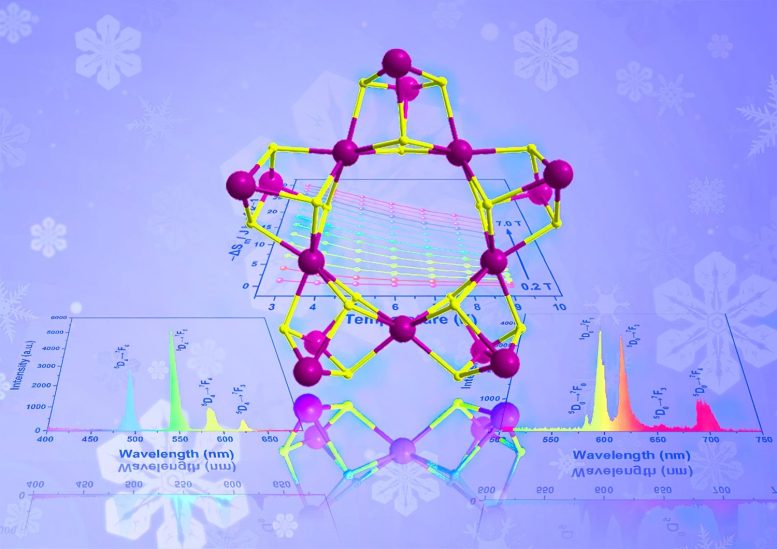
A multi-institute research team synthesized a family of nano-wheel-like metallic clusters, each with specific properties — such as fluorescence and different types of magnetism — that could advance next-generation technologies. Credit: Polyoxometalates, Tsinghua University Press
Researchers in China have developed nano-wheels, a new family of metallic compounds with unique properties for use in advanced sensors and other technologies. The team synthesized lanthanide-based nano-clusters with diverse applications, including fluorescence and magnetic cooling.
While the wheel does not need to be reinvented, there are benefits to the development of new nano-wheels, according to a multi-institute research team based in China. The group fabricated a novel family of metallic compounds, each of which exhibits unique properties desirable for next-generation technologies, such as advanced sensors.
Their findings were published recently in Polyoxometalates, a peer-reviewed, international, and interdisciplinary research journal that focuses on all aspects of polyoxometalates.
“Polymetallic complexes are of great interest not only for their appealing molecular structure but also for their versatile applications in various fields,” said co-corresponding author Yan-Zhen Zheng, professor in the Frontier Institute of Science and Technology (FIST) at Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Polymetallic complexes, which comprise multiple atoms of various metals or a combination of metals and other elements, have the potential to imbue materials with specific properties if the molecules can be synthesized, Zheng said. Such properties include the ability to fluoresce, or glow, and magnetic quirks that allow drastic temperature changes and control.
Zheng and his team focused on creating polymetallic complexes made with lanthanide elements, a group of 15 metallic materials also known as rare earth elements. They specifically used europium, terbium, and gadolinium.
“Among all polymetallic complexes, lanthanide-based compounds have drawn unprecedented attention due to their interesting magnetic and luminescence behaviors,” Zheng said. “Several such compounds have been successfully isolated, but direct synthesis has been a challenge.”
The components of the complexes require are geometrically diverse, requiring significant coordination, according to Zheng.
“Previous findings revealed that controlling the hydrolysis — breaking down a compound with water — of lanthanide metal ions in the presence of appropriate organic ligands would be a powerful strategy to obtain desired species,” Zheng said. A ligand is a molecule that bonds to a metal atom. Its addition to the complex can stabilize the structure.
The researchers used hydrolysis to break down lanthanides in a bath containing a ligand called tricine. Tricine contains multiple arms of oxygen and hydrogen, meaning it can accommodate a large range of metals and help stabilize the resulting clusters.
“Through the simple hydrolysis reaction, we synthesized three lanthanide nano-clusters, and used X-ray diffraction analyses to reveal their stable, wheel-like structure,” Zheng said. “Owing to the presence of different lanthanide metal ions in these analogs, each compound shows distinctive properties.”
The europium-based cluster fluoresced red emissions, while the terbium-based cluster fluoresced green emissions. The gadolinium-based cluster exhibited potential applications in magnetic cooling. According to Zheng, the research group is continuing to investigate the synthesis and application of these clusters.
Reference: “Tricine-supported polyoxo(alkoxo)lanthanide cluster {Ln15} (Ln = Eu, Gd, Tb) with magnetic refrigerant and fluorescent properties” by Peng-Fei Sun, Xiao-Nan Zhang, Cai-Hong Fan, Wei-Peng Chen and Yan-Zhen Zheng, 12 March 2023, Polyoxometalates.
DOI: 10.26599/POM.2023.9140026
Other contributors include Peng-Fei Sun, Xiao-Nan Zhang, Cai-Hong Fan and co-corresponding author Wei-Peng Chen, all with FIST, the State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Behavior for Materials, the MOE Key Laboratory for Nonequilibrium Synthesis of Condensed Matter, the Xi’an Key Laboratory of Sustainable Energy and Materials Chemistry and the School of Chemistry at Xi’an Jiaotong University
The National Science Foundation of China, the Special Support Plan of Shaanxi Province for Young Top-Notch Talent, the Instrument Analysis Center of Xi’an Jiaotong University and the Fundamental Research Fund for Central Universities supported this work.





Be the first to comment on "Nano-Wheels: Metallic Clusters With Unique Properties for Advanced Technology"