using NASA’s powerful James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), researchers set out to capture the weather on a pair of brown dwarfs – cosmic bodies that are bigger than planets but smaller than stars.
These brown dwarfs, named collectively as WISE 1049AB, are the brightest and closest objects of their type to Earth, around six light years away.
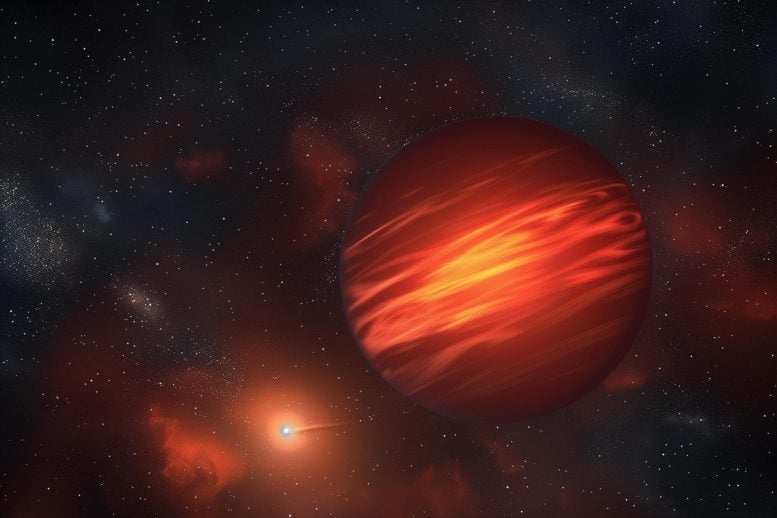

Brown dwarfs, often referred to as failed stars, occupy an interesting middle ground in the cosmos. These objects are larger than the biggest planets but do not have enough mass to trigger the hydrogen fusion that powers true stars. This results in a fascinating, dimly lit state where they emit mostly infrared light. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Advanced Techniques in Weather Mapping
The team tracked each brown dwarf’s atmosphere by measuring the light waves emitted from their surfaces, which change as more or less cloudy regions revolve in and out of view.
By visualizing this data through light curves – a plot of how the brightness of light from each object changes over time – the team was able to build up a detailed 3D picture of how the brown dwarfs’ weather changed over the course of a full rotation or day, between five and seven hours.
The team was also able to plot how the light from each object varied by wavelength, to demonstrate the presence and complex interplay of gases such as water, methane, and carbon monoxide in their atmospheres.

As the most powerful space telescope ever built, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is NASA’s flagship mission for exploring the deeper universe. Operating in the infrared, JWST explores phenomena from the earliest galaxies to the detailed atmospheres of nearby exoplanets. Credit: Northrup Grumman
Implications for Astronomy and Exoplanet Research
The insights may help astronomers develop the understanding of brown dwarfs as a potential missing link between stars and planets – promising new insights into both.
By observing the infrared part of the light spectrum, the JWST is able to observe wavelengths of light that are blocked by our own atmosphere.
This capability opens frontiers in the study of the early universe, star formation, and so-called exoplanets such as brown dwarfs which lie beyond our solar system.
Challenges and Progress in Brown Dwarf Studies
The latest study builds on previous studies of brown dwarfs, which have mainly been confined to capturing static snapshots of their atmosphere on only one side. This approach is limited, as brown dwarfs are known to rotate relatively quickly and their weather can vary greatly over time, researchers say.
Their findings will pave the way for more detailed studies into brown dwarfs and other distant celestial objects.
The study, published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, was led by the University of Edinburgh in collaboration with researchers from Trinity College Dublin, the University of Virginia, and other institutes from around the world.
Professor Beth Biller, Personal Chair of Exoplanet Characterisation, Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, said: “Our findings show that we are on the cusp of transforming our understanding of worlds far beyond our own. Insights such as these can help us understand the conditions not just on celestial objects like brown dwarfs, but also on giant exoplanets beyond our solar system. Eventually, the techniques we are refining here may enable the first detections of weather on habitable planets like our own, which orbit other stars.”
Reference: “The JWST weather report from the nearest brown dwarfs I: multiperiod JWST NIRSpec + MIRI monitoring of the benchmark binary brown dwarf WISE 1049AB” by Beth A Biller, Johanna M Vos, Yifan Zhou, Allison M McCarthy, Xianyu Tan, Ian J M Crossfield, Niall Whiteford, Genaro Suarez, Jacqueline Faherty, Elena Manjavacas, Xueqing Chen, Pengyu Liu, Ben J Sutlieff, Mary Anne Limbach, Paul Molliere, Trent J Dupuy, Natalia Oliveros-Gomez, Philip S Muirhead, Thomas Henning, Gregory Mace, Nicolas Crouzet, Theodora Karalidi, Caroline V Morley, Pascal Tremblin and Tiffany Kataria, 15 July 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stae1602








Be the first to comment on "Webb Unveils Scorching Storms on Distant Worlds in Unprecedented Detail"