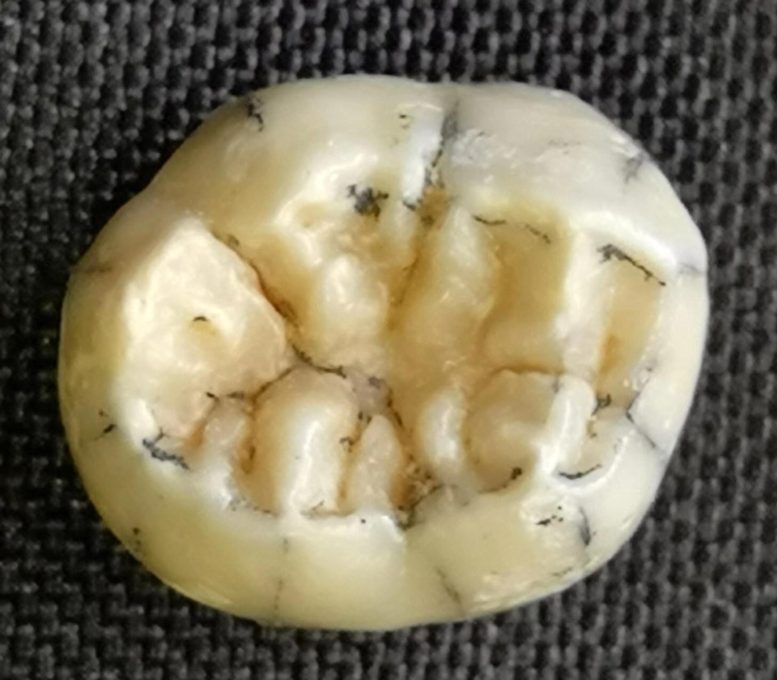
A close-up of the tooth from a ‘birds-eye’ viewpoint. Credit: Fabrice Demeter (University of Copenhagen/CNRS Paris)
Denisovans, a sister species of modern humans, inhabited Laos from 164,000 to 131,000 years ago with important implications for populations out of Africa and Australia.
What connects a finger bone and some fossil teeth discovered in a cave in the remote Altai Mountains of Siberia to a single tooth found in a cave in the limestone landscapes of tropical Laos?
The answer to this question has been established by an international team of researchers from Laos, Europe, the United States, and Australia.
The human tooth was chanced upon during an archaeological survey in a remote area of Laos. Scientists have shown it originated from the same ancient human population first recognized in Denisova Cave (dubbed the Denisovans), in the Altai Mountains of Siberia (Russia).
The team of researchers made the major discovery during their 2018 excavation campaign in northern Laos. The new cave Tam Ngu Hao 2, also known as Cobra Cave, is located near the famous Tam Pà Ling Cave, where another important 70,000-year-old human (Homo sapiens) fossils had been previously found.
The international team of scientists are confident the two ancient sites are linked to Denisovans’ occupations despite being thousands of miles apart.
Their findings have been published in Nature Communications, led by The University of Copenhagen (Denmark), the CNRS (France), University of Illinois Urbanna-Champaign (USA), the Ministry of Information Culture and Tourism, Laos and supported by microarchaeological work undertaken at Flinders University (Australia), and geochronological analyses at Macquarie University and Southern Cross University in Australia.
What links a finger bone and some fossil teeth found in a cave in the remote Altai Mountains of Siberia to a single tooth found in a cave in the limestone landscapes of tropical Laos? The answer to this question has been established by an international team of researchers from Laos, Europe, the US, and Australia. Credit: Flinders University
Lead Author and Assistant Professor of Palaeoanthropology at the University of Copenhagen, Fabrice Demeter, says the cave sediments contained teeth of giant herbivores, ancient elephants, and rhinos that were known to live in woodland environments.
“After all this work following the many clues written on fossils from very different geographic areas our findings are significant,” Professor Demeter says.
“This fossil represents the first discovery of Denisovans in Southeast Asia and shows that Denisovans were in the south at least as far as Laos. This is in agreement with the genetic evidence found in modern-day Southeast Asian populations.”
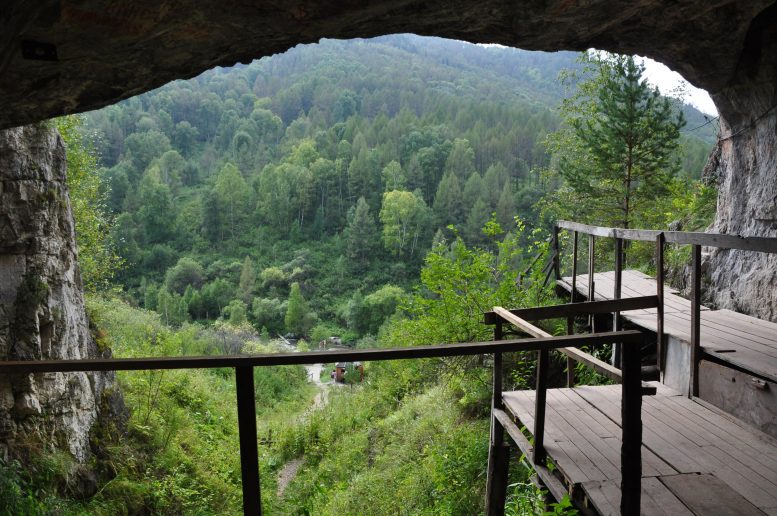

A view from inside Denisova cave in the Altai Mountains of Russia. Note the very different vegetation and climate compared to Laos. Credit: Mike Morley, Flinders University
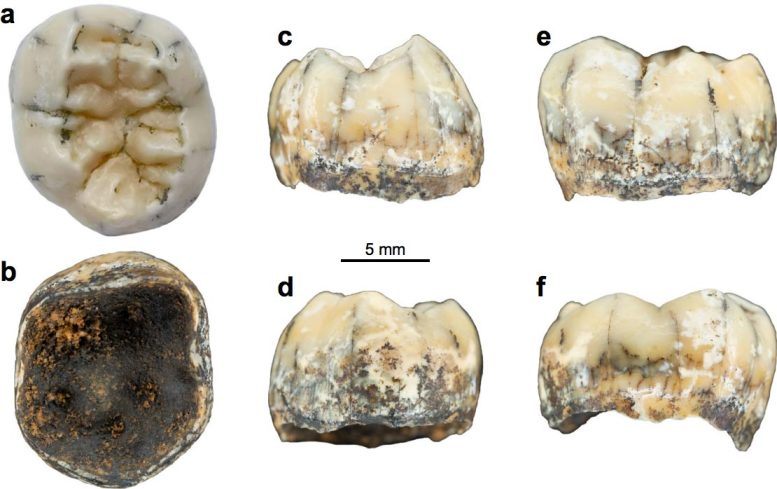
Following a very detailed analysis of the shape of this tooth, the research team identified many similarities to Denisovan teeth found on the Tibetan Plateau – the only other location that Denisovan fossils have ever been found.
This suggested it was most likely a Denisovan who lived between 164,000 and 131,000 years ago in the warm tropics of northern Laos.
Associate Professor Mike Morley from the Microarchaeology Laboratory at Flinders University says the cave site named Tam Ngu Hao 2 (Cobra cave), was found high up in the limestone mountains containing remnants of an old cemented cave sediment packed with fossils.
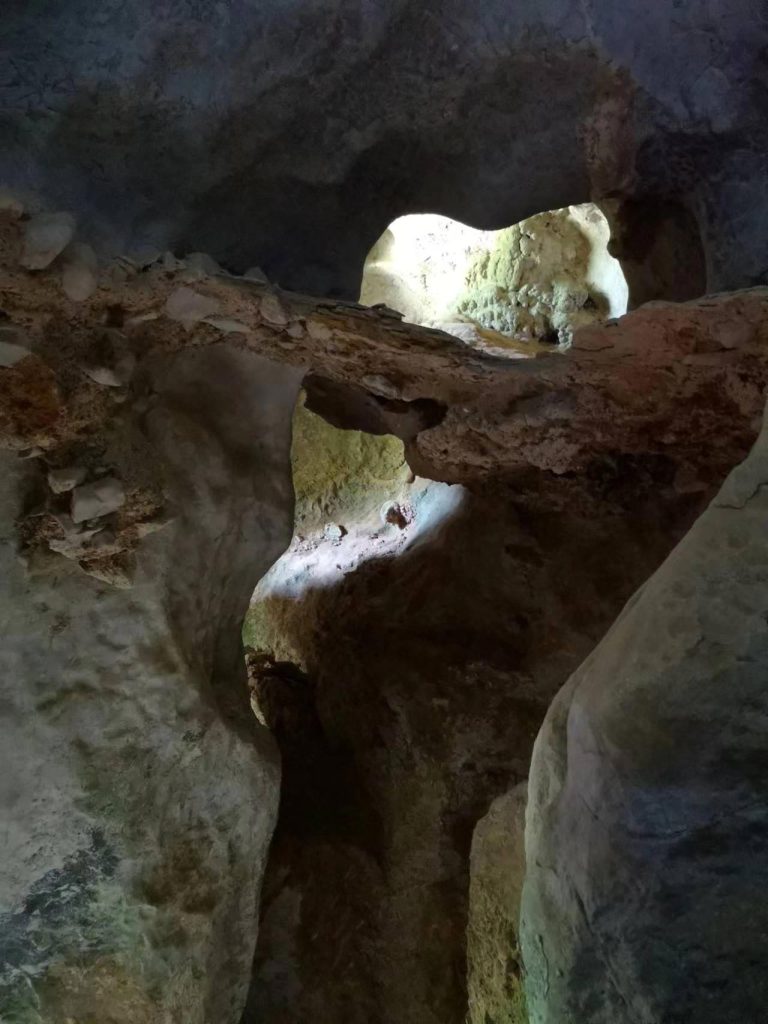

Inside Ngu Hao 2 cave showing the concreted remnant cave sediments adhering to the cave wall. The overlying whitish rock is a flowstone that caps the entire deposit. Credit: Fabrice Demeter (University of Copenhagen/CNRS Paris)
“We have essentially found the ’smoking gun’ – this Denisovan tooth shows they were once present this far south in the karst landscapes of Laos,” says Associate Professor Morley.
The complexity of the site created a challenge for dating and required two Australian teams.
The team from Macquarie University, led by Associate Professor Kira Westaway, provided dating of the cave sediments surrounding the fossils; and the team from Southern Cross University led by Associate Professor Renaud Joannes-Boyau conducted the direct dating of unearthed fossil remains.
“Establishing a sedimentary context for the fossils’ final resting place provides an internal check on the integrity of the find– if the sediments and fossils return a similar age, as seen in Tam Ngu Hao 2, then we know that the fossils were buried not long after the organism died,” says Associate Professor Kira Westaway.
A short video clip of Ngu Hao 2 (Cobra Cave) in northern Laos. The cave entrance is on the left. Credit: Fabrice Demeter (University of Copenhagen/CNRS Paris)
Dating directly the fossil remains is crucial if we want to understand the succession of events and species in the landscape.
“The good agreement of the different dating techniques, on both the sediment and fossils, attest to the quality of the chronology for the species in the region. And this has a lot of implications for population mobility in the landscape,” says A. Prof Renaud Joannes-Boyau from Southern Cross University
The fossils were likely scattered on the landscape when they were washed into the cave during a flooding event that deposited the sediments and fossils.
Unfortunately, unlike Denisova Cave, the humid conditions in Laos meant the ancient DNA was not preserved. However, the archaeological scientists did find ancient proteins suggesting the fossil was a young, likely female, human likely aged between 3.5 – 8.5 years old.
The finding suggests Southeast Asia was a hotspot of diversity for humans with at least five different species setting up camp at different times; H. erectus, the Denisovans/Neanderthals, H. floresiensis, H. luzonensis, and H. sapiens.
Southeast Asian caves could provide the next clue and further hard evidence to understand these complex demographic relationships.
Reference: “A Middle Pleistocene Denisovan molar from the Annamite Chain of northern Laos” by Fabrice Demeter, Clément Zanolli, Kira E. Westaway, Renaud Joannes-Boyau, Philippe Duringer, Mike W. Morley, Frido Welker, Patrick L. Rüther, Matthew M. Skinner, Hugh McColl, Charleen Gaunitz, Lasse Vinner, Tyler E. Dunn, Jesper V. Olsen, Martin Sikora, Jean-Luc Ponche, Eric Suzzoni, Sébastien Frangeul, Quentin Boesch, Pierre-Olivier Antoine, Lei Pan, Song Xing, Jian-Xin Zhao, Richard M. Bailey, Souliphane Boualaphane, Phonephanh Sichanthongtip, Daovee Sihanam, Elise Patole-Edoumba, Françoise Aubaile, Françoise Crozier, Nicolas Bourgon, Alexandra Zachwieja, Thonglith Luangkhoth, Viengkeo Souksavatdy, Thongsa Sayavongkhamdy, Enrico Cappellini, Anne-Marie Bacon, Jean-Jacques Hublin, Eske Willerslev and Laura Shackelford, 17 May 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29923-z





If the DNA did not survive, what proteins did on a single tooth to identify the gender of the tooth? Or is this assumptions?