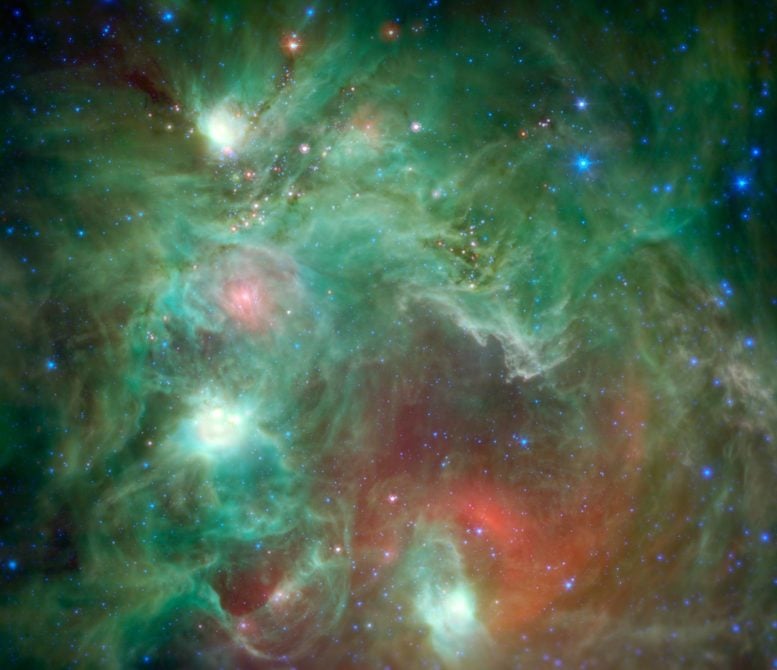

The infrared image captured by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope of the star-forming region NGC 2174, located in the constellation Orion about 6,400 light-years away, reveals numerous young stars enshrouded in dust. Nicknamed the “Monkey Head” Nebula, this area appears differently in infrared images compared to visible light, showcasing star formation through glowing warm dust and distinct colors representing various elements and dust temperatures. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope provides an infrared glimpse into the NGC 2174 or “Monkey Head” Nebula, uncovering young stars forming amidst dust columns in the Orion constellation.
Scores of baby stars shrouded by dust are revealed in this infrared image of the star-forming region NGC 2174, as seen by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope. Some of the clouds in the region resemble the face of a monkey in visible-light images, hence the nebula’s nickname: the “Monkey Head.” However, in infrared images such as this, the monkey disappears. That’s because different clouds are highlighted in infrared and visible-light images.
Found in the northern reaches of the constellation Orion, NGC 2174 is located around 6,400 light-years away. Columns of dust, slightly to the right of center in the image, are being carved out of the dust by radiation and stellar winds from the hottest young stars recently born in the area.
Spitzer’s infrared view provides us with a preview of the next clusters of stars that will be born in the coming millennia. The reddish spots of light scattered through the darker filaments are infant stars swaddled by blankets of warm dust. The warm dust glows brightly at infrared wavelengths. Eventually, these stars will pop out of their dusty envelopes and their light will carve away at the dust clouds surrounding them.
In this image first published in 2015, infrared wavelengths have been assigned visible colors we see with our eyes. Light with a wavelength of 3.5 microns is shown in blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns in red. The greens show the organic molecules in the dust clouds, illuminated by starlight. Reds are caused by the thermal radiation emitted from the very hottest areas of dust.
Areas around the edges that were not observed by Spitzer have been filled in using infrared observations from NASA’s Wide Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE.







Be the first to comment on "Scores of Baby Stars Revealed in the Orion Constellation"