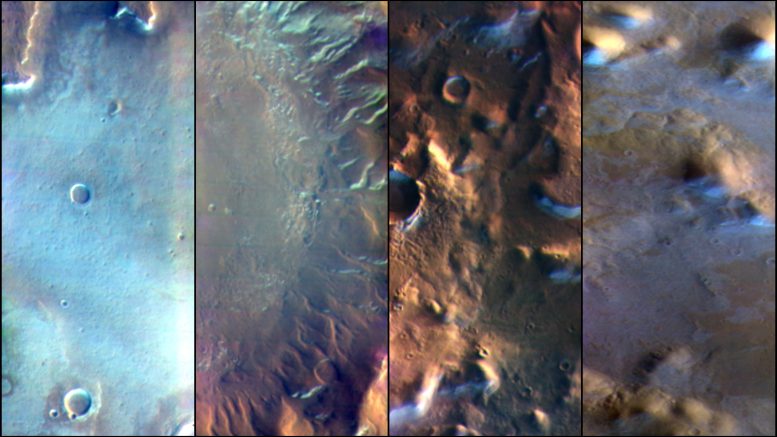

Martian surface frost, made up largely of carbon dioxide, appears bluish-white in these images from the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera aboard NASA’s 2001 Odyssey orbiter. THEMIS takes images in both visible light, perceptible to the human eye, and heat-sensitive infrared. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU
A new research study using data from NASA’s Mars Odyssey orbiter may explain why Martian frost can be invisible to the naked eye and why dust avalanches appear on some slopes.
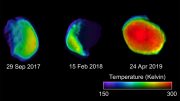
Last year, scientists were perplexed after analyzing photographs of the Martian landscape obtained at dawn by NASA’s Mars Odyssey orbiter. They could see ghostly, blue-white morning frost illuminated by the rising Sun when they peered at the surface with visible light — the sort that the human eye senses. However, when the orbiter’s heat-sensitive camera was used, the ice appeared more extensively, including in locations where none was previously observed.
The scientists knew they were looking at frost that forms overnight and is largely formed of carbon dioxide – essentially, dry ice, which often appears as frost on the Red Planet rather than as water ice. But why was this dry ice frost visible in some locations and not others?
In a paper published recently in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, these scientists proposed a surprising answer that may also explain how dust avalanches, which are reshaping the planet, are triggered after sunrise.
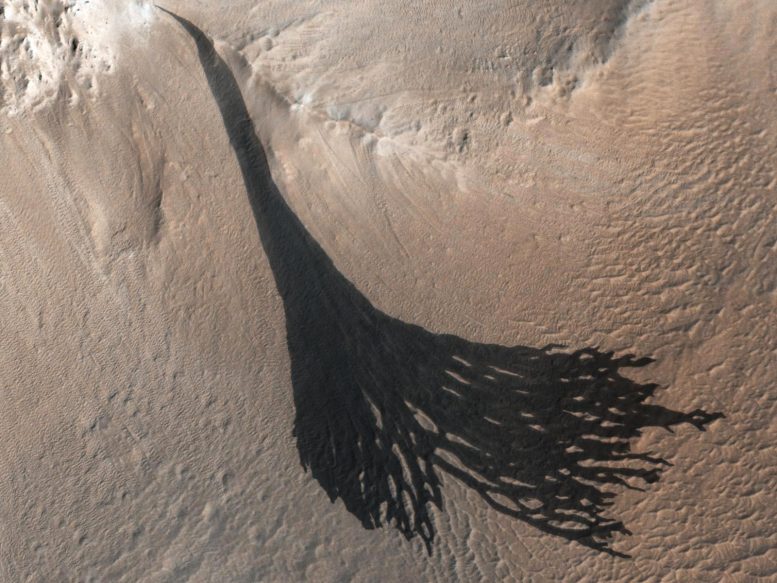

These dark streaks, also known as “slope streaks,” resulted from dust avalanches on Mars. The HiRISE camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured them on December 26, 2017. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona
From Frost to Vapor
Launched in 2001, Odyssey is NASA’s longest-lived Mars mission and carries the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), an infrared, or temperature-sensitive, camera that provides a one-of-a-kind view of the Martian surface. Odyssey’s current orbit provides a unique look at the planet at 7 a.m. local Mars time.
“Odyssey’s morning orbit produces spectacular pictures,” said Sylvain Piqueux of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, who led the paper. “We can see the long shadows of sunrise as they stretch across the surface.”
Because Mars has so little atmosphere (just 1% the density of Earth’s), the Sun quickly warms frost that builds up overnight. Instead of melting, dry ice vaporizes into the atmosphere within minutes.
Lucas Lange, a JPL intern working with Piqueux, first noticed the cold-temperature signature of frost in many places where it couldn’t be seen on the surface. These temperatures were appearing just tens of microns underground – less than the width of a human hair “below” the surface.
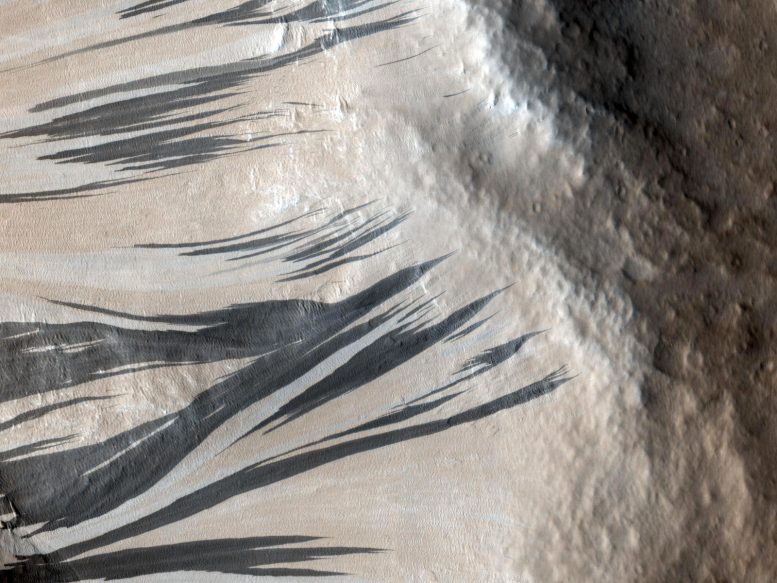

These dark streaks, also known as “slope streaks,” resulted from dust avalanches in an area of Mars called Acheron Fossae. The HiRISE camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured them on December 3, 2006. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona
“Our first thought was ice could be buried there,” Lange said. “Dry ice is plentiful near Mars’ poles, but we were looking closer to the equator of the planet, where it’s generally too warm for dry ice frost to form.”
In their paper, the authors propose they were seeing “dirty frost” – dry ice frost mixed with fine grains of dust that obscured it in visible light but not in infrared images.
Thawing Frost and Avalanches
The phenomenon led the scientists to suspect dirty frost might also explain some of the dark streaks that can stretch 3,300 feet (1,000 meters) or more down Martian slopes. They knew the streaks resulted from, essentially, dust avalanches that slowly reshape mountainsides across the planet. Scientists think these dust avalanches probably look something like a ground-hugging river of dust releasing a trail of fluffy material behind. As the dust travels downhill over several hours, it exposes streaks of darker material underneath.
These dark streaks are not the same as a better-documented variety called recurring slope lineae, which recur in the same places, season after season, for weeks (instead of hours) at a time. Once thought to result from briny water slowly seeping from mountainsides, recurring slope lineae are now generally believed to result from flows of dry sand or dust.
Mapping the slopes streaks for their recent study, the authors found they tend to appear in places with morning frost. The researchers propose the streaks resulted from the vaporizing frost creating just enough pressure to loosen the dust grains, causing an avalanche.
The hypotheses are further evidence of just how surprising the Red Planet can be.
“Every time we send a mission to Mars, we discover exotic new processes,” said Chris Edwards, a paper co-author at Northern Arizona University in Flagstaff. “We don’t have anything exactly like a slope streak on Earth. You have to think beyond your experiences on Earth to understand Mars.”
Reference: “Gardening of the Martian Regolith by Diurnal CO2 Frost and the Formation of Slope Streaks” by L. Lange, S. Piqueux, C. S. Edwards, 27 March 2022, Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
DOI: 10.1029/2021JE006988
More About the Mission
JPL manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) was developed by Arizona State University. The THEMIS investigation is led by Dr. Philip Christensen at ASU. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver is the prime contractor for the Odyssey project and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena.






If Mars is anything like Earth then there could be microbes living down deep that are exuding some sort of oily substance, perhaps even hydrocarbon oil that is bursting out of strata that is like water springs here on Earth. This might explain why these flows are slow traveling and quickly get covered in dust that hides them again, being quite sticky and viscous. This process might also be the source of methane being detected during the summer months.