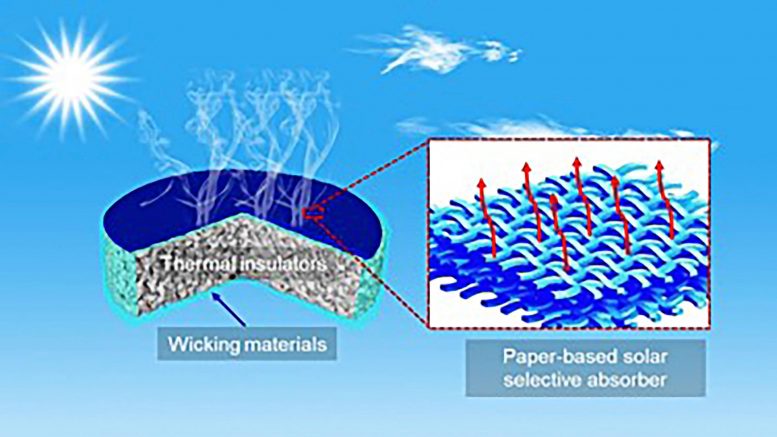
Solar-powered desalination unit consists of three layers: a wicking material, a thermal insulator, and a paper-based solar light absorber containing titanium. Credit: Chao Chang
Scientists develop a low-cost, highly efficient technique that uses solar energy to remove salt from seawater, producing safe drinking water.
Despite the vast amount of water on Earth, most of it is nonpotable seawater. Freshwater accounts for only about 2.5% of the total, so much of the world experiences serious water shortages.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, scientists in China report the development of a highly efficient desalination device powered by solar energy. The device consists of a titanium-containing layer, TiNO, or titanium nitride oxide, capable of absorbing solar energy. The TiNO is deposited on a special type of paper and foam that allows the solar absorber to float on seawater.
When sunlight strikes the titanium layer, it heats rapidly and vaporizes the water. By placing the unit in a transparent container with a sloped quartz roof, the water vapor can be condensed and collected, producing a copious amount of freshwater.
“In the solar energy field, TiNO is a common commercial solar absorbing coating, widely used in solar hot water systems and in photovoltaic units,” author Chao Chang said. “It has a high solar absorption rate and a low thermal emittance and can effectively convert solar energy into thermal energy.”
The investigators developed a method for depositing a layer of TiNO using a technique known as magnetron sputtering. They used a special type of highly porous paper known as airlaid paper that acts as a wicking material to supply water from the seawater reservoir. Airlaid paper is made from wood fibers and is commonly used in disposable diapers.
The evaporation unit included three parts: the TiNO layer on top, a thermal insulator, and the airlaid paper on the bottom. The insulation layer is polyethylene foam, which has many air-filled pores that trap heat and allow the multi-layer unit to float on top of a reservoir of seawater, minimizing heat loss to the surroundings.
“The porous airlaid paper used as the substrate for the TiNO solar absorber can be reused and recycled more than 30 times,” said Chang.
Salt precipitation on the TiNO surface could interfere with efficiency, but the investigators found even after a long time, no salt layer formed on the surface. They suggest the porous nature of the paper wicks away any salt that might form on the surface, returning it to the seawater reservoir.
The salinity of ordinary seawater is over 75,000 milligrams of salt per liter. Ordinary drinking water has a salinity of about 200 milligrams per liter. The desalination unit was able to decrease the seawater salinity to less than 2 milligrams per liter.
The combination of low cost, high efficiency, and lack of fouling for this desalination technology shows it has the potential to help solve the world’s freshwater shortage.
Reference: “Porous TiNO solar-driven interfacial evaporator for high-efficiency seawater desalination” by Chao Chang, Min Liu, Lilin Pei, Guowei Chen, Zongyu Wang and Yulong Ji, 27 April 2021, AIP Advances.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0047390







The larger problem now since desalination has been widely implemented and established is the slow but steady increase in our ocean salinity created from the process. Locations such as Red Sea and Persian Gulf are rapidly increasing their salinity due to limited dispersion of the desalination byproducts. A solution is badly needed. We now have a means to partially deflect that problem but much more work is needed in that sensitive discussion.
Lol comment above
I’m sure the meltwater from Greenland more than makes up for it