Eight months after the space telescope CHEOPS started its journey into space, the first scientific publication using data from CHEOPS has been issued.
CHEOPS is the first ESA mission dedicated to characterizing known exoplanets. Exoplanets, i.e. planets outside the Solar system, were first found in 1995 by two Swiss astronomers, Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, who were last year awarded the Nobel Prize for this discovery. CHEOPS was developed as part of a partnership between ESA and Switzerland. Under the leadership of the University of Bern and ESA, a consortium of more than a hundred scientists and engineers from eleven European states was involved in constructing the satellite over five years. The Science Operations Center of CHEOPS is located at the observatory of the University of Geneva.
Using data from CHEOPS, scientists have recently carried out a detailed study of the exoplanet WASP-189b. The results have just been accepted for publication in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. Willy Benz, professor of astrophysics at the University of Bern and head of the CHEOPS consortium, was delighted about the findings: “These observations demonstrate that CHEOPS fully meets the high expectations regarding its performance.”
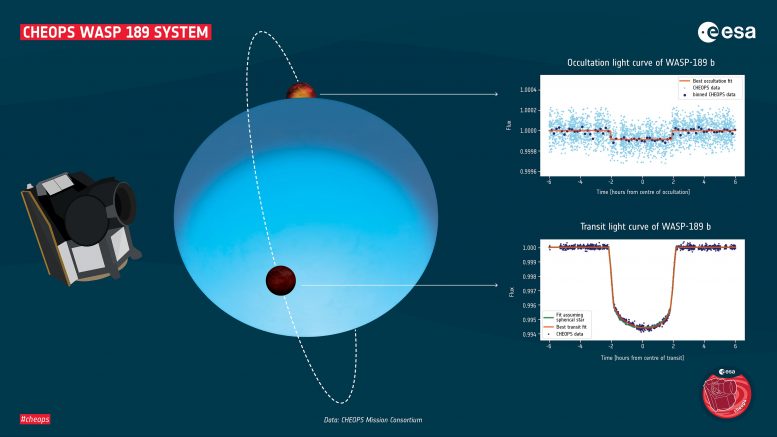
When a planet passes in front of its star as seen from Earth, the star seems fainter for a short time. This phenomenon is called a transit. When the planet passes behind the star, the light emitted and/or reflected by the planet is obscured by the star for a short time. This phenomenon is called occultation. Credit: © ESA
One of the most extreme planets in the universe
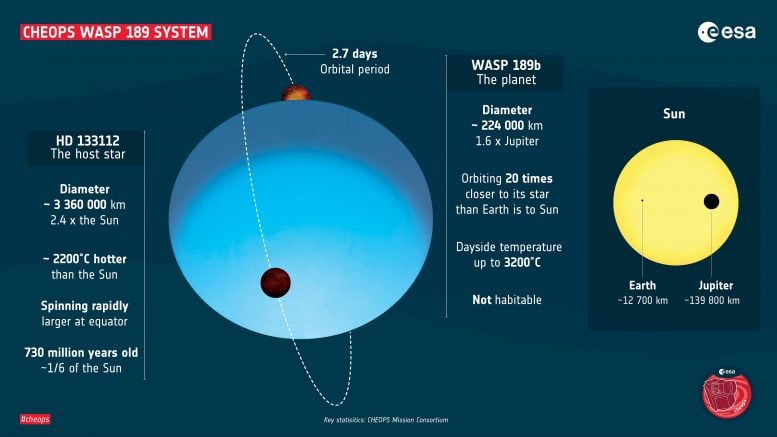
WASP-189b, the target of the CHEOPS observations, is an exoplanet orbiting the star HD 133112, one of the hottest stars known to have a planetary system. “The WASP-189 system is 322 light years away and located in the constellation Libra (the weighing scales),” explains Monika Lendl, lead author of the study from the University of Geneva, and member of the National Centre of Competence in Research PlanetS.
“WASP-189b is especially interesting because it is a gas giant that orbits very close to its host star. It takes less than 3 days for it to circle its star, and it is 20 times closer to it than Earth is to the Sun,” Monika Lendl describes the planet, which is more than one and a half times as large as Jupiter, the largest planet of the Solar system.
Monika Lendl further explains that planetary objects like WASP-189b are very exotic: “They have a permanent day side, which is always exposed to the light of the star, and, accordingly, a permanent night side.” This means that its climate is completely different from that of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn in our solar system. “Based on the observations using CHEOPS, we estimate the temperature of WASP-189b to be 3,200 degrees Celsius. Planets like WASP-189b are called “ultra-hot Jupiters.” Iron melts at such a high temperature, and even becomes gaseous. This object is one of the most extreme planets we know so far,” says Lendl.
Highly precise brightness measurements
“We cannot see the planet itself as it is too far away and too close to its host star, so we have to rely on indirect methods,” explains Lendl. For this, CHEOPS uses highly precise brightness measurements: When a planet passes in front of its star as seen from Earth, the star seems fainter for a short time. This phenomenon is called a transit. Monika Lendl explains: “Because the exoplanet WASP-189b is so close to its star, its dayside is so bright that we can even measure the ‘missing’ light when the planet passes behind its star; this is called an occultation. We have observed several such occultations of WASP-189b with CHEOPS,” says Lendl. “It appears that the planet does not reflect a lot of starlight. Instead, most of the starlight gets absorbed by the planet, heating it up and making it shine.” The researchers believe that the planet is not very reflective because there are no clouds present on its dayside: “This is not surprising, as theoretical models tell us that clouds cannot form at such high temperatures.”
And the star is special too
“We also found that the transit of the gas giant in front of its star is asymmetrical. This happens when the star possesses brighter and darker zones on its surface,” adds Willy Benz. “Thanks to CHEOPS data, we can conclude that the star itself rotates so quickly that its shape is no longer spherical; but ellipsoidal. The star is being pulled outwards at its equator.” continues Benz.
The star around which WASP-189b orbits is very different from the sun. Monika Lendl says: “The star is considerably larger and more than two thousand degrees Celsius hotter than our sun. Because it is so hot, the star appears blue and not yellow-white like the sun.” Willy Benz adds: “Only a handful of planets are known to orbit such hot stars, and this system is the brightest by far.” As a consequence, it forms a benchmark for further studies.
In conclusion, Willy Benz explains: “We are expecting further spectacular findings on exoplanets thanks to observations with CHEOPS. The next papers are already in preparation.”
Reference: “The hot dayside and asymmetric transit of WASP-189 b seen by CHEOPS” by M. Lendl, Sz. Csizmadia, A. Deline, L. Fossati, D. Kitzmann, K. Heng, S. Hoyer, S. Salmon, W. Benz, C. Broeg, et al. Accepted 17 September 2020, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202038677









Excuse me, all you super smart scientists. Please explain just what the term “most extreme” could possibly mean. Very bad English. “extreme” implies “most.” It is like saying “most unique” (a hamburger chain used this recently for its signs or something) or “most iconic.” Really. Something is either iconic or not, or unique or not.
Do you ask rhetorically, or do you really think scientists have time to read press releases on science aggregators?
A press release may be sourced – and checked later – by the scientists at the university that releases on a new paper (as here), but that is communicators or journalists. Who are supposed to know written exposition, albeit straitjacketed to fit the accepted form.
If you want to check the precise language, you have to read the paper. You should do it in any case, if you are interested in the science and not in nitpicking university office workers products. (Sometimes you may have to do both of course, or the aggregator has slapped on a click bait title to sell more ads which may elicit another type of protestation.)
” but that is communicators or journalists” – but it is communicators or journalists that produce the result.
Self nitpicking is an acquired taste. 👹
Extreme “implies” Most? Disregard the previous comment. What an idiot.
If you had two planets, one had a temp of 3200 C and the other 3300 C, I’d say both are extreme relative to Earth. However, my perception would be that 3300 C is the most extreme of the two. It’s the most extreme relative to what i’ve seen up to that point. I don’t see the problem with the language in the article.
This has to be the most exceedingly extremely extreme planet ever.
A person can demonstrate their extreme ignorance of the English language, but there is always another person That will prove to be “more” extreme than the original winner of this distinct award, however you have proven to be the “most” extreme example