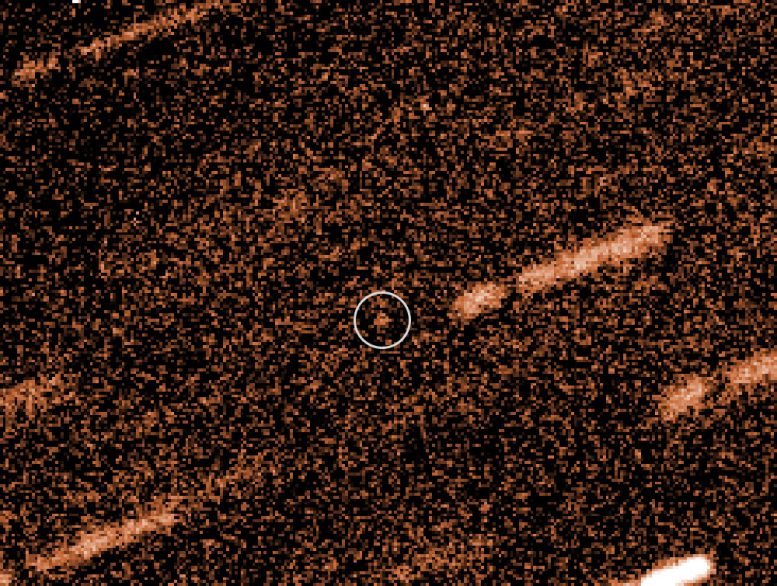
The faint spot at the center of this picture from ESO’s Very Large Telescope is the Near-Earth Object 2009 FD. It may look insignificant, but there was a possibility that this asteroid would collide with the Earth in the future and cause devastation. Fortunately, the latest VLT observations, part of a collaboration with the European Space Agency, have shown that this is much less likely than initially feared. The stars in this picture appear trailed as the telescope was tracking the motion of the asteroid during the exposures. Credit: ESO
The new collaboration between ESA and ESO has successfully tracked its first potentially threatening Near-Earth Object.
The first Near-Earth Object (NEO) recovery campaign has been successfully carried out by a new collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and ESO. Up to now the asteroid 2009 FD had been ranked among the top five objects in a list of the most dangerous objects, but new observations with ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have now shown that it is far less likely to hit the Earth than had been feared.[1]
NEOs are asteroids or comets with orbits around the Sun that come very close to the Earth’s orbit. More than 600,000 asteroids are known in the Solar System, and more than 10,000 of them are NEOs. Their sizes range from meters to tens of kilometers. Some NEOs could hit our planet and, depending on their size, produce considerable damage. While the chance of a large object hitting the Earth is very small, it could produce a great deal of destruction and loss of life.
A new collaboration between ESA and ESO takes place within a global effort by the United Nations and its Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS). In the wake of the Chelyabinsk event over Russia last February, there is renewed interest in global action on the NEO threat. The UNCOPUOS Action Team, including ESO, put forward recommendations for an international response to the NEO impact threat to form an International Asteroid Warning Network, which the UN General Assembly approved in October 2013.
ESO’s unique capabilities to observe very faint (but still threatening) NEOs complement ESA’s efforts to discover and track these objects. New observations of asteroid 2009 FD performed with ESO’s 8.2-meter (27-foot) Very Large Telescope on Cerro Paranal in Chile resulted in good-quality position measurements. These data have now been accepted by the IAU Minor Planet Center, the official organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets. Both the European NEODyS system and the JPL-based Sentry system performed orbit determination and impact monitoring using these new VLT observations.
The NEO Segment of ESA’s Space Situational Awareness (SSA) aims to coordinate and combine information from different sources, and analyze them to predict possible impact with the Earth, assess danger, and analyze possible mitigations, including the deflection of a menacing asteroid.
The successful observations of 2009 FD show that having access to a large telescope such as the VLT is a great opportunity for the NEO Coordination Center, since it gives a chance to obtain accurate positional observations of very faint objects,[2] which is only possible using the largest telescopes.
The observations were performed by the Paranal staff on behalf of the team, which includes Olivier Hainaut (ESO), Detlef Koschny (ESA), and Marco Micheli (NEOCC team, ESA/Serco).
Notes
- The associated value on the Palermo scale has dropped by almost a factor of ten to a value of -2.6 (from -1.8 on the logarithmic scale). The computations indicate that there is still a small chance of an impact between the years 2185 and 2198.
- Down to visual magnitude 26.5.







Be the first to comment on "ESA/ESO Collaboration Successfully Tracks Its First Near-Earth Object"