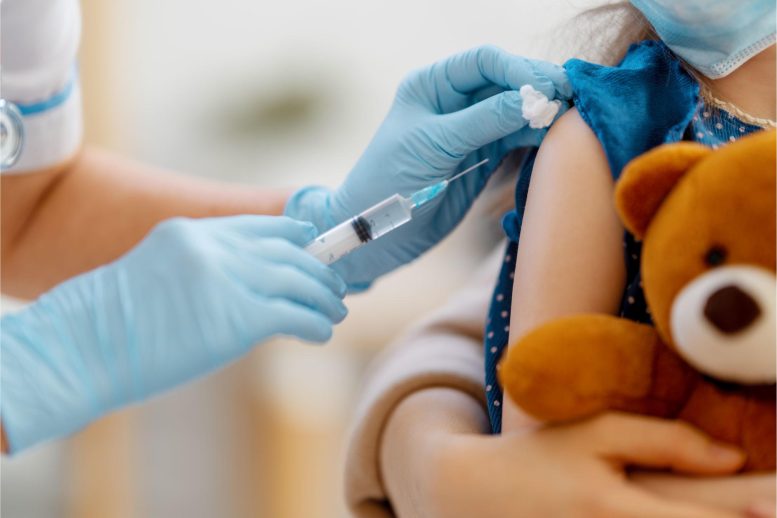
According to the research, babies born via natural childbirth were found to have higher antibody levels after receiving vaccinations against bacteria that cause lung infections and meningitis, compared to those born via Caesarian section.
A new study suggests that the way a baby is delivered may impact their immune system’s response to two key childhood vaccines.
Babies who are born vaginally were found to have higher antibody levels after receiving vaccines for lung infections and meningitis compared to those born via Caesarian section. These findings may influence discussions about C-sections between expectant mothers and healthcare providers, and may also inform the development of more personalized vaccination plans.
Researchers studied the relationship between gut microbes and antibody levels after vaccination in a cohort of 120 babies, who were vaccinated at 8 and 12 weeks against lung infections and meningitis. The researchers tracked the development of the gut microbiome – the community of microbes that lives in our body – in the child’s first year of life and their immune response to the vaccines by testing saliva samples at 12 and 18 months.
The research was carried out by a team from the University of Edinburgh, Spaarne Hospital and University Medical Centre in Utrecht, and the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment in The Netherlands.
In the 101 babies tested for antibodies as a result of the vaccine that protects against lung infections, the investigators found double the antibody levels in babies delivered naturally compared with those delivered by C-section. Breastfeeding was linked with 3.5 times higher antibody levels compared with formula-fed children who had been delivered naturally.
Levels of antibodies as a result of the vaccine that protects against meningitis were tested in 66 babies. Experts found the levels of antibodies were 1.7 times higher for naturally delivered babies, regardless of breastfeeding, compared with those delivered via C-section. The gut microbiome is seeded at birth, developing rapidly over the first few months of life, and is influenced mostly by delivery mode, breastfeeding, and antibiotic use.
The team found a clear relationship between microbes in the gut of those babies and levels of antibodies. For example, among a host of bacteria in the gut, high levels of two in particular – Bifidobacterium and E. Coli – were associated with a high antibody response to the vaccine that protects against lung infections.
High levels of E. Coli were also linked with a high antibody response to the vaccine that protects against meningitis. The baby acquires the Bifidobacterium and E.coli bacteria through natural birth and human milk is needed to provide the sugars for these bacteria to thrive on.
The team concludes that the babies’ microbiome in early life contributes to the immune system’s response to the vaccines and sets the level of protection against certain infections in childhood. Vaccination schedules could also be adjusted based on the mode of delivery or an analysis of the baby’s microbiome in the future, experts say.
Dr. Emma de Koff, the first author and microbiology trainee at the Amsterdam University Medical Center, said: “We expected to find a link between the gut microbiome and the babies’ vaccine responses, however, we never thought to find the strongest effects in the first weeks of life.”
Professor Debby Bogaert, the study lead and Chair of Paediatric Medicine at the University of Edinburgh said “I think it is especially interesting that we identified several beneficial microbes to be the link between mode of delivery and vaccine responses. In the future, we may be able to supplement those bacteria to children born by C-section shortly after birth through, for example, mother-to-baby ‘fecal transplants’ or the use of specifically designed probiotics.”
Reference: “Mode of delivery modulates the intestinal microbiota and impacts the response to vaccination” by Emma M. de Koff, Debbie van Baarle, Marlies A. van Houten, Marta Reyman, Guy A. M. Berbers, Femke van den Ham, Mei Ling J. N. Chu, Elisabeth A. M. Sanders, Debby Bogaert and Susana Fuentes, 15 November 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34155-2
The study was funded by Scotland’s Chief Scientist Office and the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research.





Be the first to comment on "New Research: How Your Baby Was Delivered May Impact How They Respond to Key Childhood Vaccines"