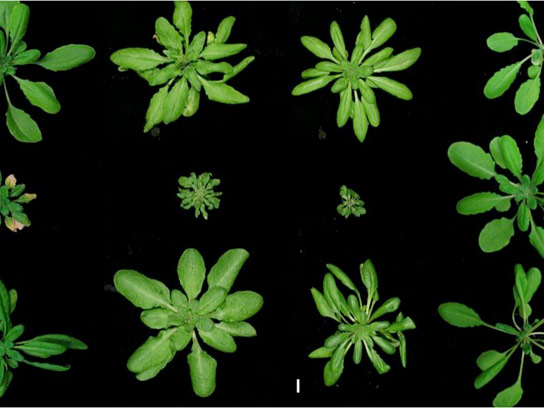

Top and Bottom row: wild Arabidopsis strains originating from different places around the world. Middle row: Hybrids of the above and below parents. Credit: MPI f. Developmental Biolog
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology have now pinpointed the most common culprits for autoimmunity in plants.
Plants are under permanent attack by a multitude of pathogens. To win the battle against fungi, bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, they have developed a complex and effective immune system. And just as in humans, this can also overshoot its target when some of the plant’s own proteins are mistakenly identified as foreign. Such autoimmune reactions can lead to tissue defects and growth arrest, and is particularly apparent in hybrids, where two divergent immune systems meet. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Tübingen, Germany, have now pinpointed the most common culprits for autoimmunity. Surprisingly, these are components of the immune system itself, which are mistakenly recognized by other immune receptors as intruders.
Similar to the situation in animals, immunity in plants relies on highly variable immune receptors. “Not only do plants often have hundreds of so-called NLR immune genes, but each individual in a population tends to have its own collection of NLR genes, and is thus resistant against a unique spectrum of microbes, insects and worms,” explains Detlef Weigel, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology. With this arsenal at hand, a plant can successfully defy a multitude of pathogens. Because each individual in a field has a different recognition spectrum, it is difficult for pathogens to wipe out the entire population. This great diversity can, however, also lead to accidents, such that a plant no longer reliably distinguishes between self and non-self and fights its own proteins. The misfortune occurs particularly often when two different immune systems are combined in the offspring of crosses.
To investigate the genetic basis of autoimmunity after crosses, the Max Planck scientists generated over 6400 crosses between natural strains of Arabidopsis thaliana. The parental lines were from different locations around the world and covered almost the entire genetic bandwidth of the species. The progeny of the crosses were then examined for evidence of autoimmunity. Roughly every 50th cross led to typical autoimmune symptoms; in the most extreme cases, the progeny died already as seedlings and no longer reproduced. Because this occurred in the absence of pathogens, it must have been plant proteins that were mistakenly detected as foreign by the immune system of these hybrid plants. “Remarkably, the responsible proteins originated from only very few of the highly variable immune genes, even though Arabidopsis has more than a hundred of them”, says Eunyoung Chae, the lead author of the study.
Growth and defense in balance
According to Weigel, it was a surprise that certain combinations of immune genes are so often lethal. The causal variants presumably are advantageous on their own, normally providing resistance to pathogens without hurting the plant, but the wrong combinations can be detrimental. Still, the individual advantages must be sufficiently great, so that such variants can occur even in the same field.
The researchers suggest that the observed cases of autoimmunity in hybrids represent only the tip of the iceberg. “Because we applied strict criteria for classifying crosses as being associated with autoimmunity, it is likely that there are many other crosses where there is no apparent tissue damage, but still a growth penalty,” explains Chae. By systematically analyzing which immune receptors are particularly dangerous and which combinations are best avoided, the Max Planck researchers hope to derive rules that will be useful in optimizing the trade-off between growth and defense, not only in wild plants such as Arabidopsis, but also in crops. Given the ever-increasing needs of a growing world population, streamlined ways to improve food crops are of great importance.
Reference: “Species-wide Genetic Incompatibility Analysis Identifies Immune Genes as Hot Spots of Deleterious Epistasis” by Eunyoung Chae, Kirsten Bomblies, Sang-Tae Kim, Darya Karelina, Maricris Zaidem, Stephan Ossowski, Carmen Martín-Pizarro, Roosa A.E. Laitinen, Beth A. Rowan, Hezi Tenenboim, Sarah Lechner, Monika Demar, Anette Habring-Müller, Christa Lanz, Gunnar Rätsch and Detlef Weigel, 20 November 2014, Cell.
DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.049






Immunity in plants is synonymous to adaptation to surroundings. A plant is economising its environment resources to adapt its survival.Some dessidious plants drop their leaves to conserve waater and in deserts plants do develop thorns to help them save the hot weather as well as small resources of leaves left over for their transpiration. It is nothing but an act of survival which is logical for all the living beings in nature. Short shrubs save themselves with bitter tasting leaves so that they may not be grazed. Here the immunity works for the taste. Some creepers become saprophytes and parasites for their survival clinging on to the other plants. Medicinal plants of the mountains develop their properties only to save themselves, which incidentally helps teh mankind also to some extent to prevent some diseases. Immunity is an inborn set up for all living beings for survival. Man’s immunity is however is very poor because we came very late into this world and we have to meet many challenges as we experience more and more in this world.Thank You.