The development of NeuM, a novel neuron labeling technology, represents a major step forward in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases. By enabling selective labeling and high-resolution imaging of neuronal membranes, NeuM facilitates the detailed study of neuron structures and their changes over time. This technology promises to be a vital asset in understanding and developing treatments for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, offering hope for advancements in neurodegenerative disease research and therapy. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Scientists have developed ‘NeuM’, a neuron labeling technology enabling detailed observation of neuronal structure. Successful monitoring of neuronal changes for up to 72 hours.
Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke stand as the leading trio of neurodegenerative conditions. These disorders are marked by the dysfunction and gradual deterioration of neurons, the nerve cells. To grasp the underlying mechanisms of these neurological conditions and to forge treatments, it is essential to have labeling technologies that enable the visualization of neuronal changes under both healthy and diseased conditions.
A research team led by Dr. Kim Yun Kyung from the Brain Science Institute at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Professor Chang Young-Tae’s team from Pohang University of Science and Technology, has announced the development of a next-generation neuron labeling technology called NeuM. NeuM (Neuronal Membrane-selective) selectively labels neuronal membranes, visualizing neuronal structures and allowing real-time monitoring of neuronal changes.
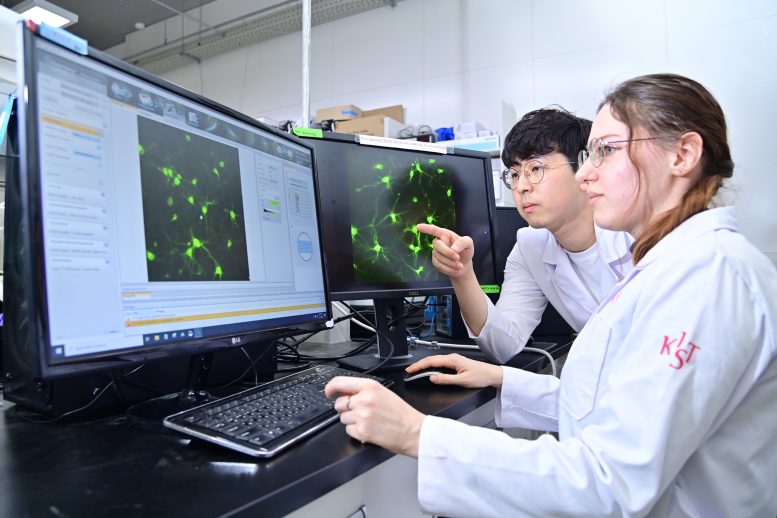

Researchers from Dr. Kim Yoon-kyung’s team at KIST are utilizing the next-generation neuron labeling technology, ‘NeuM,’ to visualize neurons in real-time and examine high-resolution images. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Neurons continuously modify their structure and function to transmit information from sensory organs to the brain, regulating thoughts, memories, and behaviors. Therefore, to overcome degenerative neurological diseases, it is essential to develop techniques that selectively label living neurons for real-time monitoring. However, current gene-based and antibody-based labeling technologies, commonly used to observe neurons, suffer from low accuracy and difficulty in long-term tracking due to their dependence on specific gene expression or proteins.
Advantages and Capabilities of NeuM
NeuM, developed by the research team through the molecular design of neuronal cells, possesses excellent binding affinity to neuronal membranes, enabling long-term tracking and high-resolution imaging of neurons. The fluorescent probes within NeuM bind to neuronal membranes utilizing the activity of living cells, emitting fluorescent signals upon excitation by specific wavelengths of light. This visualization of neuronal membranes allows for detailed observation of neuronal terminal structures and high-resolution monitoring of neuronal differentiation and interactions.
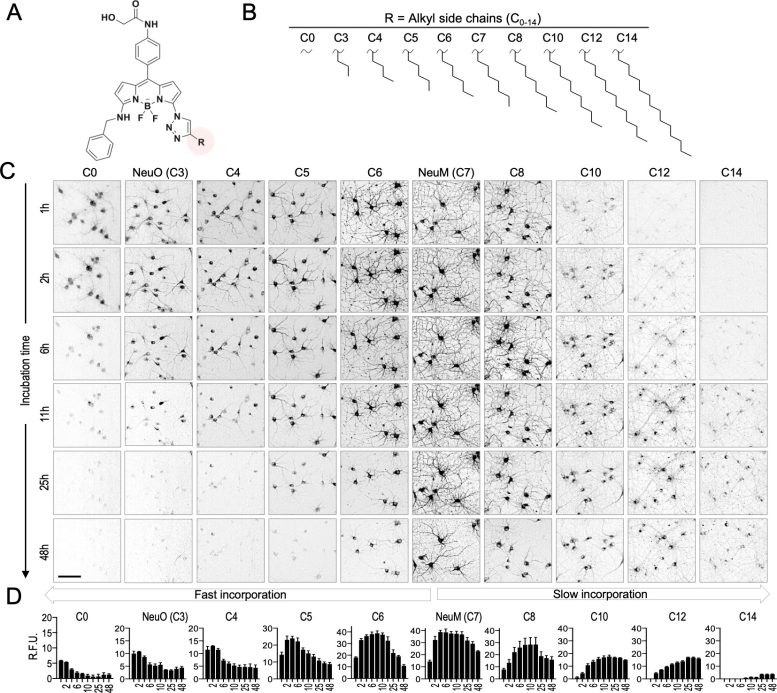
Molecular design for selective labeling of neuronal membranes. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology
NeuM, as the first technology to stain cell membranes through endocytosis in living neurons, exhibits selective reactivity towards living cells, excluding dead cells without internalization. Moreover, the research team has succeeded in extending the observation time of neurons from a mere 6 hours to up to 72 hours, enabling the capture of dynamic changes in living neurons over an extended period in response to environmental changes.
NeuM is expected to provide insights into research and therapy development for degenerative neurological diseases, for which there are currently no cures. These diseases, including Alzheimer’s, result from neuronal damage due to the production of toxic proteins such as amyloid and the influx of inflammatory substances. NeuM’s precise observation of neuronal changes can effectively facilitate the evaluation of candidate therapeutic compounds.
Dr. Kim stated, “NeuM, developed this time, can distinguish aging and degenerating neurons, becoming a crucial tool in elucidating the mechanisms of degenerative brain disorders and developing treatments.” He further added, “In the future, we plan to refine NeuM for even more precise analysis of neurons by designing fluorescence wavelengths to distinguish colors such as green and red.”
Reference: “NeuM: A Neuron-Selective Probe Incorporates into Live Neuronal Membranes via Enhanced Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in Primary Neurons” by Yoonsik Sung, Lizaveta Gotina, Kyu Hyeon Kim, Jung Yeol Lee, Seulgi Shin, Hira Aziz, Dong Min Kang, Xiao Liu, Na-Kyeong Hong, Hong-Guen Lee, Jun-Seok Lee, Hyeyeong Ku, Cherlhyun Jeong, Ae Nim Pae, Sungsu Lim, Young-Tae Chang and Yun Kyung Kim, 07 December 2023, Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202312942
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through KIST’s major projects and the Dementia Overcoming Project (RS-2023-00261784).








Be the first to comment on "Scientists Discover Key to Unlocking the Secret of Degenerative Brain Disorders Like Alzheimer’s"