Ernest Shackleton Endurance Shipwreck
The wreck of Endurance is a bridge to a bygone age, and a reminder of Antarctica’s uncertain future.
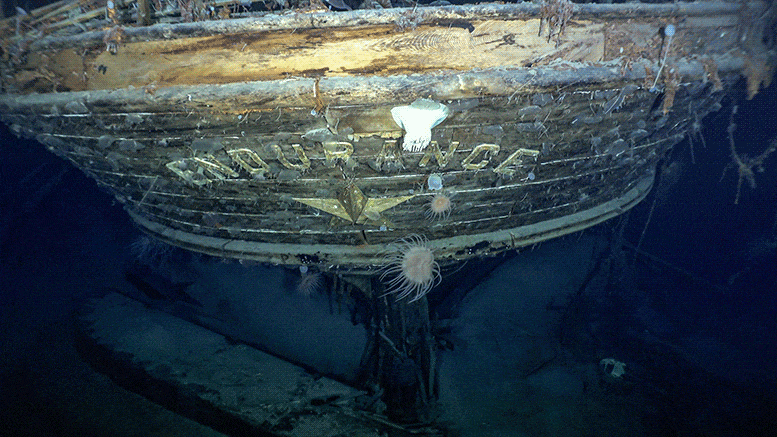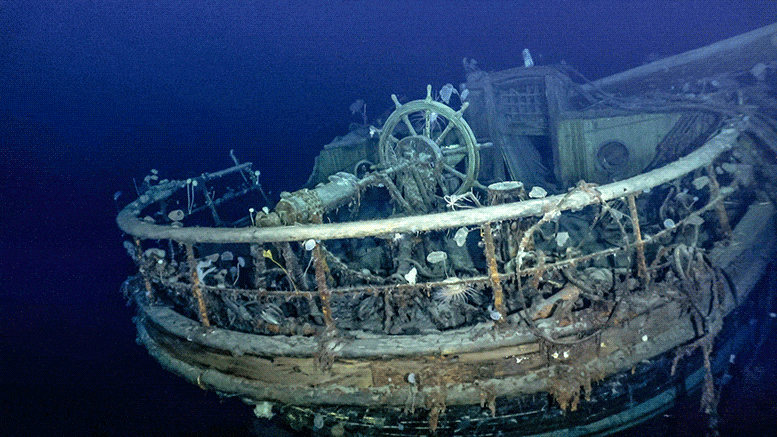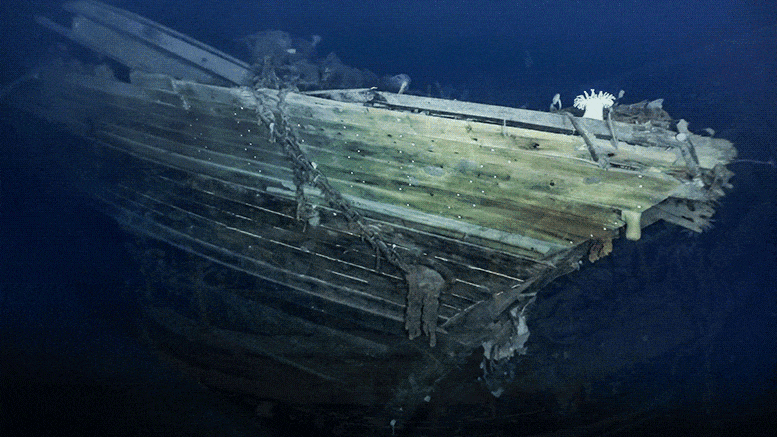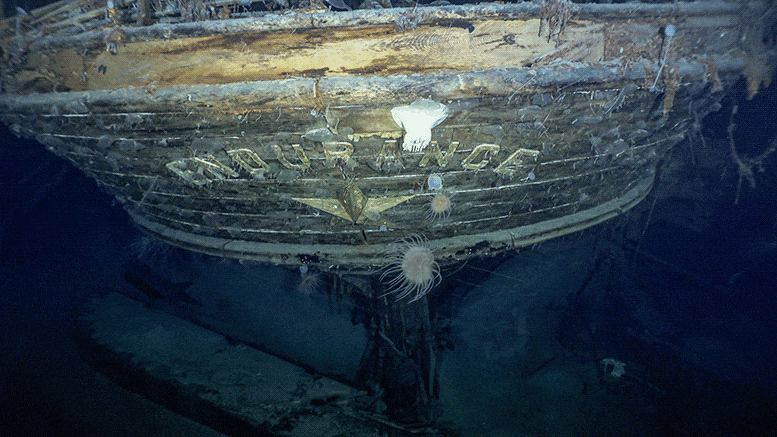
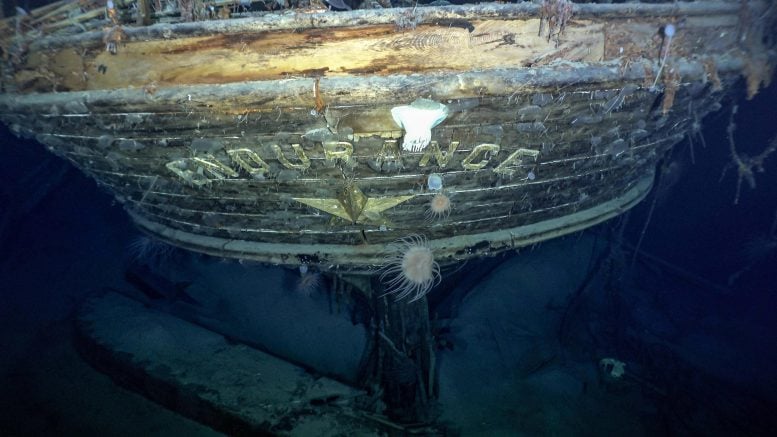
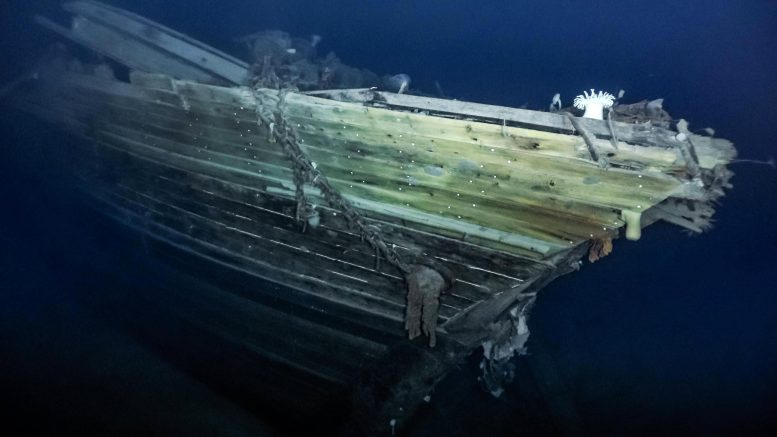
Superbly clear images of the shipwreck Endurance, 3,000 meters (~10,000 feet) below the ocean’s surface in Antarctica’s Weddell Sea, were broadcast around the world last week. Found by the Endurance 22 Expedition using a state-of-the-art autonomous underwater vehicle, we now have images almost as iconic as those taken of the stricken ship by Australian photographer and expedition member Frank Hurley in 1915.
Endurance was the ship of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. Led by British-Irish explorer Sir Ernest Shackleton, the expedition aimed to cross Antarctica on foot for the first time, from the Weddell Sea (south of the Atlantic Ocean) to the Ross Sea (south of New Zealand), via the South Pole.
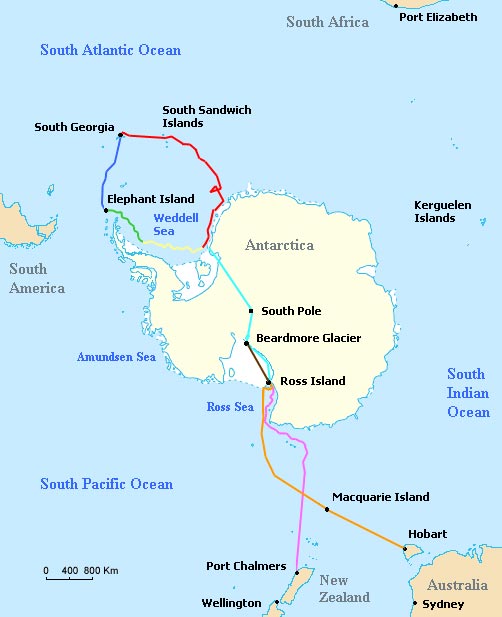
Voyages of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. Red, voyage of Endurance; yellow, drift of Endurance in pack ice; green, sea ice drift after sinking of Endurance; blue, voyage of James Caird; cyan, planned trans-Antarctic route; orange, voyage of Aurora; pink, retreat of Aurora; brown, supply depot route. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Endurance departed England in August 1914, just as the First World War was breaking out. The ship entered Antarctica’s pack ice in December 1914 and by February 1915 was firmly ice-bound in the Weddell Sea. By October, the shifting pack ice began to crush the ship, which sank the following month.
Hurley famously dived into the flooded interior of the sinking Endurance to retrieve about 120 photographic plates, leaving some 400 behind. The crew then trekked to the edge of the sea ice, and got to Elephant Island in April 1916. From there, Shackleton led a smaller team, using the lifeboat James Caird to cross the stormy Southern Ocean and reach the island of South Georgia to raise the alarm.
The expedition crew – and Hurley’s plates – were finally rescued in August 1916. His evocative images of the sinking ship helped the expedition gain widespread attention and cemented Endurance’s place in Antarctic history. But what became of the sunken ship?
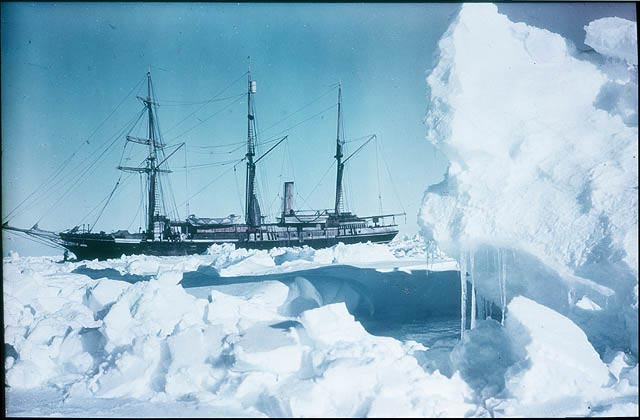

One of Hurley’s photographs of the stricken Endurance trapped in pack ice. Credit: Frank Hurley/Wikimedia Commons
The search for Endurance
The last known coordinates of the vessel were recorded by skipper Frank Worsley as 68°39’30 “S, 52°26’30 “W, but this was not verified until this week. The successful discovery came during the second major attempt in recent years to find the wreck.
In early 2019, the Weddell Sea Expedition, also privately financed and conducting a broader, multidisciplinary scientific survey of the area, was unsuccessful, having lost its autonomous submarine.
The current Endurance 22 Expedition has been similarly multidisciplinary, and benefited from an anonymous US$10 million private donation. This private sponsorship echoes Shackleton’s situation; his expeditions were funded through donations of both cash and supplies (which later appeared in advertisements).
Endurance is now an international heritage site
Even before its rediscovery, Endurance was a protected heritage site. In 2019, countries within the Antarctic Treaty System designated the unknown site of the wreck a “Historic Site and Monument.”
Other uncertain sites have also been preemptively recognized in this way, such as the tent left behind by Norwegian pioneer Roald Amundsen at the South Pole in 1911, now buried under snow, and the wreck of the San Telmo, a Spanish warship that sank south of Cape Horn in 1819.
These designations point to the importance of imagination whenever we deal with the very far south. Most people will never visit Antarctica, but the stories we carry with us about the place have broad cultural circulation.
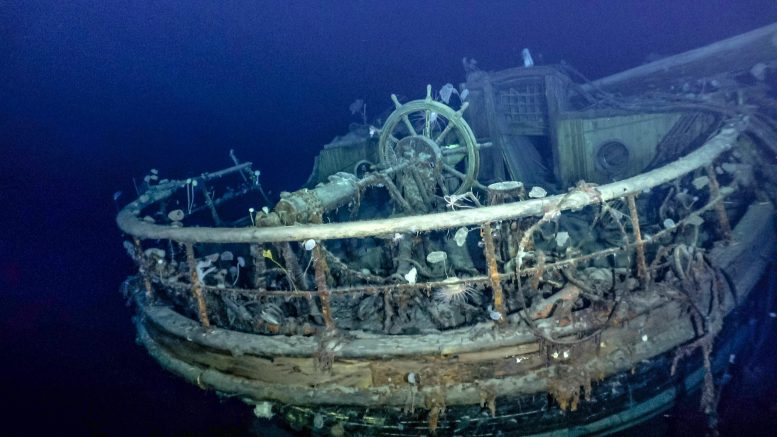

Wreckage of Ernest Shackleton’s Endurance. Taffrail and ship’s wheel, aft well deck. Credit: Falklands Maritime Heritage Trust
The “historic site” designation protects “all artifacts contained within or formerly contained within the ship, which may be lying on the seabed in or near the wreck within a 150-meter radius.”
Accordingly, the Endurance 22 Expedition did not take anything physical from the wreck. But the new photographs of the ship’s final resting place tell a powerful story.
Changing views on Antarctica
The photographs not only bring Endurance vividly back to life; they invite new ways of picturing Antarctica in general. Deep sea fauna, including sea anemones, sea squirts, and even a crab, crawl over the wreck, showing the vitality of the Antarctic seafloor and providing a window into an underwater world about which little is known. In much the same way, the recent remarkable discovery of 60 million ice fish nests in the Weddell Sea also demonstrates this vitality.
The images also raise questions about why we look to Antarctica, and what we see when we do. Is it a place for daring travelers to test their mettle – the view that prevailed during the “heroic age” of Antarctic exploration that ended with Shackleton’s voyage? Or is it a place for collaboration and collective endeavor between nations, as typified by the Antarctic Treaty and the continent’s latter-day status as primarily a place for scientific research?
These days, Antarctica is viewed through an environmental lens; rather than a place for humans to conquer, it is closely linked in the cultural imagination to climate change and images of melting ice. That makes the discovery of the ship even more interesting, given the recent discovery of the wreck benefited from a record low sea ice extent this summer.
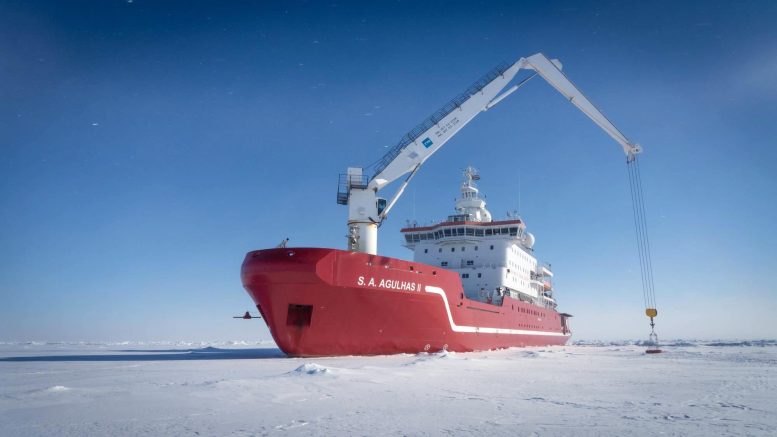

Endurance 22 Expedition worked out of the South African polar research and logistics vessel, S.A. Agulhas II. Credit: Falklands Maritime Heritage Trust
Technology such as satellites and autonomous underwater vehicles mean Antarctica and the Southern Ocean are more surveilled than ever before. Yet much remains unknown about the frozen continent, and particularly about the deep seas that encircle it.
The discovery of Endurance shows how modern technology can help us find past artifacts and also look to the future. The ship provides a conceptual bridge between Antarctica’s history as a frontier of exploration, to our modern ideas of heritage preservation, international cooperation, scientific research, and climate action.
Put more simply, finding the wreck of the Endurance presents us with a key moment to think about Antarctica’s storied past and its uncertain future.
Written by:
- Hanne E.F. Nielsen – Lecturer, University of Tasmania
- Alessandro Antonello – Senior Research Fellow in History, Flinders University
This article was first published in The Conversation.![]()








Is it practical to recover any of Mr. Hurley’s photographic plates? By “practical,” I mean without destruction of the Endurance or her environment.