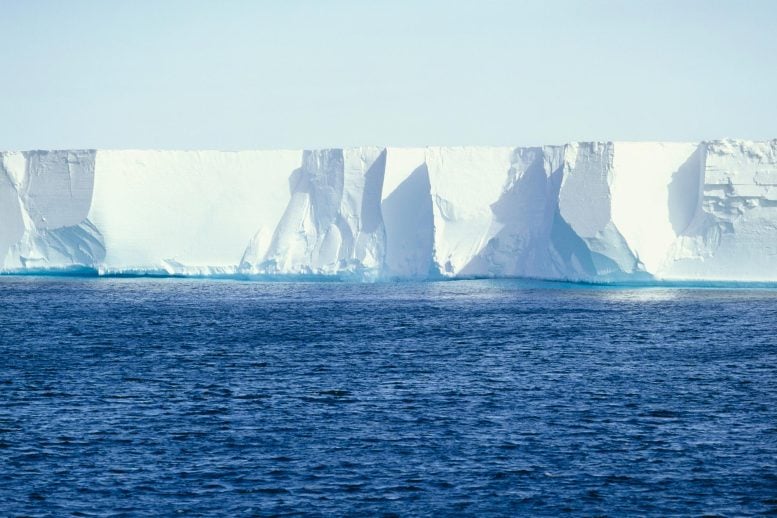

Research from Washington University in St. Louis reveals that the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica, roughly the size of France, is dislocated daily by an ice stream. This movement, caused by a sudden slip in the ice stream, could influence icequakes and shelf fractures, raising concerns about ice shelf stability in a warming world.
The activity of an ice stream has caused the Ross Ice Shelf to suddenly displace.
In Antarctica, massive glaciers are constantly shifting. Ice streams, which act like conveyor belts, are the pathways of accelerated movement that transport the majority of the ice and sediment debris from these extensive glaciers towards the ocean.
One such ice stream jostles the entire Ross Ice Shelf out of place at least once daily, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
This finding is significant because of the scale of the Ross Ice Shelf: It is the largest ice shelf in Antarctica, about the same size as the country of France.
“We found that the whole shelf suddenly moves about 6 to 8 centimeters (or 3 inches) once or twice a day, triggered by a slip on an ice stream that flows into the ice shelf,” said Doug Wiens, the Robert S. Brookings Distinguished Professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences. “These sudden movements could potentially play a role in triggering icequakes and fractures in the ice shelf.”
The Ross Ice Shelf is a floating lip of ice that extends out over the ocean from inland glaciers.
Scientists are interested in interactions between ice shelves and ice streams in part because they are concerned about the stability of Antarctica’s ice shelves in a warming world.
Ice shelves act as brakes for glaciers and ice streams, slowing their journey to the sea where they melt, thus allowing more ice to accumulate on the continent. If an ice shelf collapses, this support disappears and the glaciers are free to flow faster. Once they flow into the ocean, they contribute to sea level rise.
The new study, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, focuses on movement triggered by the Whillans Ice Stream, one of about a half-dozen of the large, fast-moving rivers of ice pouring into the Ross Ice Shelf.
“One would not detect the movement just by feeling it,” Wiens said. “The movement occurs over a time period of several minutes, so it is not perceptible without instrumentation. That’s why the movement has not been detected until now, even though people have been walking and camping on the Ross Ice Shelf since the time of the great explorers Robert F. Scott and Roald Amundsen.”
Sudden slipping
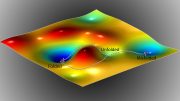
The movement of the Ross Ice Shelf is triggered by a relatively sudden — in glacial terms — movement of the ice stream called a slip event. It is somewhat similar to the “stick-slip” that occurs along a fault before and during an earthquake.
Under the scenario that Wiens and his team observed, a large section of the Whillans Ice Stream, measuring more than 100 km by 100 km, remains stationary while the rest of the ice stream creeps forward. Then, once or twice per day, the large section lurches forward against the Ross Ice Shelf.
It can move as much as 40 cm (16 inches) in a few minutes, Wiens said.
Studies of ice streams over the past 50 years show some ice streams speeding up, others slowing down. Scientists can use seismographs to detect the sudden motion of the ice streams to help understand what controls this motion. Wiens and his team traveled to Antarctica in 2014 to place the seismographs used in this study.
“I’ve published several papers about the Whillans Ice Stream slip events in the past, but had not discovered that the whole Ross Ice Shelf also moves until now,” Wiens said.
The researchers do not think that these slip events are directly related to human-caused global warming. One theory is that they are caused by the loss of water in the bed of the Whillans Ice Stream, making it more “sticky.”
The stress and strains associated with slip events is similar to the stress and strain observed to trigger icequakes under different conditions.
“At this point, icequakes and fractures are just part of the normal life of the ice shelf,” Wiens said. “There is a worry that the Ross Ice Shelf will someday disintegrate, since other smaller and thinner ice shelves have done so. We also know that the Ross Ice Shelf disintegrated during the last interglacial period — about 120,000 years ago — and that caused rapid ice loss to the other glaciers and ice streams feeding into it.”
Reference: “Ross Ice Shelf Displacement and Elastic Plate Waves Induced by Whillans Ice Stream Slip Events” by Douglas A. Wiens, Richard C. Aster, Andrew A. Nyblade, Peter D. Bromirski, Peter Gerstoft and Ralph A. Stephen, 27 March 2024, Geophysical Research Letters.
DOI: 10.1029/2023GL108040







Has anyone taken into account that the more moisture on the planet due to ice melt and rising sea levels results in more cloud cover, thus resulting in a cooler planet.the planet will heal itself over time , obviously in a shorter period if we weren’t here.
Will “Heal itself”?
Questionable.
As we will continue to accelerate this phenomenon, until a catastrophic event occurs.
Global CO2 emissions are accelerating Warming.
Snow piles up over millennia, compacts into ice. Forms the ice sheets. After getting so enormous gravity takes over and eventually calving happens. Massive icebergs break off. The earth has its cycles of ice ages. Possibly this cycle is the cause and is non stoppable.
Will, the additional cloud cover stops the heat from radiating into space and traps it, therefore aiding the heating of the planet not slowing it.
Mostly at night. The increased albedo from clouds has a more profound effect on the surface insolation. Have you ever experienced the impact of a cloud drifting over you and noticed what a relief it is from a mid-Summer scorching sun?
Not to mention water vapor is a stronger greenhouse gas than. CO2 or even some types of methane.
I’m not sure what the time is but it’s sure time for AI.
You are exactly right and too frequently. It’s all wasted data…just streaming garbage and using unnecessary energy
Has anyone been running a freq domain analysis of the stick slip data?
First time user and a pensioner with a meager state pension
That’s cool thanks aj