
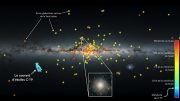
A map of stars in the outer region of the Milky Way as traced by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Streams of stars are seen throughout both the Northern (top) and Southern Galactic hemispheres, corresponding to small galaxies and star clusters which are in the process of being ingested by the Milky Way. The newest discovery is designated as the Triangulum Stream. Credit: SDSS; Yale University
Using the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, a team of scientists have discovered a band of stars, named the Triangulum stream, in the southern Galactic sky that is believed to be the remnant of an ancient star cluster slowly being ingested by the Milky Way.
Yale astronomers have caught the Milky Way having a snack.
Using the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, researchers have discovered a band, or stream, of stars believed to be the remnant of an ancient star cluster slowly being ingested by the Milky Way, Earth’s home galaxy.
“The Milky Way is constantly gobbling up small galaxies and star clusters,” said Ana Bonaca, a Yale graduate student and lead author of a study forthcoming in Astrophysical Journal Letters. “The more powerful gravity of our Milky Way pulls these objects apart and their stars then become part of the Milky Way itself.”
Researchers have previously found evidence of the Milky Way eating up dwarf galaxies. Bonaca argues that the newly found stellar stream is the remnant of a star cluster rather than of a larger galaxy, because the stream is very narrow.
“Our discovery is more of a light snack than a big meal for the Milky Way,” says Marla Geha, associate professor of astronomy at Yale and a co-author of the study. “Studying this digestion process in detail is important because it gives us new insight into how all galaxies form and evolve.”
The new band of stars, or stellar stream, is the first of its kind found in the southern Galactic sky, a region that has been hard to examine due to a relative lack of deep-sky imaging there. Deeper imaging enables astronomers to detect fainter stars.
Named the Triangulum stream, the newly discovered stellar stream could also help astronomers reconstruct how the Milky Way’s mass is distributed, further revealing its dynamic structure.
Galaxies are believed to form hierarchically through the merger of smaller galaxies and still smaller star clusters. Stellar streams form as they are ripped apart by the gravitational force of galaxies. This process may be the primary way galaxies such as the Milky Way grow in mass, the researchers say.
Triangulum was found by searching a region recently surveyed by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey III (SDSS-III), an international collaboration that is mapping the sky through wide-field photometry.
Bonaca, Geha and co-author Nitya Kallivayalil, a Yale postdoctoral fellow, relied specifically on the survey’s Data Release 8, which included information about vast new areas of the southern galactic sky.
Reference: “A Cold Milky Way Stellar Stream in the Direction of Triangulum” by Ana Bonaca, Marla Geha and Nitya Kallivayalil, 31 October 2012, The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
DOI: 10.1088/2041-8205/760/1/L6
Research support was provided by the National Science Foundation and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.







All the galaxies are cannibals. Nebula Andromeda cannibalizes the neighboring galaxies. Milky Way galaxy is set to devour its neighbors like Large Magellanic Cloud and Small Magellanic Cloud. Now this article states that our Milky Way Galaxy stars devouring the minor star cluster like Triangulum. In another 4 billion years our own Milky Way will be eaten by the Great Andromeda Nebula. Thank You.