A team of researchers has discovered a method to activate a bacterial defense system, known as CBASS, to self-destruct and prevent the spread of viruses among bacteria, potentially offering a new way to manage bacterial infections and combat antibiotic resistance. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Researchers unveil how the self-killing activity of bacteria can be harnessed in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified a new approach to controlling bacterial infections. The findings were described in the February 6 online issue of Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
The team found a way to turn on a vital bacterial defense mechanism to fight and manage bacterial infections. The defense system, called cyclic oligonucleotide-based antiphage signaling system (CBASS), is a natural mechanism used by certain bacteria to protect themselves from viral attacks. Bacteria self-destruct as a means to prevent the spread of virus to other bacterial cells in the population.
CBASS Defense Mechanism Explored
“We wanted to see how the bacterial self-killing CBASS system is activated and whether it can be leveraged to limit bacterial infections,” says co-senior author Aneel Aggarwal, PhD, Professor of Pharmacological Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai. “This is a fresh approach to tackling bacterial infections, a significant concern in hospitals and other settings. It’s essential to find new tools for fighting antibiotic resistance. In the war against superbugs, we need to constantly innovate and expand our toolkit to stay ahead of evolving drug resistance.”
According to a 2019 report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 2.8 million antimicrobial-resistant infections occur in the United States each year, with over 35,000 people dying as a result.
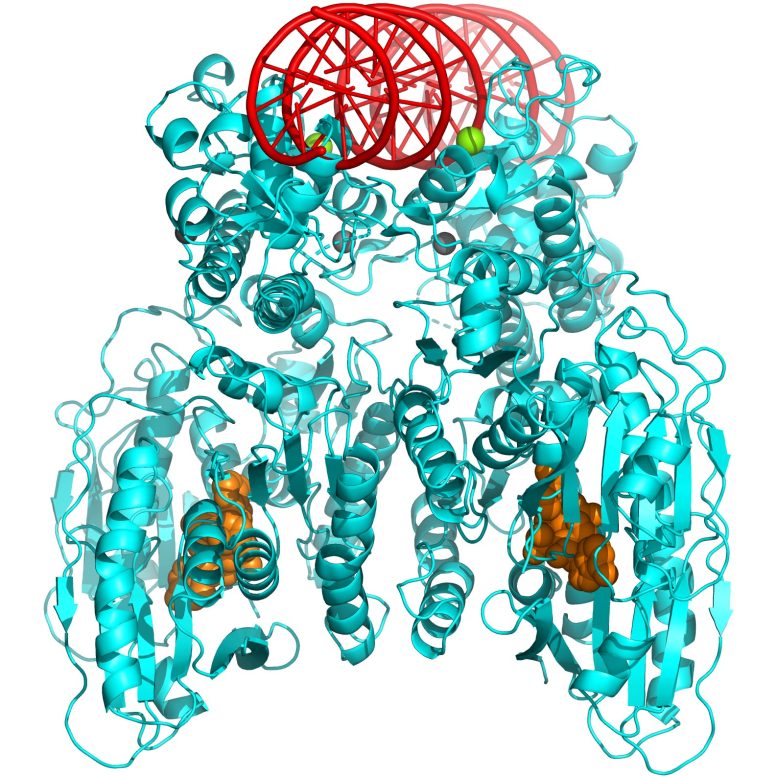
Icahn Mount Sinai researchers unveil how the self-killing activity of bacteria can be used in the fight against antibiotic resistance. Above: 3-D structure of CBASS Cap5 protein tetramer (shown in cyan) formed upon binding to the cyclic dinucleotide (shown in orange) to destroy bacteria’s own DNA (model, shown in red). Essential magnesium ions for DNA cleavage are shown in green. Credit: Rechkoblit et al., Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
Innovative Strategies Against Superbugs
As part of the experiments, the researchers studied how “Cap5,” or CBASS-associated protein 5, is activated for DNA degradation and how it could be used to control bacterial infections through a combination of structural analysis and various biophysical, biochemical, and cellular assays. Cap5 is a key protein that becomes activated by cyclic nucleotides (small signaling molecules) to destroy the bacterial cell’s own DNA.
“In our study, we started by identifying which of the many cyclic nucleotides could activate the effector Cap5 of the CBASS system,” says co-senior author Olga Rechkoblit, PhD, Assistant Professor of Pharmacological Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai. “Once we figured that out, we looked closely at the structure of Cap5 when it’s bound to these small signaling molecules. Then, with expert help from Daniela Sciaky, PhD, a researcher at Icahn Mount Sinai, we showed that by adding these special molecules to the bacteria’s environment, these molecules could potentially be used to eliminate the bacteria.”
Overcoming Technical Challenges
The researchers found that determining the structure of Cap5 with cyclic nucleotides posed a technical challenge, requiring expert help from Dale F. Kreitler, PhD, AMX Beamline Scientist at Brookhaven National Laboratory. It was achieved by using micro-focused synchrotron X-ray radiation at the same facility. Micro-focused synchrotron X-ray radiation is a type of X-ray radiation that is not only produced using a specific type of particle accelerator (synchrotron) but is also carefully concentrated or focused on a tiny area for more detailed imaging or analysis.
Future Directions
Next, the researchers will explore how their discoveries apply to other types of bacteria and assess whether their method can be used to manage infections caused by various harmful bacteria.
Reference: “Activation of CBASS Cap5 endonuclease immune effector by cyclic nucleotides” by Olga Rechkoblit, Daniela Sciaky, Dale F. Kreitler, Angeliki Buku, Jithesh Kottur and Aneel K. Aggarwal, 6 February 2024, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01220-x
Other authors who contributed to this work are Angeliki Buku, PhD, and Jithesh Kottur, PhD, both with Icahn Mount Sinai.
The work was funded by National Institutes of Health grants R35-GM131780, P41GM111244, KP1605010, P30 GM124165, S10OD021527, GM103310, and by the Simons Foundation grant SF349247.





Be the first to comment on "Unlocking Bacterial Self-Destruction to Combat Infections"