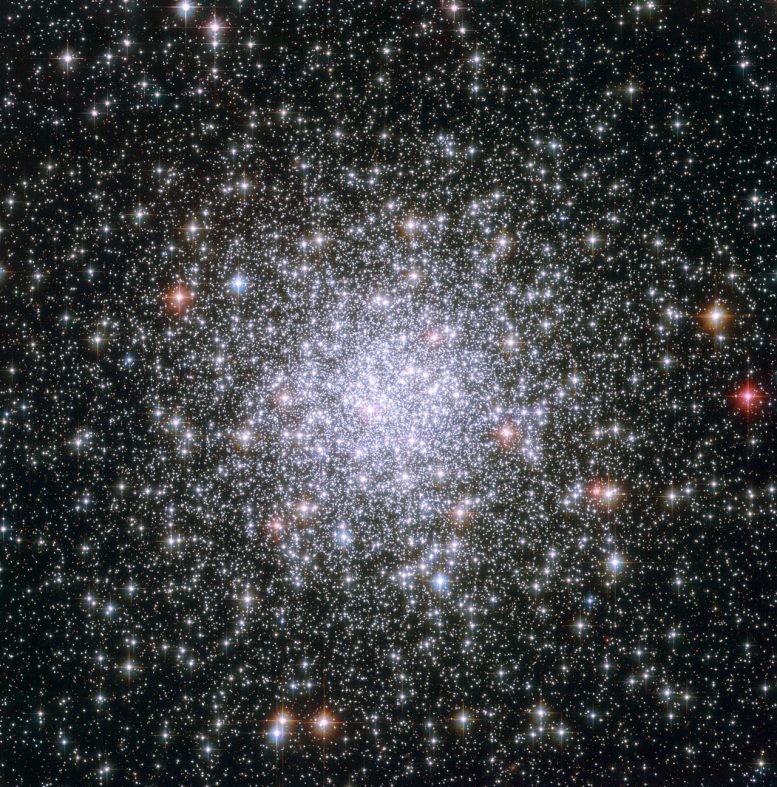

Hubble Space Telescope image of the globular cluster Messier 69, also known as NGC 6637. Credit: ESA/NASA
This Hubble image shows the globular cluster Messier 69, also known as NGC 6637, which is located 29,700 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
This dazzling image shows the globular cluster Messier 69, or M69 for short, as viewed through the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Globular clusters are dense collections of old stars. In this picture, foreground stars look big and golden when set against the backdrop of the thousands of white, silvery stars that make up M69.
Another aspect of M69 lends itself to the bejeweled metaphor: As globular clusters go, M69 is one of the most metal-rich on record. In astronomy, the term “metal” has a specialized meaning: it refers to any element heavier than the two most common elements in our Universe, hydrogen and helium. The nuclear fusion that powers stars created all of the metallic elements in nature, from the calcium in our bones to the carbon in diamonds. Successive generations of stars have built up the metallic abundances we see today.
Because the stars in globular clusters are ancient, their metallic abundances are much lower than more recently formed stars, such as the Sun. Studying the makeup of stars in globular clusters like M69 has helped astronomers trace back the evolution of the cosmos.
M69 is located 29,700 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius (the Archer). The famed French comet hunter Charles Messier added M69 to his catalog in 1780. It is also known as NGC 6637.
The image is a combination of exposures taken in visible and near-infrared light by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys, and covers a field of view of approximately 3.4 by 3.4 arcminutes.








Be the first to comment on "Hubble Views the Cosmic Riches of Messier 69"