
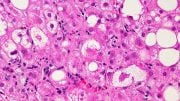
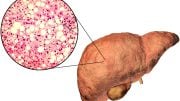
Fatty liver disease is a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver cells, leading to inflammation and scarring. This can impair liver function and potentially progress to more serious health problems.
A study conducted by the Roger Williams Institute of Hepatology, affiliated with King’s College London and the University of Lausanne, found a connection between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and brain dysfunction. The accumulation of fat in the liver reduces oxygen flow to the brain and causes inflammation, both of which have been linked to the development of severe brain diseases.
Around 25% of the general population and over 80% of severely obese individuals are affected by NAFLD. While prior studies have shown the harm that an unhealthy diet and obesity can inflict on brain function, this study is believed to be the first to clearly associate NAFLD with brain decline and identify a potential therapeutic target.
The research, conducted in collaboration with Inserm (the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research) and the University of Poitiers in France, involved feeding two different diets to mice. Half of the mice consumed a diet with no more than 10% fat in their calorie intake, while the other half’s calorie intake contained 55% fat; intended to resemble a diet of processed foods and sugary drinks.
After 16 weeks researchers conducted a series of tests to compare the effects of these diets on the body and more specifically, on the liver and the brain. They found that all mice consuming the higher levels of fat were considered obese, and developed NAFLD, insulin resistance, and brain dysfunction.
The study which was funded by the University of Lausanne and the Foundation for Liver Research also showed that the brain of mice with NAFLD suffered from lower oxygen levels. This is because the disease affects the number and thickness of the brain blood vessels, which deliver less oxygen to the tissue, but also due to specific cells consuming more oxygen while the brain is becoming inflamed. These mice were also more anxious and showed signs of depression.
By comparison, the mice consuming the healthy diet did not develop NAFLD or insulin resistance, they behaved normally, and their brain was completely healthy.
“It is very concerning to see the effect that fat accumulation in the liver can have on the brain, especially because it often starts off mild and can exist silently for many years without people knowing they have it,” said lead author Dr. Anna Hadjihambi, sub-team lead in the Liver-Brain Axis group at the Roger Williams Institute of Hepatology and honorary lecturer at King’s College London.
To try and combat the dangerous effect that NAFLD has on the brain, the scientists bred mice with lower levels of a whole-body protein known as Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) – a protein specialized in the transport of energy substrates used by various cells for their normal function.
When these mice were fed the same unhealthy fat- and sugar-rich diet as those in the initial experiment, they had no fat accumulation in the liver and exhibited no sign of brain dysfunction – they were protected from both ailments.
“Identifying MCT1 as a key element in the development of both NAFLD and its associated brain dysfunction opens interesting perspectives,” said Professor Luc Pellerin, director of the Inserm U1313 research unit at the University of Poitiers in France and senior researcher in the study. “It highlights potential mechanisms at play within the liver-brain axis and points to a possible therapeutic target.”
Dr. Hadjihambi added: “This research emphasizes that cutting down the amount of sugar and fat in our diets is not only important for tackling obesity, but also for protecting the liver to maintain brain health and minimize the risk of developing conditions like depression and dementia during aging, when our brain becomes even more fragile.
Reference: “Partial MCT1 invalidation protects against diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the associated brain dysfunction” by Anna Hadjihambi, Christos Konstantinou, Jan Klohs, Katia Monsorno, Adrien Le Guennec, Chris Donnelly, I. Jane Cox, Anjali Kusumbe, Patrick S. Hosford, Ugo Soffientini, Salvatore Lecca, Manuel Mameli, Rajiv Jalan, Rosa Chiara Paolicelli and Luc Pellerin, 19 August 2022, Journal of Hepatology.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.008




Be the first to comment on "Fatty Liver Disease: A Hidden Danger to Your Brain?"