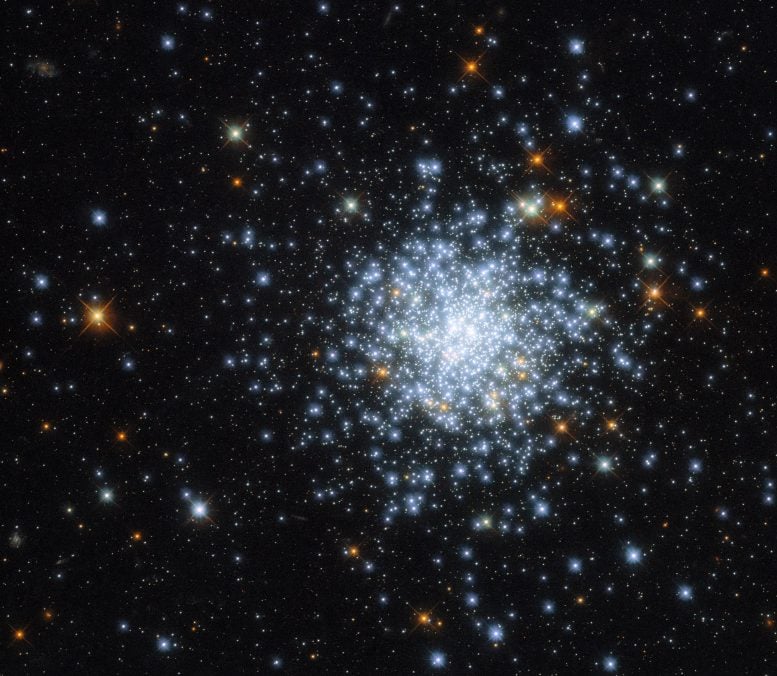

This Hubble Space Telescope image shows an open cluster known as NGC 2164, which was first discovered in 1826 by a Scottish astronomer named James Dunlop. NGC 2164 is located within one of the Milky Way galaxy’s closest neighbors — the satellite galaxy known as the Large Magellanic Cloud. The Large Magellanic Cloud is a relatively small galaxy that lies about 160,000 light-years from Earth. It is considered a satellite galaxy because it is gravitationally bound to the Milky Way. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, J. Kalirai, A. Milone
What Is an Open Cluster?
Open clusters are loosely bound groups of a few tens to a few hundred stars. They are found in spiral and irregular galaxies.
Open clusters are significantly smaller and less densely populated than globular clusters. Open clusters may contain anything from a few dozen stars up to a few hundred stars. Open clusters have been observed with a range of ages — they may be made up of young stars or older stars.
Owing to their open and diffuse structure, they are not particularly stable, and their constituent stars might disperse after a few million years. For this reason, open clusters are found in spiral and irregular galaxies, where new stars are being formed, but not in elliptical galaxies, which are not forming stars and in which any open clusters would have long since broken up.
Within the Milky Way, open clusters are found in and between the spiral arms. All star clusters are of great interest to astronomers, because the stars in them all formed at approximately the same time and location. Open clusters are typically easier to observe than globular clusters, because the individual stars can be studied. The study of star clusters offers unique insights into how stars form and evolve.
Open clusters are loosely bound groups of a few tens to a few hundred stars. They are found in spiral and irregular galaxies. Credit: NASA & ESA
Discoveries and Characteristics
Around 1100 open clusters have so far been discovered within the Milky Way, although many more are thought to exist. Trumpler 14 is one of these, located some 8000 light-years away towards the center of the well-known Carina Nebula, which has been beautifully captured by Hubble. This region of space houses one of the highest concentrations of massive, luminous stars in the entire Milky Way.
Unique Clusters and Observations by Hubble
NGC 1872 in our small neighboring galaxy the Large Magellanic Cloud. This cluster has characteristics of both cluster types — it is as rich as a typical globular but is much younger, and, like many open clusters, has bluer stars. Such intermediate clusters are common in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Hubble has also targeted a spectacular section of the well-known Eagle Nebula known as NGC 6611, an open star cluster that formed about 5.5 million years ago and is found approximately 6500 light-years from Earth. It is a very young cluster, containing many hot, blue stars, whose fierce ultraviolet glow makes the surrounding Eagle Nebula glow brightly.








Be the first to comment on "Astronomy & Astrophysics 101: Open Cluster"