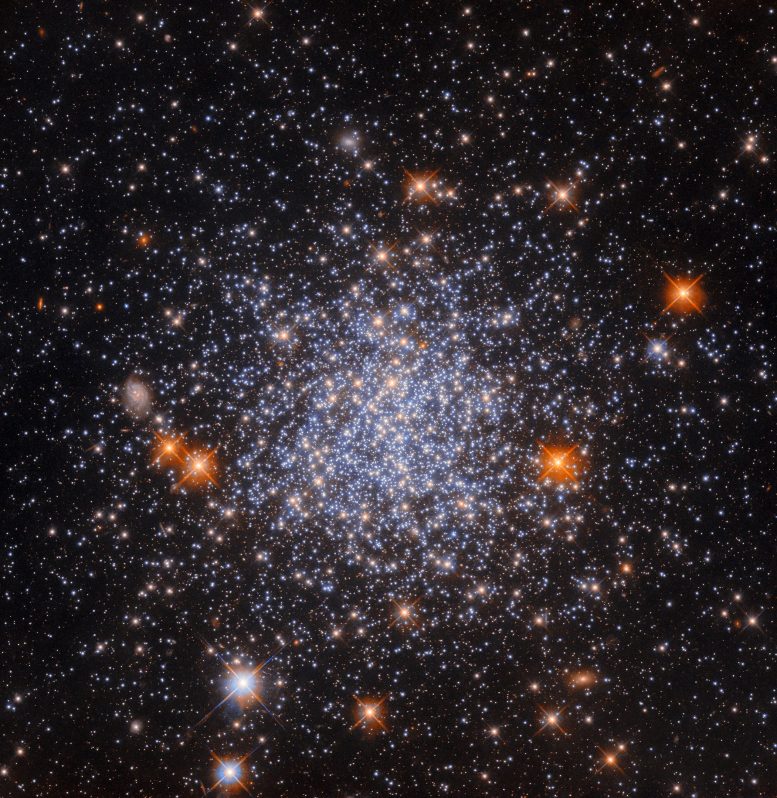

This image of NGC 1651, a globular cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud, exemplifies how celestial objects of varying sizes appear in Hubble’s images due to its fixed field of view and the object’s distance from Earth Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, L. Girardi, F. Niederhofer
Hubble captures varied cosmic scales, from the close globular cluster NGC 1651 to distant galaxies, using its fixed observational scope and mosaicing when necessary.
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a globular cluster known as NGC 1651. Like the object in another recent Picture of the Week, it is located about 162,000 light-years away in the largest and brightest of the Milky Way’s satellite galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
A notable feature of this image is that the globular cluster almost fills the entire image, even though globular clusters are only about 10 to 300 light-years in diameter (NGC 1651 has a diameter of roughly 120 light-years). In contrast, there are numerous Hubble Pictures of the Week that feature entire galaxies — which can be tens or hundreds of millions of light-years in diameter — that also more or less fill the whole image.
Telescope Field of View Explained
A common misconception is that Hubble and other large telescopes manage to observe wildly differently sized celestial objects by zooming in on them, as one would with a specialized camera here on Earth. However, whilst small telescopes might have the option to zoom in and out to a certain extent, large telescopes do not. Each telescope’s instrument has a fixed ‘field of view’ (the size of the region of sky that it can observe in a single observation).
For example, the ultraviolet/visible light channel of Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), the channel and instrument that were used to collect the data used in this image, has a field of view roughly one-twelfth the diameter of the Moon as seen from Earth. Whenever WFC3 makes an observation, that is the size of the region of sky that it can observe.
Capturing Cosmic Scale
The reason that Hubble can observe objects of such wildly different sizes is two-fold. Firstly, the distance to an object will determine how big it appears to be from Earth, so entire galaxies that are relatively far away might take up the same amount of space in the sky as a globular cluster like NGC 1651 which is relatively close by.
In fact, there’s a distant spiral galaxy lurking in this image, directly left of the cluster — though undoubtedly much larger than this star cluster, it appears small enough here to blend in with foreground stars! Secondly, multiple images spanning different parts of the sky can be mosaiced together to create single images of objects that are too big for Hubble’s field of view.
This is a very complex task and is not typically done for Pictures of the Week, but it has been done for some of Hubble’s most iconic images.








Universe can not be judged/covered neither by Hubble nor James Web Space Telescope…..
Efforts of Hubble and JWST may be admired indeed….