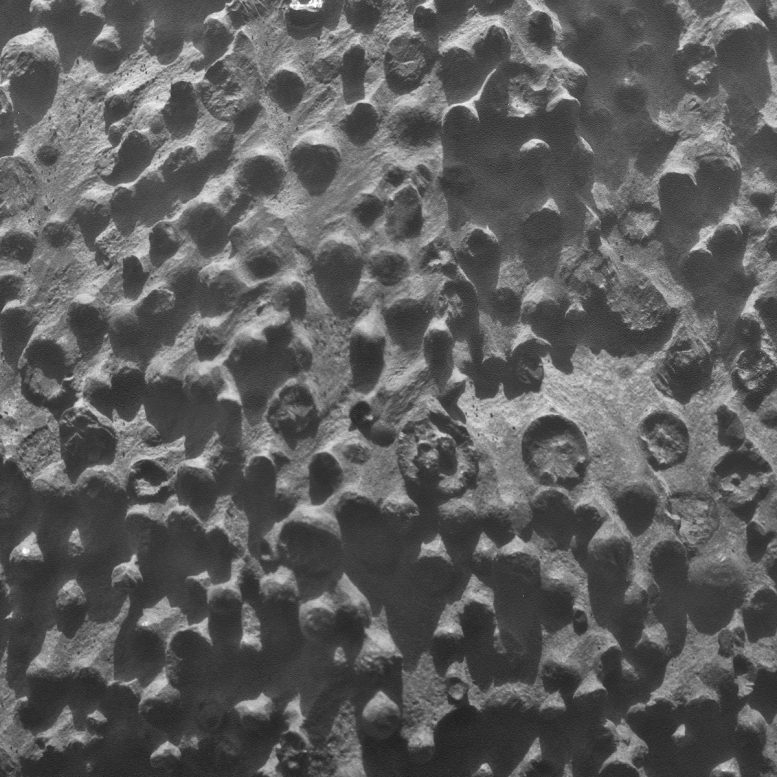

Small spherical objects fill the field in this mosaic combining four images from the Microscopic Imager on NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. The view covers an area about 2.4 inches (6 centimeters) across, at an outcrop called “Kirkwood” in the Cape York segment of the western rim of Endeavour Crater. The individual spherules are up to about one-eighth inch (3 millimeters) in diameter. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell Univ./ USGS/Modesto Junior College
NASA’s Opportunity rover discovered puzzling spherical objects on Mars at a rock outcrop called Kirkwood. The spherules vary in composition, concentration, distribution, and structure from the spherules that were discovered eight-and-a-half years earlier and nicknamed “blueberries.”
NASA’s long-lived rover Opportunity has returned an image of the Martian surface that is puzzling researchers.
Spherical objects concentrated at an outcrop Opportunity reached last week differ in several ways from iron-rich spherules nicknamed “blueberries” the rover found at its landing site in early 2004 and at many other locations to date.
Opportunity is investigating an outcrop called Kirkwood in the Cape York segment of the western rim of Endeavour Crater. The spheres measure as much as one-eighth of an inch (3 millimeters) in diameter. The analysis is still preliminary, but it indicates that these spheres do not have the high iron content of Martian blueberries.
“This is one of the most extraordinary pictures from the whole mission,” said Opportunity’s principal investigator, Steve Squyres of Cornell University in Ithaca, N.Y. “Kirkwood is chock full of a dense accumulation of these small spherical objects. Of course, we immediately thought of the blueberries, but this is something different. We never have seen such a dense accumulation of spherules in a rock outcrop on Mars.”
The Martian blueberries found elsewhere by Opportunity are concretions formed by action of mineral-laden water inside rocks, evidence of a wet environment on early Mars. Concretions result when minerals precipitate out of water to become hard masses inside sedimentary rocks. Many of the Kirkwood spheres are broken and eroded by the wind. Where wind has partially etched them away, a concentric structure is evident.
Opportunity used the microscopic imager on its arm to look closely at Kirkwood. Researchers checked the spheres’ composition by using an instrument called the Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer on Opportunity’s arm.
“They seem to be crunchy on the outside, and softer in the middle,” Squyres said. “They are different in concentration. They are different in structure. They are different in composition. They are different in distribution. So, we have a wonderful geological puzzle in front of us. We have multiple working hypotheses, and we have no favorite hypothesis at this time. It’s going to take a while to work this out, so the thing to do now is keep an open mind and let the rocks do the talking.”
Just past Kirkwood lies another science target area for Opportunity. The location is an extensive pale-toned outcrop in an area of Cape York where observations from orbit have detected signs of clay minerals. That may be the rover’s next study site after Kirkwood. Four years ago, Opportunity departed Victoria Crater, which it had investigated for two years, to reach different types of geological evidence at the rim of the much larger Endeavour Crater.
The rover’s energy levels are favorable for the investigations. Spring equinox comes this month to Mars’ southern hemisphere, so the amount of sunshine for solar power will continue increasing for months.
“The rover is in very good health considering its 8-1/2 years of hard work on the surface of Mars,” said Mars Exploration Rover Project Manager John Callas of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “Energy production levels are comparable to what they were a full Martian year ago, and we are looking forward to productive spring and summer seasons of exploration.”
NASA launched the Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity in the summer of 2003, and both completed their three-month prime missions in April 2004. They continued their bonus, extended missions for years. Spirit finished communicating with Earth in March 2010. The rovers have made important discoveries about wet environments on ancient Mars that may have been favorable for supporting microbial life.
JPL manages the Mars Exploration Rover Project for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.







Gas bubbles maybe similar to some types of geological formations on Earth?
Mars has an even more older history than earth in cosmos. If sheets of ice on earth during great ice-ages can form rocks fossilised over eons, why can`t such things happen in Mars also? May be that they could be snow balls of ice or even carbon ice fossilised into spherules today found in Martian terrain. That is why they seem to soft and undergoing granulations. Thank You.
what about ‘Manganese Nodules’