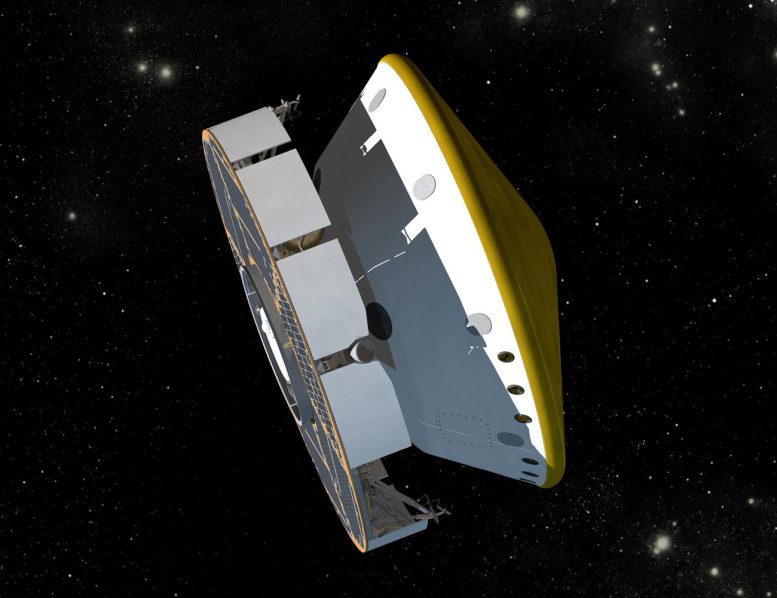

This is an artist’s concept of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft during its cruise phase between launch and final approach to Mars. The spacecraft includes a disc-shaped cruise stage (on the left) attached to the aeroshell. The spacecraft’s rover (Curiosity) and descent stage are tucked inside the aeroshell. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
On January 11, 2012, NASA is planning to conduct the biggest trajectory maneuver for the Science Laboratory Spacecraft on its mission to Mars. By precisely firing the spacecraft’s 8 thrusters in a carefully designed sequence that lasts for almost 3 hours, it will more accurately aim for its target, the Gale Crater on Mars.
An engine firing on January 11, 2012 will be the biggest maneuver that NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft will perform on its flight between Earth and Mars.
The action will use a choreographed sequence of firings of eight thruster engines during a period of about 175 minutes beginning at 3 p.m. PST (6 p.m. EST or 2300 Universal Time). It will redirect the spacecraft more precisely toward Mars to land at Gale Crater. The trajectory resulting from the mission’s November 26, 2011, launch intentionally missed Mars to prevent the upper stage of the launch vehicle from hitting the planet. That upper stage was not cleaned the way the spacecraft itself was to protect Mars from Earth’s microbes.
The maneuver is designed to impart a velocity change of about 12.3 miles per hour (5.5 meters per second).
“We are well into cruise operations, with a well-behaved spacecraft safely on its way to Mars,” said Mars Science Laboratory Cruise Mission Manager Arthur Amador, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. “After this trajectory correction maneuver, we expect to be very close to where we ultimately need to be for our entry point at the top of the Martian atmosphere.”
The mission’s schedule before arrival at Mars on August 5 PDT (August 6 in Universal Time and EDT) includes opportunities for five more flight path correction maneuvers, as needed, for fine-tuning.
The Jan. 11 maneuver has been planned to use the spacecraft’s inertial measurement unit to measure the spacecraft’s orientation and acceleration during the maneuver. A calibration maneuver using the gyroscope-containing inertial measurement unit was completed successfully on December 21. The inertial measurement unit is used as an alternative to the spacecraft’s onboard celestial navigation system due to an earlier computer reset.
Diagnostic work continues in response to the reset triggered by the use of star-identifying software on the spacecraft on November 29. In tests at JPL, that behavior has been reproduced a few times out of thousands of test runs on a duplicate of the spacecraft’s computer, but no resets were triggered during similar testing on another duplicate. The spacecraft itself has redundant main computers. While the spacecraft is operating on the “A side” computer, engineers are beginning test runs of the star-identifying software on the redundant “B side” computer to check whether it is susceptible to the same reset behavior.
The Mars Science Laboratory mission will use its car-size rover, Curiosity, to investigate whether the selected region on Mars inside Gale Crater has offered environmental conditions favorable for supporting microbial life and favorable for preserving clues about whether life existed.
On Jan. 15, the spacecraft operations team will begin a set of engineering checkouts. The testing will last about a week and include tests of several components of the system for landing the rover on Mars and for the rover’s communication with Mars orbiters.
The spacecraft’s cruise-stage solar array is producing 780 watts. The telecommunications rate is 2 kilobits per second for uplink and downlink. The spacecraft is spinning at 2.04 rotations per minute. The Radiation Assessment Detector, one of 10 science instruments on the rover, is collecting science data about the interplanetary radiation environment.
As of 9 a.m. PST (noon EST, or 1700 Universal Time) on Saturday, January 7, 2012, the spacecraft will have traveled 72.9 million miles (117.3 million kilometers) of its 352-million-mile (567-million-kilometer) flight to Mars. It will be moving at about 9,500 mph (15,200 kilometers per hour) relative to Earth and at about 69,500 mph (111,800 kilometers per hour) relative to the sun.








Be the first to comment on "NASA Plans Trajectory Maneuver for Mars Science Laboratory Spacecraft"