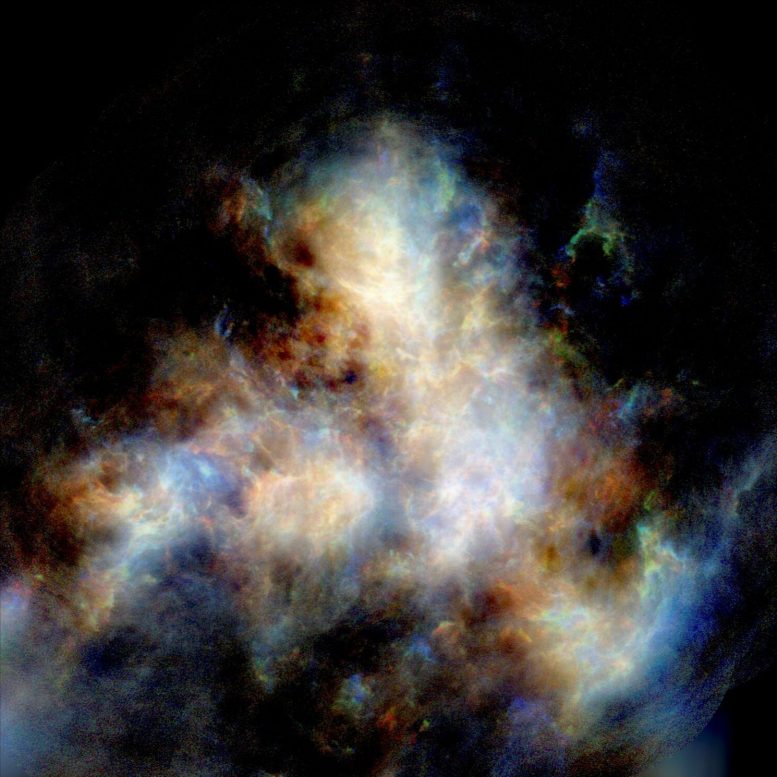

A radio image of hydrogen gas in the Small Magellanic Cloud as observed by CSIRO’s ASKAP telescope. Credit: Naomi McClure-Griffiths et al, CSIRO’s ASKAP telescope.
The new peer-reviewed study of the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), which is a tiny fraction of the size and mass of the Milky Way galaxy, uses images taken with CSIRO’s powerful Australian SKA Pathfinder (ASKAP) radio telescope array.
Lead researcher Professor Naomi McClure-Griffiths from ANU said the features of the radio images were more than three times finer than previous SMC images, which allowed the team to probe the interactions between the small galaxy and its environment with more accuracy.
“We were able to observe a powerful outflow of hydrogen gas from the Small Magellanic Cloud,” said Professor McClure-Griffiths from the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics at ANU.
“The implication is the galaxy may eventually stop being able to form new stars if it loses all of its gas. Galaxies that stop forming stars gradually fade away into oblivion. It’s sort of a slow death for a galaxy if it loses all of its gas.”
Professor McClure-Griffiths said the discovery, which is part of a project that investigates the evolution of galaxies, provided the first clear observational measurement of the amount of mass lost from a dwarf galaxy.
“The result is also important because it provides a possible source of gas for the enormous Magellanic Stream that encircles the Milky Way,” she said.
“Ultimately, the Small Magellanic Cloud is likely to eventually be gobbled up by our Milky Way.”
CSIRO co-researcher Dr. David McConnell said ASKAP was unrivaled in the world for this kind of research due to its unique radio receivers that give it a panoramic view of the sky.
“The telescope covered the entire SMC galaxy in a single shot and photographed its hydrogen gas with unprecedented detail,” he said.
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the Universe, and is the main ingredient of stars.
“ASKAP will go on to make state-of-the-art pictures of hydrogen gas in our own Milky Way and the Magellanic Clouds, providing a full understanding of how this dwarf system is merging with our own galaxy and what this teaches us about the evolution of other galaxies,” Dr. McConnell said.
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
The ARC Center of Excellence in All Sky Astrophysics (ASTRO 3D) at ANU supports some of the researchers who were part of this study.
Reference: “Cold gas outflows from the Small Magellanic Cloud traced with ASKAP” by N. M. McClure-Griffiths, H. Dénes, J. M. Dickey, S. Stanimirović, L. Staveley-Smith, Katherine Jameson, Enrico Di Teodoro, James R. Allison, J. D. Collier, A. P. Chippendale, T. Franzen, Gülay Gürkan, G. Heald, A. Hotan, D. Kleiner, K. Lee-Waddell, D. McConnell, A. Popping, Jonghwan Rhee, C. J. Riseley, M. A. Voronkov and M. Whiting, 29 October 2018, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-018-0608-8







very good