The NLRP3 inflammasome, vital to the human immune system, is also linked to various diseases. Its core component, the ASC protein, forms a dense structure that was previously difficult to analyze. A recent study by an international team, using innovative fluorescence microscopy techniques, has successfully visualized the 3D structure of the ASC speck, resolving long-standing controversies and marking a significant advancement in the understanding of inflammasome biology. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
A new study has unveiled the detailed structure of the NLRP3 inflammasome, crucial for immune response and disease research, using innovative imaging techniques.
A central component of the human immune system, the NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in fighting off infections. However, its chronic activation is also implicated in a variety of common diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, atherosclerosis, gout, and type II diabetes. The NLRP3 inflammasome occurs primarily in specialized immune cells in the blood and elsewhere. It is a dense complex in which several proteins interact with each other.
A key protein in this complex is known by the abbreviation ASC. In non-activated immune cells, it is distributed homogeneously throughout the cell. If the NLRP3 inflammasome is activated, all of the ASC protein present in the cell aggregates in the inflammasome complex. Under an ordinary fluorescence microscope, the ASC protein, once labeled, appears as a single, bright, nearly round spot. Due to the small size and high density of this ASC speck, scientists have been unable to elucidate details of its structure inside cells. Different models were proposed in the scientific literature but a comprehensive understanding was missing.
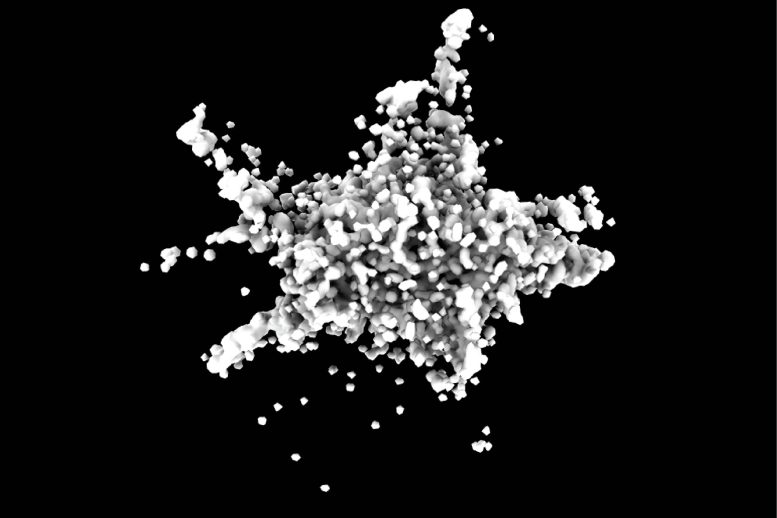

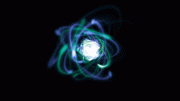
Endogenous ASC speck imaged in 3D by dSTORM. The ASC speck is a central component of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Credit: © Science
An international team of researchers, including the research groups of LMU professors Don Lamb, Ralf Jungmann, and Veit Hornung, has now visualized the 3D structure of the ASC speck inside cells using various fluorescence microscopy methods. Recently published in the journal iScience, their study shows that the ASC speck has an amorphous structure with a dense core from which filaments reach out into the periphery. To be able to fully label and image the structure, the researchers had to combine two different approaches. They labeled the less dense periphery of the ASC speck with antibodies and the dense interior with nanobodies.
“This is a paramount example of modern, interdisciplinary research, which has yielded important insights for several fields.”
— Don C. Lamb
“When we used just one of the labeling methods, it led to artifacts and thus to data that would be falsely interpreted,” says Professor Christian Sieben from the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research in Braunschweig. “By combining the two approaches, we could overcome this limitation” adds Lamb. This is an important insight for the imaging of dense structures with high-resolution fluorescence microscopy in general. An elegant analysis of the microscopy images of a large number of ASC specks also indicates that as the ASC protein accumulates within the speck, the speck scarcely grows at all, but primarily becomes denser.
“Our results solve the existing controversies in relation to the structure of the ASC speck and are an important step on the road to the complete visualization of the inflammasome in cells,” says Dr. Ivo Glück, first author of the new study. “These results could only have been achieved by an international collaboration of leading researchers in the fields of fluorescence microscopy and inflammasome biology. It is a paramount example of modern, interdisciplinary research, which has yielded important insights for several fields,” adds Lamb.
Reference: “Nanoscale organization of the endogenous ASC speck” by Ivo M. Glück, Grusha Primal Mathias, Sebastian Strauss, Virgile Rat, Irene Gialdini, Thomas Sebastian Ebert, Che Stafford, Ganesh Agam, Suliana Manley, Veit Hornung, Ralf Jungmann, Christian Sieben and Don C. Lamb, 3 November 2023, iScience.
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108382







Be the first to comment on "Unlocking the Secrets of the Human Immune System: A Pivotal Discovery"