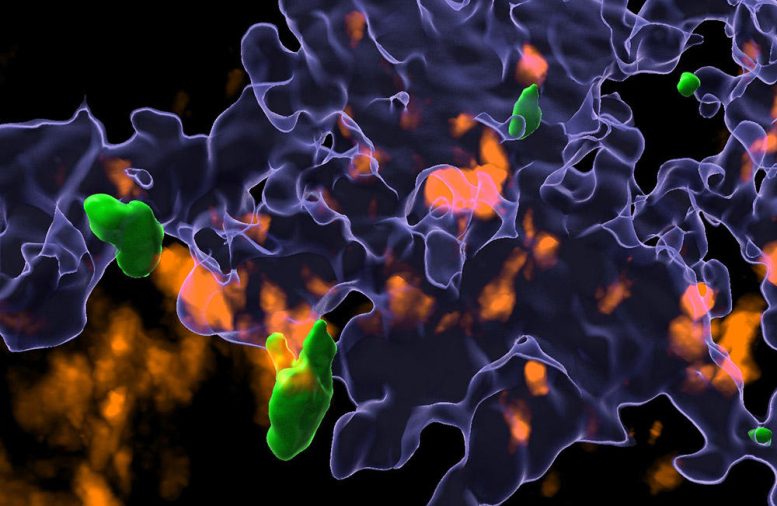
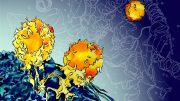
Microscopic image of helper T cells (green) and phagocytes (orange) fighting cancer cells (shown as blue outlines). The work, now published in Nature, shows that the contact between helper T cells and phagocytes is critically important for full activation of cancer immune defense. As a result of this activation, inflammatory mediators are released that act remotely to drive cancer cell death. Credit: Otto von Guericke University of Magdeburg
A cross-disciplinary group of scientists at the Otto-von-Guericke University in Magdeburg has unveiled a new understanding of how inflammatory mediators of pathogen defense can remotely drive cancer cells into death – an important contribution to improving cancer immunotherapies.
Modern immunotherapies enhance the body’s natural ability to combat cancer by activating the immune system’s killer T cells that can specifically target and eliminate cancer cells. However, in numerous patients, cancer cells evolve and become undetectable by these T cells, making the treatment no longer effective.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Magdeburg has now discovered a new mechanism that enables the immune system to also eliminate such invisible cancer cells. These findings open up new possibilities for the development of improved cancer immunotherapies. The results have now been published in the renowned journal Nature.
“In our work, we have been looking for strategies to target such cancer cells that are “invisible” to killer T cells. In doing so, we came across the special abilities of the so-called helper T cells,” says Prof. Dr. Thomas Tüting, Professor of Dermatology at the University Hospital Magdeburg and leader of the study team.
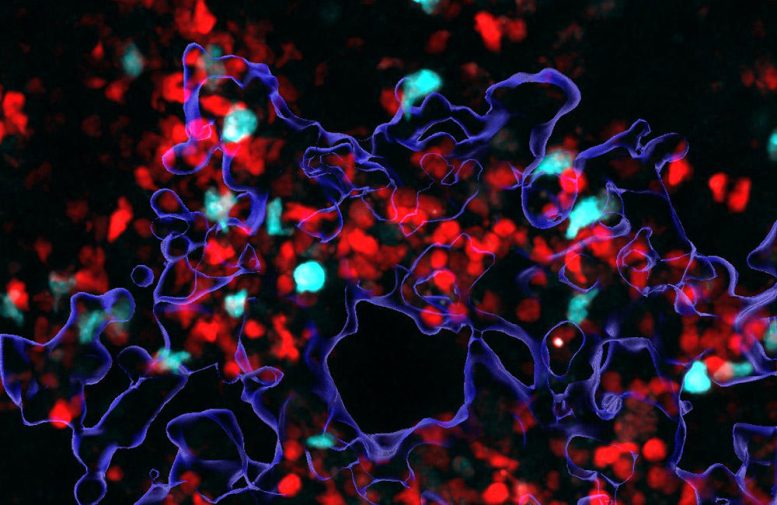
Microscopic image of helper T cells (turquoise) and killer T cells (red) fighting cancer cells (shown as blue outlines). Killer T cells must migrate into cancer tissue in large numbers for effective cancer immune defense. The work now published in Nature shows that, in contrast, helper T cells remain at the edge of cancer tissues where they orchestrate cancer cell death from a distance. This requires far fewer helper T cells than killer T cells. Both images were generated using intravital 2-photon microscopy, which allows the observation of immune cell behavior in living tissue. Credit: Otto von Guericke University of Magdeburg
Very few helper T cells are more effective than many killer T cells
Using an experimental cancer model, the researchers observed that a small number of helper T cells can eradicate advanced cancers as effectively as a much larger number of killer T cells. The helper T cells were also able to eliminate cancer cells that had become invisible to killer T cells.

The photo shows the authors at microscope. Front left: Bastian Kruse; front right: Dr. Anthony Buzzai; Back left: Prof. Dr. Andreas Müller; back right: Prof. Dr. Thomas Tüting. Credit: Sarah Kossmann/University Medical Center and Medical Faculty of the Otto-von-Guericke-University Magdeburg
Using cutting-edge microscopy techniques to study immune cells in living cancer tissue revealed that helper T cells behave fundamentally differently from killer T cells: “Killer T cells penetrate into cancer tissues and interact directly with cancer cells, while helper T cells are mainly found at the edge of cancer tissues, where they exchange signals with other immune cells,” says Prof. Dr. Andreas Müller from the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Immunology at the University of Magdeburg.
Helper T cells engage scavenger cells and remotely drive cancer cell death through inflammatory mediators of pathogen defense
Further investigations revealed that helper T cells secrete chemical mediators that attract scavenger cells of the immune system and induce them to support the destruction of cancer cells on their behalf. Together, these two cell types can effectively fight bacterial and viral infections. Their cooperation can also be exploited to mobilize the full arsenal of immune defense against cancer cells.
In search for the underlying mechanisms of action, the researchers found that the interaction between helper T cells and scavenger cells enhances their ability to release inflammatory mediators which act remotely to drive cancer cell death, as if they were infected by a pathogen. Exactly how this happens is still not completely understood, and the significance of this mechanism for cancer immunotherapies will have to be elucidated.
Prospects for new ways to improve cancer immunotherapy
The research results reveal a mechanism for how the ability of the immune system to defend against the spread of pathogens in the body can be utilized to destroy cancer cells. Based on these findings, the researchers in Magdeburg are developing new strategies for cancer immunotherapy that are also effective in patients with cancers that have become invisible to killer T cells.
Reference: “CD4+ T cell-induced inflammatory cell death controls immune-evasive tumours” by Bastian Kruse, Anthony C. Buzzai, Naveen Shridhar, Andreas D. Braun, Susan Gellert, Kristin Knauth, Joanna Pozniak, Johannes Peters, Paulina Dittmann, Miriam Mengoni, Tetje Cornelia van der Sluis, Simon Höhn, Asier Antoranz, Anna Krone, Yan Fu, Di Yu, Magnus Essand, Robert Geffers, Dimitrios Mougiakakos, Sascha Kahlfuß, Hamid Kashkar, Evelyn Gaffal, Francesca M. Bosisio, Oliver Bechter, Florian Rambow, Jean-Christophe Marine, Wolfgang Kastenmüller, Andreas J. Müller and Thomas Tüting, 14 June 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06199-x
In their research project, the Magdeburg scientists cooperated with partners at the Universities of Würzburg, Cologne, Duisburg-Essen, Leuven (Belgium), Uppsala (Sweden) and at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research in Braunschweig. The work was supported mostly by the German Research Foundation, the European Research Council, the German Cancer Aid and the Else Kröner-Fresenius Foundation.



Be the first to comment on "Researchers Discover a New Mechanism of Cancer Immune Defense"