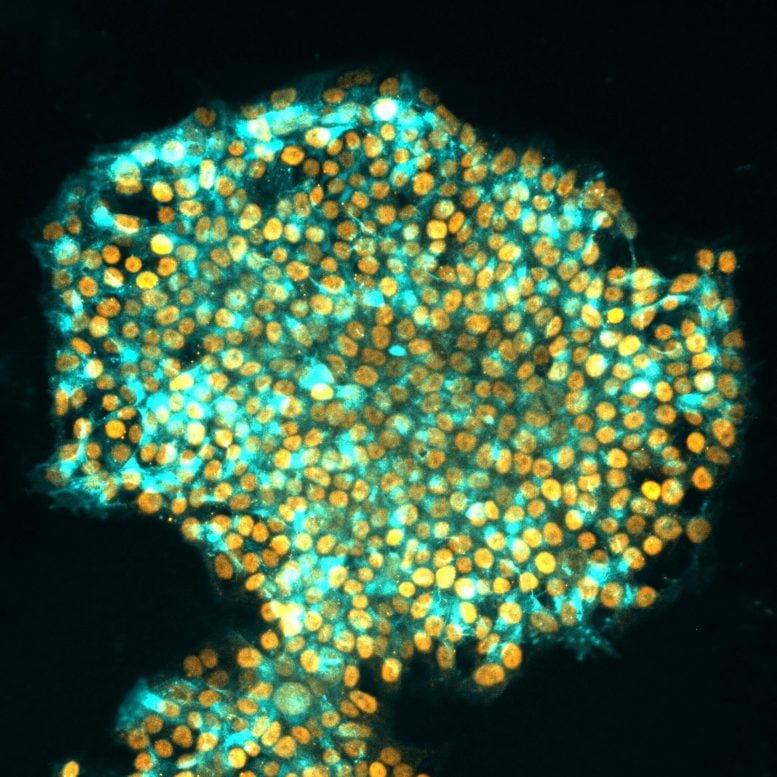
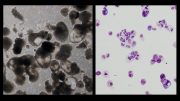
Scientists have developed a revolutionary technique, termed “transient-naive-treatment (TNT) reprogramming.” This method allows human cells to be reprogrammed to more closely resemble embryonic stem cells, addressing a longstanding issue in regenerative medicine. The team’s breakthrough promises to set new standards for cell therapies and research. (Human iPS cells.) Credit: Jia Tan, Polo Laboratory
A new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells.
In a groundbreaking study published on August 16 in the journal Nature, Australian scientists have resolved a long-standing problem in regenerative medicine. They developed a new method to reprogram human cells to better mimic embryonic stem cells, with significant implications for biomedical and therapeutic uses. The team of researchers was led by Professor Ryan Lister from the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and The University of Western Australia and Professor Jose M Polo from Monash University and the University of Adelaide.
History and Challenges of Cell Reprogramming
In a revolutionary advance in the mid-2000s, it was discovered that the non-reproductive adult cells of the body, called ‘somatic’ cells, could be artificially reprogrammed into a state that resembles embryonic stem (ES) cells which have the capacity to then generate any cell of the body.
The transformative ability to artificially reprogram human somatic cells, such as skin cells, into these so-called induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells provided a way to make an essentially unlimited supply of ES-like cells. This has widespread applications in disease modeling, drug screening, and cell-based therapies.
“However, a persistent problem with the conventional reprogramming process is that iPS cells can retain an epigenetic memory of their original somatic state, as well as other epigenetic abnormalities,” Professor Lister said. “This can create functional differences between the iPS cells and the ES cells they’re supposed to imitate, and specialized cells subsequently derived from them, which limits their use.”
Introducing the TNT Reprogramming Technique
Professor Jose Polo, who is also with the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, explained that they have now developed a new method, called transient-naive-treatment (TNT) reprogramming, that mimics the reset of a cell’s epigenome that happens in very early embryonic development.
“This significantly reduces the differences between iPS cells and ES cells and maximizes the effectiveness of how human iPS cells can be applied,” he said.
Dr. Sam Buckberry, a computational scientist from the Harry Perkins Institute, UWA, and Telethon Kids Institute, and co-first author of the study, said by studying how the somatic cell epigenome changed throughout the reprogramming process, they pinpointed when epigenetic aberrations emerged, and introduced a new epigenome reset step to avoid them and erase the memory.
Dr. Xiaodong Liu, a stem cell scientist who also spearheaded the research said the new human TNT-iPS cells much more closely resembled human ES cells – both molecularly and functionally – than those produced using conventional reprogramming.
Improved Results With TNT Method
Dr. Daniel Poppe, a cell biologist from UWA, the Harry Perkins Institute, and co-first author, said the iPS cells generated using the TNT method differentiated into many other cells, such as neuron progenitors, better than the iPS cells generated with the standard method.
Monash University student and co-first author Jia Tan said the team’s TNT method was dynamite.
“It solves problems associated with conventionally generated iPS cells that if not addressed could have severely detrimental consequences for cell therapies in the long run,” he said.
Future Implications and Research
Professor Polo said that despite their breakthrough, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying the iPS epigenome aberrations and their correction are not fully known. Further research is needed to understand them.
“We predict that TNT reprogramming will establish a new benchmark for cell therapies and biomedical research, and substantially advance their progress,” Professor Lister said.
Reference: “Transient naive reprogramming corrects hiPS cells functionally and epigenetically” by Sam Buckberry, Xiaodong Liu, Daniel Poppe, Jia Ping Tan, Guizhi Sun, Joseph Chen, Trung Viet Nguyen, Alex de Mendoza, Jahnvi Pflueger, Thomas Frazer, Dulce B. Vargas-Landín, Jacob M. Paynter, Nathan Smits, Ning Liu, John F. Ouyang, Fernando J. Rossello, Hun S. Chy, Owen J. L. Rackham, Andrew L. Laslett, James Breen, Geoffrey J. Faulkner, Christian M. Nefzger, Jose M. Polo and Ryan Lister, 16 August 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06424-7
The collaborative research project also included researchers from the Australian National University, Westlake University, Queen Mary University of London, Mater Research Institute, University of Queensland, Queensland Brain Institute, South Australian Health & Medical Research Institute, Duke-NUS Medical School, and CSIRO.



Be the first to comment on "Scientists Discover “Dynamite” Way To Wipe a Cell’s Memory To Better Reprogram It as a Stem Cell"