
Researchers highlight the overlooked global issue of urban land sinking, driven by human activities such as groundwater withdrawal. Using new satellite data, they reveal the extensive impact, including on Chinese cities, urging the integration of this hazard into future urban resilience plans.
New satellite data reveals that a third of China’s urban population faces the threat of city subsidence.
According to researchers from Virginia Tech and the University of East Anglia in the United Kingdom, sinking land is overlooked as a hazard in urban areas globally.
In an invited perspective article for the journal Science, Virginia Tech’s Manoochehr Shirzaei collaborated with Robert Nicholls of the University of East Anglia to highlight the importance of recent research analyzing how and why land is sinking — including a study published in the same issue that focused on sinking Chinese cities.
Results from the accompanying research study showed that of the 82 Chinese cities analyzed, 45 percent are sinking. Nearly 270 million urban residents may be affected with hard-hit urban areas such as Beijing and Tianjin sinking at a rate of 10 millimeters a year or more. Land sinking, or subsidence, results in increased risk to roadways, runways, building foundations, rail lines, and pipelines.
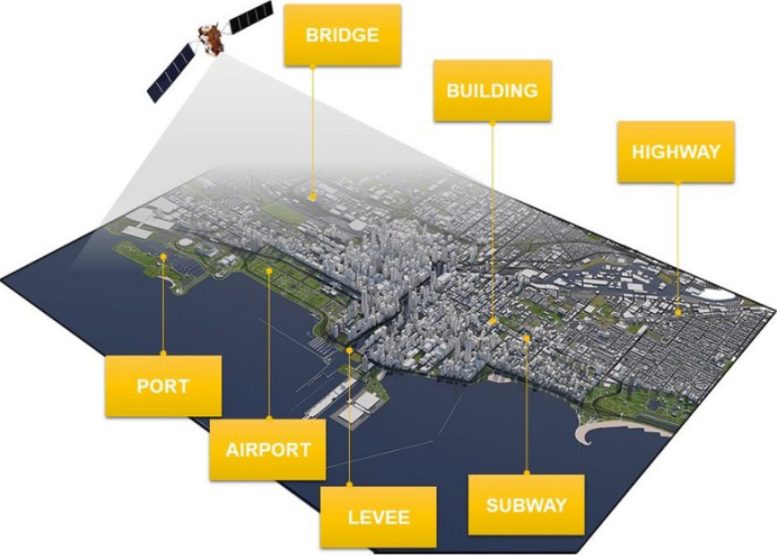
New satellite tools allow researchers to generate accurate, high-resolution measurements of sinking land, which represents a growing hazard all over the world. Credit: Illustration courtesy of Manoochehr Shirzaei
The phenomenon isn’t limited to China, said Shirzaei.
“Land is sinking almost everywhere,” said Shirzaei, who was not involved in the China-focused study but whose recent research using satellite-monitoring techniques shed light on the growing dangers of sinking land along the U.S. East Coast. “If we don’t account for it in adaption and resilience plans now, we may be looking at widespread destruction of infrastructure in the next few decades.”
Shirzaei and Nicholls expounded on this concept in the perspective article, focusing on three major points.
Advances in satellite monitoring revealed the extent of land sinking for the first time
The technique used to map consistent large-scale measurements of sinking land in China relied on space-based radar. Over the past decade, advances in satellite imaging technology granted researchers like Shirzaei the ability to measure millimeter-scale changes in land level over days to years.
“This is a relatively new technique,” said Shirzaei. “We didn’t have the data before. Now we have it, so we can use it — not only to see the problem, but to fix the problem.”
Land sinking is just an observation – more research is needed
While consistently measuring the sinking of urban land will provide a baseline to work from, predicting future subsidence requires models that consider all drivers, including human activities and climate change, and how they might change with time.
Land sinking is mainly caused by human activity, but it can also be addressed by human activity
Land sinking is mainly caused by human action in the cities. Groundwater withdrawal, which lowers the water table, is considered the most important driver of subsidence, combined with the geology and weight of buildings. Recharging the aquifer and reducing pumping can immediately mitigate land sinking.
Shirzaei and Nicholls called for the research community to move from measurement to understanding implications and supporting responses.
Reference: “Earth’s sinking surface” by Robert J. Nicholls and Manoochehr Shirzaei, 18 April 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.ado9986








Be the first to comment on "Major Chinese Cities Are Rapidly Sinking, Posing Serious Consequences"