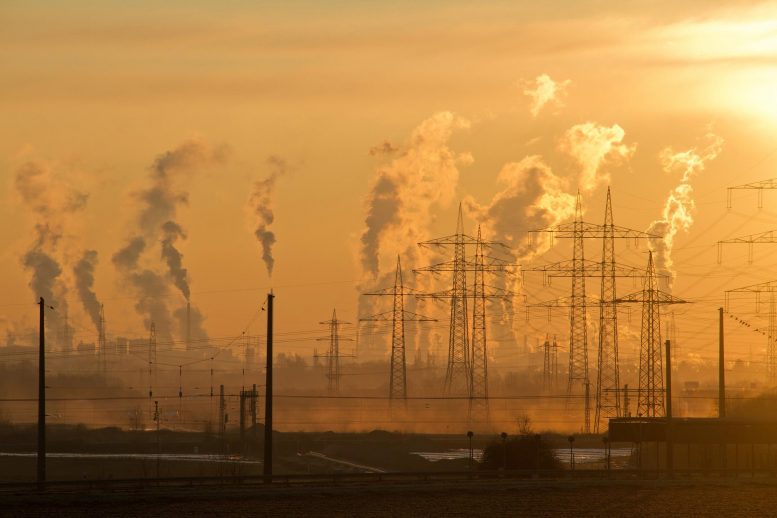

New research suggests that more than 50,000 premature deaths could be prevented each year by eliminating air pollution emissions from energy-related activities in the United States. This would also provide more than $600 billion in benefits each year from avoided illness and death.
Eliminating air pollution emissions from energy-related activities in the United States would prevent more than 50,000 premature deaths each year and provide more than $600 billion in benefits each year from avoided illness and death, according to a new analysis completed by University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers.
Published today (May 16, 2022) in the journal GeoHealth, the study reports the health benefits of removing dangerous fine particulates released into the air by electricity generation, transportation, industrial activities, and building functions like heating and cooking — also major sources of carbon dioxide emissions that cause climate change, since they predominantly rely on burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
“Our work provides a sense of the scale of the air quality health benefits that could accompany deep decarbonization of the U.S. energy system,” says Nick Mailloux, lead author of the study and a graduate student at the Center for Sustainability and the Global Environment in UW–Madison’s Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies. “Shifting to clean energy sources can provide enormous benefit for public health in the near term while mitigating climate change in the longer term.”
Working with scientists specializing in air quality and public health, Mailloux used a model from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to determine the health benefits of a complete reduction in emissions of fine particulate matter and of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. These compounds can form particulate matter once released into the atmosphere.
These pollutants contribute to health problems such as heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, and lower respiratory infections that can dramatically shorten lifespans. According to the researchers’ analysis, doing away with these pollutants would save about 53,200 lives each year in the US, providing about $608 billion in benefits from avoided healthcare costs and loss of life.
The researchers also studied the health effects if regions of the country were to act independently to reduce emissions instead of as part of a concerted nationwide effort. The effects can differ widely in different parts of the US, in part because of regional variations in energy use and population.
The Southwest, a region comprising Arizona, California, and Nevada, would retain 95 percent of the benefits if it moved alone to eliminate fine particle emissions.
“In the Mountain region, though, most of the benefit of emissions removal is felt somewhere else,” Mailloux says. “Just 32 percent of the benefit remains in states in the Mountain region. This is partly because there are large population centers downwind of the Mountain region that would also benefit.”
Every region of the country sees more benefit from nationwide action than from acting on their own to reduce emissions.
“The Great Plains, for example, gets more than twice as much benefit from nationwide efforts as it does from acting alone,” says Mailloux. “The more that states and regions can coordinate their emissions reductions efforts, the greater the benefit they can provide to us all.”
The researchers hope that by describing the near-term payoffs on top of the threats of more distant climate impacts, the new study motivates more action on climate change.
“Our analysis is timely, following last month’s report from the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change that called for urgent action to transform the world’s energy economy,” says Jonathan Patz, senior author of the study and a UW-Madison professor in the Nelson Institute and Department of Population Health Sciences. “My hope is that our research findings might spur decision-makers grappling with the necessary move away from fossil fuels, to shift their thinking from burdens to benefits.”
Reference: “Nationwide and Regional PM2.5-Related Air Quality Health Benefits From the Removal of Energy-Related Emissions in the United States” by Nicholas A. Mailloux, David W. Abel, Tracey Holloway and Jonathan A. Patz, 16 May 2022, GeoHealth.
DOI: 10.1029/2022GH000603








And a healthier population is probably more productive. Maybe that means greater gdp. Add that in to the $.
Fifty-three thousand ‘premature’ deaths is about 1.8% (2019) of all annual US deaths. That seems to me to be unrealistically high. “Chronic lower respiratory diseases” in total account for less than 6% of the total, or about 155,000 deaths. Those 53,000 ‘premature’ deaths then represent about 34% of the “Chronic lower respiratory diseases.” It is not easy to demonstrate that such illnesses are really the consequence of air pollution, let alone things like heart disease and stroke. Activities such as smoking tobacco, marijuana, and crack cocaine probably overwhelm the effects of air pollution. I think that some unjustifiable assumptions have been made regarding the long-term effects of air pollution.