
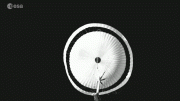
Image of an ice-rich impact crater on Mars, captured by the CaSSIS camera onboard the ESA/Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) on June 13, 2021. Credit: ESA/Roscosmos/CaSSIS, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
This feature could easily be mistaken for a tree stump with characteristic concentric rings. It’s actually an impressive bird’s-eye view into an ice-rich impact crater on Mars. Tree rings provide snapshots of Earth’s past climate and, although formed in a very different way, the patterns inside this crater reveal details of the Red Planet’s history, too.
The image was taken by the CaSSIS camera onboard the ESA/Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) on June 13, 2021, in the vast northern plains of Acidalia Planitia, centered at 51.9°N/326.7°E.
The interior of the crater is filled with deposits that are probably water-ice rich. It is thought that these deposits were laid down during an earlier time in Mars’ history when the inclination of the planet’s spin axis allowed water-ice deposits to form at lower latitudes than it does today. Just like on Earth, Mars’ tilt gives rise to seasons, but unlike Earth, its tilt has changed dramatically over long periods of time.
One of the notable features in the crater deposits is the presence of quasi-circular and polygonal patterns of fractures. These features are likely a result of seasonal changes in temperature that cause cycles of expansion and contraction of the ice-rich material, eventually leading to the development of fractures.
Understanding the history of water on Mars and if this once allowed life to flourish is at the heart of ESA’s ExoMars missions. TGO arrived at Mars in 2016 and began its full science mission in 2018. The spacecraft is not only returning spectacular images, but also providing the best-ever inventory of the planet’s atmospheric gases with a particular emphasis on geologically and biologically important gases, and mapping the planet’s surface for water-rich locations. It will also provide data relay services for the second ExoMars mission comprising the Rosalind Franklin rover and Kazachok platform, when it arrives on Mars in 2023. The rover will explore a region of Mars thought once to have hosted an ancient ocean and will search underground for signs of life.






Be the first to comment on "Crater Tree Rings: Incredible Birds-Eye View Into an Ice-Rich Impact Crater on Mars"